Abstract
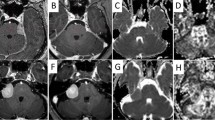
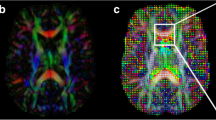
The aim of this study is to evaluate if diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can distinguish the disease process of radiation-induced brain injury when combined with apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) and fractional anisotropy (FA) values. Twenty-one rabbits received irradiation of 100 Gy in the right brain hemisphere. Twelve rabbits were screened with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and DTI before radiation, and imaged at every week until week 9 following radiation. The rabbits that had MRI were euthanized at week 9 for histologic evaluation, while other nine rabbits without MRI were randomly killed for histologic evaluation at weeks 2, 4 and 6, respectively. From the DTI, the ADC and FA values were measured, and rADC and rFA were calculated. After radiation, the trend of the ADC value can be divided into three stages. In the first stage, the ADC value of the target tissues gradually decreased. In the second stage, the ADC value of white matter in the target tissues showed a recovery trend, back to the initial level similar to that in contralateral. In the third stage, the ADC value of white matter in the target tissue continues to increase over the ADC value of baseline and contralateral white matter. The FA value of radiation-targeted area showed continuous decreasing tendency. Pathological evaluation showed the different features in three stages. DTI can distinguish the different disease stages when combined with the ADC and FA values.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.T. Chua, J.S. Sham, D.L. Kwong, G.K. Au, Cancer 98, 74–80 (2003)
R. Trivedi, A.R. Khan, P. Rana, S. Haridas, B.S. Hemanth, K. Manda, R.K. Rathore, R.P. Tripathi, S. Khushu, J. Neurosci. Res. 90, 2009–2019 (2012)
Y.X. Wang, H. Huang, S.F. Leung, D.K. Yeung, Y.L. Chan, W.S. Poon, Br J Neurosurg. 27, 662–667 (2013)
Y.X. Wang, A.D. King, H. Zhou, S.F. Leung, J. Abrigo, Y.L. Chan, C.W. Hu, D.K. Yeung, A.T. Ahuja, Radiology 254, 210–218 (2010)
C.L. Armstrong, K. Gyato, A.W. Awadalla, R. Lustig, Z.A. Tochner, Neuropsychol. Rev. 14, 65–86 (2004)
L. Pruzincova, J. Steno, M. Srbecky, P. Lalina, B. Rychly, E. Boljesikova, M. Chorvath, M. Novotny, V. Procka, I. Makaiova, V. Belan, Eur. Radiol. 19, 2716–2727 (2009)
A.M. Peiffer, L. Shi, J. Olson, J.K. Brunso-Bechtold, Brain Res. 1351, 23–31 (2010)
Y. Li, X. Shi, X. Rong, Y. Peng, Y. Tang, Radiat. Oncol. 8, 88 (2013)
S. Wang, E.X. Wu, D. Qiu, L.H. Leung, H.F. Lau, P.L. Khong, Cancer Res. 69, 1190–1198 (2009)
H.Z. Wang, S.J. Qiu, X.F. Lv, Y.Y. Wang, Y. Liang, W.F. Xiong, Z.B. Ouyang, Clin. Radiol. 67, 340–345 (2012)
K.C. Chan, P.L. Khong, M.M. Cheung, S. Wang, K.X. Cai, E.X. Wu, J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 29, 1013–1020 (2009)
S. Wang, D. Qiu, K.F. So, E.X. Wu, L.H. Leung, J. Gu, P.L. Khong, J. Neurooncol. 112, 9–15 (2013)
J.D. Rabinov, J.L. Brisman, A.J. Cole, P.L. Lee, M.R. Bussiere, P.H. Chapman, J.S. Loeffler, G.R. Cosqrove, T. Chaves, R.G. Gonzalez, Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 82, 156–164 (2004)
K. Hideghety, I. Plangar, I. Man, G. Fekete, Z. Nagy, G. Volford, T. Tokes, E. Szabo, Z. Szabo, K. Brinyiczki, P. Mozes, I. Nemeth, Int J Radiat Biol. 89, 645–655 (2013)
J.S. Cheung, S.J. Fan, A.M. Chow, E.S. Hui, E.X. Wu, J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 30, 890–895 (2009)
L. Shi, H. Zhang, Y.-F. Meng, J.-S. Su, G.-L. Shao, Appl. Magn. Reson. 38, 431–442 (2010)
M.B. Hulkower, D.B. Poliak, S.B. Rosenbaum, M.E. Zimmerman, M.L. Lipton, Am J Neuroradiol. 34(11), 2064–2074 (2013)
G. Panagiotakos, G. Alshamy, B. Chan, R. Abrams, E. Greenberg, A. Saxena, M. Bradbury, M. Edqar, P. Gutin, V. Tabar, PLoS One 2, e588 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Y2111306) and Zhejiang Provincial Medical Scientific Research Projects (2012RCA009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L., Lang, XY., Shao, GL. et al. Evaluation of Disease Stage of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury: a DTI Study with Pathological Correlation. Appl Magn Reson 45, 427–436 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-014-0521-y
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-014-0521-y