Summary.
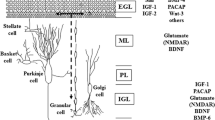
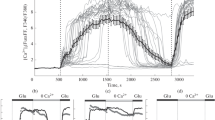
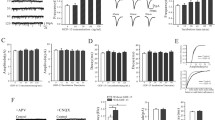
Excitotoxicity induced by NMDA receptor stimulation is able to increase the activity of many enzymes involved in neuronal cell death. Primary cultures of rat cerebellar granule cells were used to elucidate the role of transglutaminase reaction in the excitotoxic cell response, and to evaluate the role of glutamate receptors in cell survival and degeneration. Granule neurons, maintained in vitro for two weeks, were exposed to NMDA at different stages of differentiation. Following NMDA receptor activation, increases in transglutaminase activity were observed in cell cultures. The levels of enzyme activity were higher in cells at 5 days in vitro than in those at 8–9 or 13–14 days in vitro. Moreover, NMDA exposure up-regulated tTG expression in neurons as young as 5 days in vitro. These cultures also exhibited morphological changes with clear apoptotic features. Results obtained demonstrate that susceptibility of granule cells to excitotoxicity depends on the developmental stage of neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caccamo, D., Currò, M., Cusumano, G. et al. Excitotoxin-induced changes in transglutaminase during differentiation of cerebellar granule cells. Amino Acids 26, 197–201 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-003-0007-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-003-0007-y