Abstract
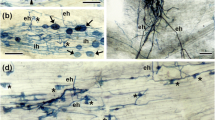
Plant symbiotic mutants are useful tool to uncover the molecular-genetic mechanisms of nodule senescence. The pea (Pisum sativum L.) mutants SGEFix−-1 (sym40), SGEFix−-3 (sym26), and SGEFix−-7 (sym27) display an early nodule senescence phenotype, whereas the mutant SGEFix−-2 (sym33) does not show premature degradation of symbiotic structures, but its nodules show an enhanced immune response. The nodules of these mutants were compared with each other and with those of the wild-type SGE line using seven marker genes that are known to be activated during nodule senescence. In wild-type SGE nodules, transcript levels of all of the senescence-associated genes were highest at 6 weeks after inoculation (WAI). The senescence-associated genes showed higher transcript abundance in mutant nodules than in wild-type nodules at 2 WAI and attained maximum levels in the mutant nodules at 4 WAI. Immunolocalization analyses showed that the ethylene precursor 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate accumulated earlier in the mutant nodules than in wild-type nodules. Together, these results showed that nodule senescence was activated in ineffective nodules blocked at different developmental stages in pea lines that harbor mutations in four symbiotic genes.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ACC:
-
1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate
- WAI:
-
Weeks after inoculation
- DAI:
-
Days after inoculation
References
Banba M, Siddique ABM, Kouchi H, Izui K, Hata S (2001) Lotus japonicus forms early senescent root nodules with Rhizobium etli. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:173–180
Berrabah F, Bourcy M, Eschstruth A, Cayrel A, Guefrachi I, Mergaert P, Wen J, Jean V, Mysore KS, Gourion B, Ratet P (2014) A nonRD receptor-like kinase prevents nodule early senescence and defense-like reactions during symbiosis. New Phytol 203:1305–1314
Borisov AY, Rozov SM, Tsyganov VE, Morzhina EV, Lebsky VK, Tikhonovich IA (1997) Sequential functioning of Sym-13 and Sym-31, two genes affecting symbiosome development in root nodules of pea (Pisum sativum L.) Mol Gen Genet 254:592–598
Borisov AY, Danilova TN, Koroleva TA, Kuznetsova EV, Madsen L, Mofett M, Naumkina TS, Nemankin TA, Ovchinnikova ES, Pavlova ZB, Petrova NE, Pinaev AG, Radutoiu S, Rozov SM, Rychagova TS, Shtark OY, Solovov II, Stougaard J, Tikhonovich IA, Topunov AF, Tsyganov VE, Vasil’chikov AG, Voroshilova VA, Weeden NF, Zhernakov AI, Zhukov VA (2007) Regulatory genes of garden pea (Pisum sativum L.) controlling the development of nitrogen-fixing nodules and arbuscular mycorrhiza: a review of basic and applied aspects. Appl Biochem Microbiol 43:237–243
Bourcy M, Brocard L, Pislariu CI, Cosson V, Mergaert P, Tadege M, Mysore KS, Udvardi MK, Gourion B, Ratet P (2013) Medicago truncatula DNF2 is a PI-PLC-XD-containing protein required for bacteroid persistence and prevention of nodule early senescence and defense-like reactions. New Phytol 197:1250–1126
Cabeza R, Koester B, Liese R, Lingner A, Baumgarten V, Dirks J, Salinas-Riester G, Pommerenke C, Dittert K, Schulze J (2014) An RNA sequencing transcriptome analysis reveals novel insights into molecular aspects of the nitrate impact on the nodule activity of Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 164:400–411
Cam Y, Pierre O, Boncompagni E, Hérouart D, Meilhoc E, Bruand C (2012) Nitric oxide (NO): a key player in the senescence of Medicago truncatula root nodules. New Phytol 196:548–560
Chua KY, Pankhurst CE, Macdonald P, Hopcroft DH, Jarvis BD, Scott DB (1985) Isolation and characterization of transposon Tn5-induced symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium loti. J Bacteriol 162:335–343
Chungopast S, Hirakawa H, Sato S, Handa Y, Saito K, Kawaguchi M, Tajima S, Nomura M (2014) Transcriptomic profiles of nodule senescence in Lotus japonicus and Mesorhizobium loti symbiosis. Plant Biotech 31:345–349
D’haeseleer K, De Keyser A, Goormachtig S, Holsters M (2010) Transcription factor MtATB2: about nodulation, sucrose and senescence. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1416–1424
De Zélicourt A, Diet A, Marion J, Laffont C, Ariel F, Moison M (2012) Dual involvement of a Medicago truncatula NAC transcription factor in root abiotic stress response and symbiotic nodule senescence. Plant J 70:220–230
Domonkos Á, Kovács S, Gombár A, Kiss E, Horváth B, Kováts GZ, Farkas A, Tóth MT, Ayaydin F, Bóka K, Fodor L, Ratet P, Kereszt A, Endre G, Kaló P (2017) NAD1 controls defense-like responses in Medicago truncatula symbiotic nitrogen fixing nodules following rhizobial colonization in a BacA-independent manner. Genes 8:387
van Doorn WG (2011) Classes of programmed cell death in plants, compared to those in animals. J Exp Bot 62:4749–4761
Engvild KC (1987) Nodulation and nitrogen fixation mutants of pea, Pisum sativum. Theor Appl Genet 74:711–713
Forrest SI, Verma DPS, Dhindsa RS (1991) Starch content and activities of starch-metabolizing enzymes in effective and ineffective root nodules of soybean. Can J Bot 69:697–701
González EM, Aparicio-Tejo PM, Gordon AJ, Minchin FR, Royuela M, Arrese-Igor C (1998) Water-deficit effects on carbon and nitrogen metabolism of pea nodules. J Exp Bot 49:1705–1714
González EM, Gálvez L, Arrese-Igor C (2001) Abscisic acid induces a decline in nitrogen fixation that involves leghaemoglobin, but is independent of sucrose synthase activity. J Exp Bot 52:285–293
Granell A, Harris N, Pisabarro AG, Carbonell J (1992) Temporal and spatial expression of a thiolprotease gene during pea ovary senescence, and its regulation by gibberellin. Plant J 2:907–915
Guinel FC (2015) Ethylene, a hormone at the center-stage of nodulation. Front Plant Sci 6:1121
Hakoyama T, Niimi K, Yamamoto T, Isobe S, Sato S, Nakamura Y, Tabata S, Kumagai H, Umehara Y, Brossuleit K (2012) The integral membrane protein SEN1 is required for symbiotic nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus nodules. Plant Cell Physiol 53:225–236
Hernández-Jiménez MJ, Lucas MM, Rosario de Felipe M (2002) Antioxidant defence and damage in senescing lupin nodules. Plant Physiol Biochem 40:645–657
Hirsch AM, Smith CA (1987) Effects of Rhizobium meliloti nif and fix mutants on alfalfa root nodule development. J Bacteriol 169:1137–1146
Horváth B, Domonkos Á, Kereszt A, Szűcs A, Ábrahám E, Ayaydin F, Bóka K, Chen Y, Chen R, Murray JD, Udvardi MK, Kondorosi É, Kaló P (2015) Loss of the nodule-specific cysteine rich peptide, NCR169, abolishes symbiotic nitrogen fixation in the Medicago truncatula dnf7 mutant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:15232–15237
Ivanova KA, Tsyganova AV, Brewin NJ, Tikhonovich IA, Tsyganov VE (2015) Induction of host defences by Rhizobium during ineffective nodulation of pea (Pisum sativum L.) carrying symbiotically defective mutations sym40 (PsEFD), sym33 (PsIPD3/PsCYCLOPS) and sym42. Protoplasma 252:1505–1517
Kardailsky IV, Brewin NJ (1996) Expression of cysteine protease genes in pea nodule development and senescence. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 9(8):689–695
Karmarkar V (2014) Transcriptional regulation of nodule development and senescence in Medicago truncatula. Doctoral thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, D.C. Available at: http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/edepot/303161
Kiers ET, Rousseau RA, West SA, Denison RF (2003) Host sanctions and the legume–rhizobium mutualism. Nature 425:78–81
Kim M, Chen Y, Xi J, Waters C, Chen R, Wang D (2015) An antimicrobial peptide essential for bacterial survival in the nitrogen-fixing symbiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:15238–15243
Kneen BE, LaRue TA, Hirsch AM, Smith CA, Weeden NF (1990) sym 13—a gene conditioning ineffective nodulation in Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol 94:899–905
Kosterin OE, Rozov SM (1993) Mapping of the new mutation blb and the problem of integrity of linkage group I. Pisum Genet 25:27–31
Krusell L, Krause K, Ott T, Desbrosses G, Krämer U, Sato S (2005) The sulfate transporter SST1 is crucial for symbiotic nitrogen fixation in Lotus japonicus root nodules. Plant Cell 17:1625–1636
Kulaeva OA, Zhernakov AI, Afonin AM, Boikov SS, Sulima AS, Tikhonovich IA, Zhukov VA (2017) Pea Marker Database (PMD)—a new online database combining known pea (Pisum sativum L.) gene-based markers. PLoS One 12:e0186713
Kumagai H, Hakoyama T, Umehara Y, Sato S, Kaneko T, Tabata S, Kouchi H (2007) A novel ankyrin-repeat membrane protein, IGN1, is required for persistence of nitrogen-fixing symbiosis in root nodules of Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol 143:1293–1305
Martin DN, Proebsting WM, Hedden P (1999) The SLENDER gene of pea encodes a gibberellins 2-oxidase. Plant Physiol 121:775–781
Matamoros MA, Baird LM, Escuredo PR, Dalton DA, Minchin FR, Iturbe-Ormaetxe I, Rubio MC, Moran JF, Gordon AJ, Becana M (1999) Stress-induced legume root nodule senescence. Physiological, biochemical, and structural alterations. Plant Physiol 121:97–111
Maunoury N, Redondo-Nieto M, Bourcy M, Van de Velde W, Alunni B, Laporte P, Durand P, Agier N, Marisa L, Vaubert D, Delacroix H, Duc G, Ratet P, Aggerbeck L, Kondorosi E, Mergaert P (2010) Differentiation of symbiotic cells and endosymbionts in Medicago truncatula nodulation are coupled to two transcriptome-switches. PLoS One 5:e9519
Morzhina EV, Tsyganov VE, Borisov AY, Lebsky VK, Tikhonovich IA (2000) Four developmental stages identified by genetic dissection of pea (Pisum sativum L.) root nodule morphogenesis. Plant Sci 155:75–83
Nemankin NF (2011) Analysis of pea (Pisum sativum L.) genetic system, controlling development of arbuscular mycorrhiza and nitrogen-fixing symbiosis. Dissertation Saint-Petersburg State University (in Russian)
Novák K, Pešina K, Nebesářová J, Škrdleta V, Lisa L, Našinec V (1995) Symbiotic tissue degradation pattern in the ineffective nodules of three nodulation mutants of pea (Pisum sativum L.) Ann Bot 76:303–313
Oono R, Anderson CG, Denison RF (2011) Failure to fix nitrogen by non-reproductive symbiotic rhizobia triggers host sanctions that reduce fitness of their reproductive clonemates. Proc Roy Soc B-Biol Sci 278:2698–2703
Pariasca JA, Sunaga A, Miyazaki T, Hisaka H, Sonoda M, Nakagawa H, Sato T (2001) Cloning of cDNAs encoding senescence-associated genes, ACC synthase and ACC oxidase from stored snow pea pods (Pisum sativum L. var saccharatum) and their expression during pod storage. Postharvest Biol Technol 22:239–247
Peck SC, Kende H (1998) Differential regulation of genes encoding 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) synthase in etiolated pea seedlings: effects of indole-3-acetic acid, wounding, and ethylene. Plant Mol Biol 38:977–982
Pérez Guerra JC, Coussens G, De Keysler A, De Rycke R, De Bodt S, Van De Velde W, Goormachtig S, Holsters M (2010) Comparison of developmental and stress-induced nodule senescence in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 152:1574–1584
Pierre O, Hopkins J, Combier M, Baldacci F, Engler G, Brouquisse R, Hérouart D, Boncompagni E (2014) Involvement of papain and legumain proteinase in the senescence process of Medicago truncatula nodules. New Phytol 202:849–863
Pladys D, Vance CP (1993) Proteolysis during development and senescence of effective and plant gene-controlled ineffective alfalfa nodules. Plant Physiol 103:379–384
Puppo A, Groten K, Bastian F, Carzaniga R, Soussi M, Lucas MM (2005) Legume nodule senescence: roles for redox and hormone signaling in the orchestration of the natural aging process. New Phytol 165:683–701
Regus JU, Quides KW, O’Neill MR, Suzuki R, Savory EA, Chang JH, Sachs JL (2017) Cell autonomous sanctions in legumes target ineffective rhizobia in nodules with mixed infections. Am J Bot 104:1299–1312
Serova TA, Tsyganov VE (2014) Symbiotic nodule senescence in legumes: molecular-genetic and cellular aspects. Agr Biol 5:3–15
Serova TA, Tikhonovich IA, Tsyganov VE (2017) Analysis of nodule senescence in pea (Pisum sativum L.) using laser microdissection, real-time PCR, and ACC immunolocalization. J Plant Physiol 212:29–44
Sinharoy S, Torres-Jerez I, Bandyopadhyay K, Kereszt A, Pislariu CI, Nakashima J, Benedito VA, Kondorosi E, Udvardi MK (2013) The C2H2 transcription factor regulator of symbiosome differentiation represses transcription of the secretory pathway gene VAMP721a and promotes symbiosome development in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 25:3584–3601
Swaraj K, Laura JS, Bishnoi NR (1993) Nitrate induced nodule senescence and changes in activities of enzymes scavenging H2O2 in clusterbean (Cyamopsis tetragonaloba Taub.). J Plant Physiol 141:202–205
Tsyganov VE, Borisov AY, Rozov SM, Tikhonovich IA (1994) New symbiotic mutants of pea obtained after mutagenesis of laboratory line SGE. Pisum Genet 26:36–37
Tsyganov VE, Morzhina EV, Stefanov SY, Borisov AY, Lebsky VK, Tikhonovich IA (1998) The pea (Pisum sativum L.) genes sym33 and sym40 control infection thread formation and root nodule function. Mol Gen Genet 256:491–503
Tsyganov VE, Voroshilova VA, Rozov SM, Borisov AY, Tikhonovich IA (2013) A new series of pea symbiotic mutants induced in the line SGE. Russ J Genet: Appl Res 3:156–162
Tsyganova AV, Tsyganov VE, Findlay KC, Borisov AY, Tikhonovich IA, Brewin NJ (2009) Distribution of legume arabinogalactan protein-extensin (AGPE) glycoproteins in symbiotically defective pea mutants with abnormal infection threads. Cell Tissue Biol 3:93–102
Tsyganova AV, Kitaeva AB, Tsyganov VE (2018) Cell differentiation in nitrogen-fixing nodules hosting symbiosomes. Funct Plant Biol 45:47–57
Van de Velde W, Pérez Guerra JC, De Keysler A, De Rycke R, Rombauts S, Maunoury N, Mergaert P (2006) Aging in legume symbiosis. A molecular view on nodule senescence in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 141:711–720
Vauclare P, Bligny R, Gout E, De Meuron V, Widmer F (2010) Metabolic and structural rearrangement during dark-induced autophagy in soybean (Glycine max L.) nodules: an electron microscopy and 31P and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance study. Planta 231:1495–1504
Vernié T, Moreau S, de Billy F, Plet J, Combier JP, Rogers C, Oldroyd G, Frugier F, Niebel A, Gamas P (2008) EFD is an ERF transcription factor involved in the control of nodule number and differentiation in Medicago truncatula. Plant Cell 20:2696–2713
Voroshilova VA, Demchenko KN, Brewin NJ, Borisov AY, Tikhonovich IA (2009) Initiation of a legume nodule with an indeterminate meristem involves proliferating host cells that harbour infection threads. New Phytol 181:913–923
Wang C, Yu H, Luo L, Duan L, Cai L, He X, Wen J, Mysore KS, Li G, Xiao A, Duanmu D, Cao Y, Hong Z, Zhang Z (2016) NODULES WITH ACTIVATED DEFENSE 1 is required for maintenance of rhizobial endosymbiosis in Medicago truncatula. New Phytol 212:176–191
Wang Q, Liu J, Li H, Yang S, Körmöczi P, Kereszt A, Zhu H (2017) Nodule-specific cysteine-rich peptides negatively regulate nitrogen-fixing symbiosis in a strain-specific manner in Medicago truncatula. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 31:240–248
Westhoek A, Field E, Rehling F, Mulley G, Webb I, Poole PS, Turnbull LA (2017) Policing the legume-Rhizobium symbiosis: a critical test of partner choice. Sci Rep 7:1419
Yamaya-Ito H, Shimoda Y, Hakoyama T, Sato S, Kaneko T, Hossain MS, Shibata S, Kawaguchi M, Hayashi M, Kouchi H, Umehara Y (2018) Loss-of-function of ASPARTIC PEPTIDASE NODULE-INDUCED 1 (APN1) in Lotus japonicus restricts efficient nitrogen-fixing symbiosis with specific Mesorhizobium loti strains. Plant J 93:5–16
Yang S, Wang Q, Fedorova E, Liu J, Qin Q, Zheng Q, Price PA, Pan H, Wang D, Griffitts JS, Bisseling T, Zhu H (2017) Microsymbiont discrimination mediated by a host-secreted peptide in Medicago truncatula. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:6848–6853
Zdunek-Zastocka E (2008) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of three aldehyde oxidase genes from Pisum sativum L. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:19–28
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation [grant number 16-16-10035]. The research was performed using equipment of the Core Centrum “Genomic Technologies, Proteomics and Cell Biology” in ARRIAM, and the “Molecular and Cell Technologies” Research Resource Centre at Saint-Petersburg State University. Jennifer Smith, PhD, and Robert McKenzie, PhD, from Edanz Group (www.edanzediting.com/ac) edited the English version of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Handling Editor: Ulrike Mathesius
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 4038 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serova, T.A., Tsyganova, A.V. & Tsyganov, V.E. Early nodule senescence is activated in symbiotic mutants of pea (Pisum sativum L.) forming ineffective nodules blocked at different nodule developmental stages. Protoplasma 255, 1443–1459 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-018-1246-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-018-1246-9