Summary.
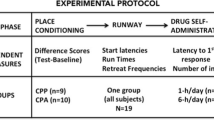
In addiction research, the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm is a widely used animal model of conditioned reward. Usually, CPP development is studied, while only few studies examine CPP expression. In the present study, the suitability of a schedule allowing repeated testing of CPP expression was evaluated. Two groups of rats were either conditioned with cocaine or morphine then the repeated-testing-schedule was applied. This schedule consisted of four repeated applications of a sequence of drug- (i.e. cocaine or morphine), saline- and anti-craving-drug- (i.e. acamprosate, naloxone, their joint administration or saline as internal control) tests. Methodologically, the repeated-testing-schedule produced stable CPP expression in both groups over 12 subsequent tests. In conclusion, it is suggested as a useful method to study effects of anti-craving-drugs on CPP expression, thereby reducing the overall number of experimental animals. The evaluation of the anti-craving-drug effects revealed that neither acamprosate and naloxone given separately nor their combined administration significantly reduced cocaine- or morphine-CPP expression. Thus, we suggest that these anti-craving-drugs are unlikely to be effective for relapse prevention in cocaine- or morphine-addicts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herzig, V., Schmidt, W. Repeated-testing of place preference expression for evaluation of anti-craving-drug effects. Amino Acids 28, 309–317 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-005-0185-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-005-0185-x