Abstract
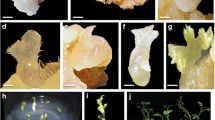
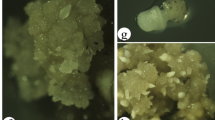
A new protocol for in vitro regeneration through direct somatic embryogenesis for two muskmelon cultivars (Cucumis melo L., “Mashhadi” and “Eivanaki”) is reported. Somatic embryos were obtained culturing 4- and 8-day-old cotyledons, seeds, and hypocotyls on Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented with three different hormonal combinations never tested so far for melon (naphthoxyacetic acid (NOA) + thidiazuron (TDZ), NOA + 6-banzylaminopurine (BAP), and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) + N-(2-chloro-4-pyridyl)-N′-phenylurea (4-CPPU)). Results were compared with those obtained when explants were cultivated in the presence of 2,4-D + BAP, previously used on melon. Embryogenesis occurred more successfully in 4-day-old cotyledons and seeds than hypocotyls and 8-day-old cotyledons. The best result was achieved with NOA + BAP. Genotypes significantly affected embryogenesis. The number of embryos in “Eivanaki” was significantly higher than that in “Mashhadi.” Embryo proliferation when explants were maintained in jars (9.3%) was found to be higher compared to that in petri dishes. For the first time, genetic stability of regenerated melon plants was evaluated using inter-simple sequence repeat markers. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products demonstrated a total of 102 well-resolved bands, and regenerants were 93% similar compared to the mother plant. Somaclonal changes during embryogenesis were evaluated by flow cytometry, showing 91% of the same patterns in regenerated plants. The results suggest that the new hormone components are effective when applied for in vitro embryogenesis of muskmelon as they show a high frequency in regeneration and genetic homogeneity.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- 4-CPPU:
-
N-(2-Chloro-4-pyridyl)-N′-phenylurea
- BAP:
-
6-Banzylaminopurine
- CI:
-
Culture initiation
- DSE:
-
Direct somatic embryogenesis
- EF:
-
Embryo formation
- ISE:
-
Indirect somatic embryogenesis
- ISSR:
-
Inter-simple sequence repeat
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- NOA:
-
Naphthoxyacetic acid
- PGR:
-
Plant growth regulator
- SE:
-
Somatic embryogenesis
- TDZ:
-
Thidiazuron
References
Adhikari S, Bandyopadhyay TK, Ghosh P (2014) Assessment of genetic stability of Cucumis sativus L. regenerated from encapsulated shoot tips. Sci Hortic 170:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2014.01.015
Akasaka-Kennedy Y, Tomita K, Ezura H (2004) Efficient plant regeneration and Agrobacterium-mediated transformation via somatic embryogenesis in melon (Cucumis melo L.) Plant Sci 166(3):763–769. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2003.11.020
Ali M, Mujib A, Tonk D, Zafa N (2016) Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis and genome size analysis of Coriandrum sativum L. Protoplasma 254:343–352
Amor MB, Guis M, Latche A, Bouzayen M, Pech JC, Roustan JP (1998) Expression of an antisense 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate oxidase gene stimulates shoot regeneration in Cucumis melo. Plant Cell Rep 17(6-7):586–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050447
Anonymous (2014) FAOSTAT Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en
Baysal T, Mercati F, Ikten H, Yildiz RT, Carimi F, Aysan Y, Teixeira da Silva JA (2011) Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganesis: tracking strains using their genetic differentiations by ISSR markers in Southern Turkey. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 75(3):113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2010.10.002
Bhattacharya C, Dam A, Karmakar J, Bandyopadhyay TK (2016) Direct somatic embryogenesis and genetic homogeneity assessment of regenerated plants of Anthurium andraeanum Linden cv. Fantasia. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 52:512–519
Carra A, De Pasquale F, Ricci A, Carimi F (2006) Diphenylurea derivatives induce somatic embryogenesis in Citrus. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 87(1):41–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-006-9132-0
Carra A, Sajeva M, Abbate L, Siragusa M, Sottile F, Carimi F (2012) In vitro plant regeneration of caper (Capparis spinosa L.) from floral explants and genetic stability of regenerants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 109(2):373–381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-0102-9
Chen N, Gan Y, Wang G (2002) Photosynthetic responses of muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) to photon flux density, leaf temperature and CO2 concentration. Can J Plant Sci 83(2):393–399
Chovelon V, Restier V, Giovinazzo N, Dogimont C, Aarrouf J (2011) Histological study of organogenesis in Cucumis melo L. after genetic transformation: why is it difficult to obtain transgenic plants? Plant Cell Rep 30(11):2001–2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1108-9
Conger BV, Hanning GE, Gray DJ, McDaniel JK (1983) Direct embryogenesis from mesophyll cells of orchardgrass. Science 221(4613):850–851. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.221.4613.850
Danso K, Ford-Lloyd B (2004) Cryopreservation of embryogenic calli of cassava using sucrose cryoprotection and air desiccation. Plant Cell Rep 22(9):623–631. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-003-0727-1
Debeaujon I, Branchard M (1992) Induction of somatic embryogenesis and caulogenesis from cotyledon and leaf protoplast-derived colonies of melon (Cucumis melo L.) Plant Cell Rep 12(1):37–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232420
Devi BC, Narmathabai V (2011) Somatic embryogenesis in the medicinal legume Desmodium motorium (Houtt.) Merr. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 106(3):409–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9937-3
Dijak M, Brown DCW (1987) Patterns of direct and indirect embryogenesis from mesophyll protoplasts of Medicago sativa. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 9(2):121–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00044247
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure from small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Dubois T, Guedira M, Dubois J, Vasseur J (1991) Direct somatic embryogenesis in leaves of Cichorium. Protoplasma 162(2-3):120–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02562555
Ezura H, Amagai H, Oosawa K (1993) Efficient production of triploid melon plants by in vitro culture of abnormal embryos excised from dried seeds of diploid × tetraploid crosses and their characteristics. Jpn J Breed 43(2):193–199. https://doi.org/10.1270/jsbbs1951.43.193
Farhoudi R, Saeedipour S, Mohammadreza D (2011) The effect of NaCl seed priming on salt tolerance, antioxidant enzyme activity, proline and carbohydrate accumulation of muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) under saline condition. Afr J Agri Res 6:1363–1370
Feyzian E, Dehghani H, Rezai AM, Javaran MJ (2009) Diallel cross analysis for maturity and yield-related traits in melon (Cucumis melo L.) Euphytica 168(2):215–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-009-9904-9
Gaj MD (2001) Direct somatic embryogenesis as a rapid and efficient system for in vitro regeneration of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 64(1):39–46. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010679614721
Gray DJ, Mccolley DW, Compton ME (1993) High-frequency somatic embryogenesis from quiescent seed cotyledons of Cucumis melo cultivars. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 118:425–432
Gao X, Yang D, Cao D, Ao M, Sui X, Wang Q, Kimatu JN, Li W (2010) In vitro micropropagation of Freesia hybrid and the assessment of genetic and epigenetic stability in regenerated plantlets. J Plant Growth Regul 29(3):257–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00344-009-9133-4
Jha TB, Mukherjee P, Datta MM (2007) Somatic embryogenesis in Jatropha curcas Linn., an important biofuel plant. Plant Biotechnol Rep 1(3):135–140. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11816-007-0027-2
Ju HJ, Jeyakumar J, Kamaraj M, Praveen N, Chung IM, Kim SH, Thiruvengadam M (2014) High frequency somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from hypocotyl and leaf explants of gherkin (Cucumis anguria L.) Sci Hortic 169:161–168
Kubalakova M, Dolezel J, Lebeda A (1996) Ploidy instability of embryogenic cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) callus culture. Biol Plant 38(3):475–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02896685
Konieczny R, Sliwinska E, Pilarska M, Tuleja M (2012) Morphohistological and flow cytometric analyses of somatic embryogenesis in Trifolium nigrescens Viv. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 109(1):131–141. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-0081-x
Kulus D (2016) Application of cryogenic technologies and somatic embryogenesis in the storage and protection of valuable genetic resources of ornamental plants. In: Mujib A (ed) Somatic embryogenesis in ornamentals and its applications. Springer, India, pp 1–27
Lambardi M, Ozudogru EA, Benelli C (2008) Cryopreservation of embryogenic cultures. In: Reed BM (ed) Plant cryopreservation, a practical guide. Springer Science and Business Media, New York, pp 177–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-72276-4_9
Lo Schiavo F, Pitto L, Giuliano G, Torti G, Nuti Ronchi V, Marazziti D, Vergara R, Oselli S, Terzi M (1989) DNA methylation of embryogenic carrot cell cultures and its variations as caused by mutation, differentiation, hormones and hypomethylating drugs. Theor Appl Genet 77(3):325–331. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305823
Lotfi M, Alan AR, Henning MJ, Jahn M, Earle ED (2003) Production of haploid and doubled haploid plants of melon (Cucumis melo L.) for use in breeding for multiple virus resistance. Plant Cell Rep 21(11):1121–1128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-003-0636-3
May RA, Sink KC (1995) Genotype and auxin influence direct somatic embryogenesis from protoplasts derived from embryogenic cell suspensions of Asparagus officinalis L. Plant Sci 108(1):71–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9452(95)04117-D
Mehta R, Sharma V, Sood A, Sharma M, Sharma RK (2011) Induction of somatic embryogenesis and analysis of genetic fidelity of in vitro-derived plantlets of Bambusa nutans Wall., using AFLP markers. Eur J Forest Res 130:729–736
Meziane M, Frasheri D, Carra A, Boudjeniba M, D’Onghia AM, Mercati F, Djelouah K, Carimi F (2016) Attempts to eradicate graft-transmissible infections through somatic embryogenesis in Citrus ssp. and analysis of genetic stability of regenerated plants. Eur J Plant Pathol 10:1–11
Mliki A, Staub JE, Sun ZY, Ghorbel A (2001) Genetic diversity in melon (Cucumis melo L.): an evaluation of African germplasm. Genet Resour Crop Evol 48(6):587–597. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1013840517032
Moradmand R, Arzani A, Saeidi G (2011) Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis in three Iranian Cucumis melo L. genotypes. J Crop Impr 25(2):183–190. https://doi.org/10.1080/15427528.2011.547399
Morais-Lino LS, Santos-Serejo JA, Amorim EP, Santana JRF, Pasqual M, Silva SO (2016) Somatic embryogenesis, cell suspension, and genetic stability of banana cultivars. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 52:99–106
Moreno V, Garcia-Sogo M, Granell I, Garcia-Sogo B, Roig LA (1985) Plant regeneration from calli of melon (Cucumis melo L., cv.‘Amarillo Oro’). Plant cell, tissue and organ culture 5(2):139–146
Munger HM, Washek RL (1983) Progress and procedures in breeding CMV resistant C. pepo L. Genetics Cucurbit Cooperative. http://cuke.hort.ncsu.edu/cgc/cgc06/1983toc.html report number 6. 1983
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15(3):473–497. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Muthukumaran C, Banupriya L, Harinee S, Sivaranjani S, Sharmila G, Rajasekar V, Kumar NM (2017) Pectin from muskmelon (Cucumis melo var. reticulatus) peels: extraction optimization and physicochemical properties. 3 Biotech 7:66
Naderi D, Mousavi A, Habashi AA, Lotfi M (2011) Optimization of somatic embryogenesis induction in Iranian melon (Cucumis melon cv. Khatooni). Afr J Biotech 10:6434–6438
Naing AH, Min JS, Park KI, Chung MY, Lim SH, Lim KB, Kim CK (2013) Primary and secondary somatic embryogenesis in Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum morifolium) cv. ‘Baeksun’ and assessment of ploidy stability of somatic embryogenesis process by flow cytometry. Acta Physiol Plant 35:2965–2974
Nakata E, Staub JE, López-Sesé AI, Katzir N (2005) Genetic diversity of Japanese melon cultivars (Cucumis melo L.) as assessed by random amplified polymorphic DNA and simple sequence repeat markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 52(4):405–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-005-2258-9
Nunez-Palenius HG, Cantliffe DJ, Huber DJ, Ciardi J, Klee HJ (2006) Transformation of a muskmelon ‘Galia’ hybrid parental line (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus Ser.) with an antisense ACC oxidase gene. Plant Cell Rep 25(3):198–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0042-0
Pareek A, Kothari SL (2003) Direct somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaf cultures of ornamental species of Dianthus. Sci Hortic 98(4):449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-4238(03)00078-5
Paul S, Dam A, Bhattacharyya A, Bandyopadhyay TK (2011) An efficient regeneration system via direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis for the medicinal tree Murraya koenigii. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 105(2):271–283. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9864-8
Pinto DLP, Barros BA, Viccini LF, Campos JMS, Silva ML, Otoni WC (2010) Ploidy stability of somatic embryogenesis-derived Passiflora cincinnata Mast. plants as assessed by flow cytometry. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 103(1):71–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-010-9756-y
Polat I, Baysal O, Mercati F, Kitner M, Cohen Y, Lebeda A, Carimi F (2014) Characterization of Pseudoperonospora cubensis isolates from Europe and Asia using ISSR and SRAP molecular markers. Eur J Plant Pathol 139(3):641–653. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0420-y
Rai MK, Phulwaria M, Harish M, Gupta AK, Shekhawat NS, Jaiswal U (2012) Genetic homogeneity of guava plants derived from somatic embryogenesis using SSR and ISSR markers. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 111(2):259–264. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-012-0190-1
Reinert J (1958) Morphogenese und ihre Kontrolle an Gewebekulturen aus Carotten. Sci Nat 14:344–345
Rhimi A, Fadhel NB, Boussaid M (2006) Plant regeneration via somatic embryogenesis from in vitro tissue culture in two Tunisian Cucumis melo cultivars Maazoun and Beji. Plant cell, tissue and organ culture 84(2):239–243
Rocha DI, Kurczyńska E, Potocka I, Steinmacher DA, Otoni WC (2016) Histology and histochemistry of somatic embryogenesis. In: Loyola V, Ochoa-Alejo N (eds) Somatic embryogenesis: fundamental aspects and applications. Springer International Publisher, Switzerland, pp 471–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-33705-0_26
Roustan JP, Latche A, Fallot J (1992) Enhancement of shoot regeneration from cotyledons of Cucumis melo by AgNO3, an inhibitor of ethylene action. Journal of plant physiology 140(4):485–488
Sahijram L, Bahadur B (2015) Plant biology and biotechnology. In: Bahadur B, Rajam MV, Sahijram L, Krishnamurthy KV (eds). Somatic embryogenesis. Springer India, pp 315–327
Sanchez-Teyer LF, Quiroz-Figueroa F, Loyola-Vargas V, Infante D (2003) Culture-induced variation in plants of Coffea arabica cv. Caturra Rojo, regenerated by direct and indirect somatic embryogenesis. Mol Biotechnol 23(2):107–115. https://doi.org/10.1385/MB:23:2:107
Sandhu JS, Kaur M, Kaur A, Kalia A (2016) Single step direct transgenic plant regeneration from adventive embryos of agro-infected sugarcane (Saccharum spp.) spindle leaf roll segments with assured genetic fidelity. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 125(1):149–162. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0936-7
Sebastiani MS, Ficcadenti N (2016) In vitro plant regeneration from cotyledonary explants of Cucumis melo L. var. cantalupensis and genetic stability evaluation using RAPD analysis. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 124(1):69–79. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-015-0875-3
Shibli RA (2000) Cryopreservation of black iris (Iris nigricans) somatic embryos by encapsulation-dehydration. Cryo letters 21(1):39–46
Singh R, Kashyap SP, Kumari N, Singh M (2016) Regeneration of soapnut tree through somatic embryogenesis and assessment of genetic fidelity through ISSR and RAPD markers. Physiol Mol Biol Plants 22(3):381–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-016-0364-0
Siragusa M, Carra A, Salvia L, Puglia AM, De Pasquale F, Carimi F (2007) Genetic instability in calamondin (Citrus madurensis Lour.) plants derived from somatic embryogenesis induced by diphenylurea derivatives. Plant Cell Rep 26(8):1289–1296. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-007-0326-7
Sohrabikertabad S, Ghanbari A, Mohasel HR, Mahalati MN, Gherekhloo J (2013) Effect of desiccation and salinity stress on seed germination and initial plant growth of Cucumis melo. Planta Daninha 31(4):833–841. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-83582013000400009
Steward FC, Mapes MO, Mears K (1958) Growth and organized development of cultured cells. Am J Bot 1:705–708
Sujatha M, Visarada K (2013) Biolistic DNA delivery. In: Sudowe S, Reske-Kunz AB (eds) Transformation of nuclear DNA in meristematic and embryogenic tissues. Springer New York, pp 27–44
Tyagi RK, Agrawal A, Mahalakshmi C, Hussain Z, Tyagi H (2007) Low-cost media for in vitro conservation of turmeric (Curcuma longa L.) and genetic stability assessment using RAPD markers. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:51–58
Valladares S, Sanchez CS, Martinez MT, Ballester A, Vieitez AM (2006) Plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis from tissues of mature oak trees: true-to-type conformity of plantlets by RAPD analysis. Plant Cell Rep 25(9):879–886. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0108-z
Vicient CM, Martínez FX (1998) The potential uses of somatic embryogenesis are not limited to synthetic seed technology. Braz J Plant Physiol 10:1–12
Wedzony M, Szechyńska-Hebda M, Zur I, Dubas E, Krzewska M (2014) Tissue culture and regeneration: a prerequisite for alien genetransfer. In: Pratap A, Kumar J (eds) Alien gene transfer in crop plants. Volume 1: innovations, methods and risk assessment. Springer, New York, pp 43–75
Yang JL, Seong ES, Kim MJ, Ghimire BK, Kang WH, Chang YY, Cheng HL (2010) Direct somatic embryogenesis from pericycle cells of broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica) root explants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 100(1):49–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-009-9615-x
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Mohsen Hamedpour-Darabi for editing the English of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by grant no. 951002 of the Biotechnology Development Council of the Islamic Republic of Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ML, FC, and MT conceived and designed research. MRR conducted molecular experiment. MRR and LA conducted flow cytometry experiment. MRR and AC conducted tissue culture experiment. MRR, BZ, and LA analyzed data. MRR, AC, and FC wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Pavla Binarova
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raji, M.R., Lotfi, M., Tohidfar, M. et al. Somatic embryogenesis of muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) and genetic stability assessment of regenerants using flow cytometry and ISSR markers. Protoplasma 255, 873–883 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1194-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1194-9