Abstract
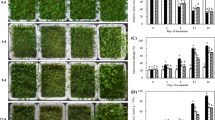
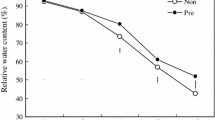
Changes of endogenous polyamine (PA) levels could be a key adaptive response to drought in plants. White clover pretreated with or without dicyclohexylamine (DCHA), an inhibitor of PA biosynthesis, was subjected to drought stress induced by 18% polyethylene glycol 6000 for 8 days in controlled growth chambers. Results showed that drought stress significantly increased endogenous PA content, whereas DCHA significantly decreased PA accumulation under drought stress. The attenuate PA biosynthesis was unfavorable for plant growth and drought tolerance, as reflected by significantly lower relative water content, relative growth rate, instantaneous water use efficiency, and cell membrane stability in leaves in response to drought. On the basis of proteomic analysis, the inhibition of PA synthesis decreased the accumulation of many key differentially expressed proteins including (1) ribosomal structure and biogenesis: elongation factor, ribosomal protein S10E, and 30S ribosomal protein; (2) amino acid transport and metabolism: cysteine synthase, delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase, and glutamate decarboxylase; (3) carbohydrate metabolism and energy production: photosystem apoprotein, sucrose-phosphate synthase, phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, sucrose-phosphatase, NADH oxidoreductase, and ATP synthase; (4) antioxidant metabolism: catalase, peroxidase I, ascorbate peroxidase, and glutathione S-transferase; and (5) other biological processes: heat shock protein 70, heat shock protein 90, and calcium-dependent protein kinase associated with the decreased drought tolerance in white clover. These findings indicate that PAs play a critical role in the regulation of growth, ribosome, amino acid and energy metabolism, and antioxidant reactions in white clover under drought stress. Drought-induced increases in endogenous PAs could be one of key adaptive responses against drought stress in white clover.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APX:
-
Ascorbate peroxidase
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- CDPK:
-
Calcium-dependent protein kinase
- Chl:
-
Chlorophyll
- DEPs:
-
Differentially expressed proteins
- DCHA:
-
Dicyclohexylamine
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatograph
- HSPs:
-
Heat shock proteins
- LSD:
-
Least significant difference
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- PAs:
-
Polyamines
- Pn:
-
Net photosynthetic rate
- POD:
-
Peroxidase
- Put:
-
Putrescine
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RWC:
-
Relative water content
- RGR:
-
Relative growth rate
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- Spd:
-
Spermidine
- Spm:
-
Spermine
- Tr:
-
Transpiration rate
- WUE:
-
Water use efficiency
References
Alcázar R, Altabella T, Marco F, Bortolotti C, Reymond M, Koncz C, Carrasco P, Tiburcio AF (2010) Polyamines: molecules with regulatory functions in plant abiotic stress tolerance. Planta 231:1237–1249
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase Beta Vulgaris Plant Physiol 24:1–18
Bala S, Asthir B, Bains NS (2016) Syringaldazine peroxidase stimulates lignification by enhancing polyamine catabolism in wheat during heat and drought stress. Cereal Res Commun 44:1–11
Barbour M, Caradus JR, Woodfield DR, Silvester WB (1996) Water stress and water use efficiency of ten white clover cultivars. Agrono Soc N Z 11:159–162
Barrs HD, Weatherley PE, Barrs HD, Weatherley PE (1961) A re-examination of the relative turgidity technique for estimating eater deficits in leaves. Aust J Biol Sci 15:413–428
Blum A (1996) Crop responses to drought and the interpretation of adaptation. Plant Growth Regul 20:135–148
Blum A, Ebercon A (1981) Cell membrane stability as a measure of drought and heat tolerance in wheat. Crop Sci 21:43–47
Burg MB, Ferraris JD (2008) Intracellular organic osmolytes: function and regulation. J Biol Chem 283:7309–7313
Campo S, Baldrich P, Messeguer J, Lalanne E, Coca M, San SB (2014) Overexpression of a calcium-dependent protein kinase confers salt and drought tolerance in rice by preventing membrane lipid peroxidation. Plant Physiol 165:688–704
Cuellar-Ortiz SM, De LPA-MM, Acosta-Gallegos J, Covarrubias AA (2008) Relationship between carbohydrate partitioning and drought resistance in common bean. Plant Cell Environ 31:1399–1409
Dhindsa RS, Plumb-Dhindsa P, Thorpe TA (1981) Leaf senescence: correlated with increased levels of membrane permeability and lipid peroxidation, and decreased levels of superoxide dismutase and catalase. J Exp Bot 32:93–101
Duan J, Li J, Guo S, Kang Y (2008) Exogenous spermidine affects polyamine metabolism in salinity-stressed Cucumis sativus roots and enhances short-term salinity tolerance. J Plant Physiol 165:1620–1635
Elia M, Cummings JH (2007) Physiological aspects of energy metabolism and gastrointestinal effects of carbohydrates. Eur J Clin Nutr 61:S40–S74
Farooq M, Wahid A, Kobayashi N, Fujita D, Basra SMA (2009a) Plant drought stress: effects, mechanisms and management. Agron Sustain Dev 29:185–212
Farooq M, Wahid A, Lee DJ (2009b) Exogenously applied polyamines increase drought tolerance of rice by improving leaf water status, photosynthesis and membrane properties. Acta Physiol Plant 31:937–945
Ge P, Ma C, Wang S, Gao L, Li X, Guo G, Ma W, Yan Y (2012) Comparative proteomic analysis of grain development in two spring wheat varieties under drought stress. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:1297–1313
Gupta AK, Kaur N (2005) Sugar signalling and gene expression in relation to carbohydrate metabolism under abiotic stresses in plants. J Biosci 30:761–776
Gupta DK, Palma JM, Corpas FJ (2015) Reactive oxygen species and oxidative damage in plants under stress. Springer, Germany
Gupta K, Gupta B, Ghosh B, Sengupta DN (2012) Spermidine and abscisic acid-mediated phosphorylation of a cytoplasmic protein from rice root in response to salinity stress. Acta Physiol Plant 34:29–40
Hamdani S, Yaakoubi H, Carpentier R (2011) Polyamines interaction with thylakoid proteins during stress. J Photochem Photobiol B-Biol 104:314–319
Hasanuzzaman M, Nahar K, Gill SS, Fujita M (2013) Drought stress responses in plants, oxidative stress, and antioxidant defense. In: (eds) Climate change and plant abiotic stress tolerance. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, pp 209-250
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1950) The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Stn Circ 347:357–359
Jiang Q, Zhang JY, Guo X, Mohamed B, Lloyd S, Joseph B, Wang ZY (2010) Improvement of drought tolerance in white clover (Trifolium repens) by transgenic expression of a transcription factor gene WXP1. Funct Plant Biol 37:157–165
Jiang S, Zhang D, Wang L, Pan J, Liu Y, Kong X, Zhou Y, Li D (2013) A maize calcium-dependent protein kinase gene, ZmCPK4, positively regulated abscisic acid signaling and enhanced drought stress tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol Biochem 71:112–120
Krishnan S, Laskowski K, Shukla V, Merewitz EB (2013) Mitigation of drought stress damage by exogenous application of a non-protein amino acid gamma aminobutyric acid on perennial ryegrass. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 138:358–366
Legocka J, Zajchert I (1999) Role of spermidine in the stabilization of the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-protein complex of photosystem II during leaf senescence process. Acta Physiol Plant 21:127–132
Li Z, Jing W, Peng Y, Zhang XQ, Ma X, Huang LK, Yan Y (2015a) Spermine alleviates drought stress in white clover with different resistance by influencing carbohydrate metabolism and dehydrins synthesis. PLoS One 10:e0120708
Li Z, Peng Y, Ma X (2013) Different response on drought tolerance and post-drought recovery between the small-leafed and the large-leafed white clover (Trifolium repens L.) associated with antioxidative enzyme protection and lignin metabolism. Acta Physiol Plant 35:213–222
Li Z, Yu J, Peng Y, Huang B (2017) Metabolic pathways regulated by abscisic acid, salicylic acid, and γ-aminobutyric acid in association with improved drought tolerance in creeping bentgrass (Agrostis stolonifera). Physiol Plant 159:42–58
Li Z, Zhang Y, Peng D, Wang X, Peng Y, He X, Zhang X, Ma X, Huang L, Yan Y (2015b) Polyamine regulates tolerance to water stress in leaves of white clover associated with antioxidant defense and dehydrin genes via involvement in calcium messenger system and hydrogen peroxide signaling. Front Physiol 6:280
Li Z, Yan Z, Yi X, Zhang XQ, Peng Y, Ma X, Huang LK, Yan YH (2016a) Physiological and iTRAQ-based proteomic analyses reveal the function of spermidine on improving drought tolerance in white clover. J Proteome Res 15:1563–1579
Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Peng Y, Merewitz E, Ma X, Huang L, Yan Y (2016b) The alterations of endogenous polyamines and phytohormones induced by exogenous application of spermidine regulate antioxidant metabolism, metallothionein and relevant genes conferring drought tolerance in white clover. Environ Exp Bot 124:22–38
Li Z, Zhou H, Peng Y, Zhang X, Ma X, Huang L, Yan Y (2015c) Exogenously applied spermidine improves drought tolerance in creeping bentgrass associated with changes in antioxidant defense, endogenous polyamines and phytohormones. Plant Growth Regul 76:71–82
Ma Q, Yue LJ, Zhang JL, Wu GQ, Bao AK, Wang SM (2012) Sodium chloride improves photosynthesis and water status in the succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum. Tree Physiol 32:4–13
Merewitz EB, Gianfagna T, Huang B (2011) Protein accumulation in leaves and roots associated with improved drought tolerance in creeping bentgrass expressing an ipt gene for cytokinin synthesis. J Exp Bot 62:5311–5333
Moore PB, Steitz TA (2002) The involvement of RNA in ribosome function. Nature 418:229–235
Nichols SN, Hofmann RW, Williams WM (2015) Physiological drought resistance and accumulation of leaf phenolics in white clover interspecific hybrids. Environ Exp Bot 73:40–47
Peng Y, Xu C, Xu L, Huang B (2012) Improved heat tolerance through drought preconditioning associated with changes in lipid composition, antioxidant enzymes, and protein expression in kentucky bluegrass. Crop Sci 52:807–812
Radyukina NL, Mapelli S, Ivanov YV, Kartashov AV, Brambilla I, Kuznetsov VV (2009) Homeostasis of polyamines and antioxidant systems in roots and leaves of Plantago major under salt stress. Russ J Plant Physiol 56:323–331
Ramanjulu S, Sudhakar C (1997) Drought tolerance is partly related to amino acid accumulation and ammonia assimilation: a comparative study in two mulberry genotypes differing in drought sensitivity. J Plant Physiol 150:345–350
Sánchezrodríguez E, Romero L, Ruiz JM (2016) Accumulation on free polyamines enhanced antioxidant response in fruit of grafting tomato plants under water stress. J Plant Physiol 190:72–78
Sarwar MB, Batool F, Rashid B, Aftab B, Hassan S, Husnain T (2014) Integration and expression of heat shock protein gene in segregating population of transgenic cotton for drought tolerance. Pakistan J Agr Sci 51:935–941
Sato Y, Yokoya S (2008) Enhanced tolerance to drought stress in transgenic rice plants overexpressing a small heat-shock protein, sHSP17.7. Plant Cell Rep 27:329–334
Schulz P, Herde M, Romeis T (2013) Calcium-dependent protein kinases: hubs in plant stress signaling and development. Plant Physiol 163:523–530
Shi H, Ye T, Chan Z (2013) Comparative proteomic and physiological analyses reveal the protective effect of exogenous polyamines in the bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) response to salt and drought stresses. J Proteome Res 12:4951–4964
Sudhakar C, Veeranagamallaiah G, Nareshkumar A, Sudhakarbabu O, Sivakumar M, Pandurangaiah M, Kiranmai K, Lokesh U (2015) Polyamine metabolism influences antioxidant defense mechanism in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.) cultivars with different salinity tolerance. Plant Cell Rep 34:1–16
Szabados L, Savouré A (2010) Proline: a multifunctional amino acid. Trends Plant Sci 15:89–97
Takahashi T, Tong W (2015) Regulation and diversity of polyamine biosynthesis in plants. In: Suzuki H (ed) KusanoT. Polyamines. Springer, Japan, pp 27–44
Talaat NB, Shawky BT (2016) Dual application of 24-epibrassinolide and spermine confers drought stress tolerance in maize (Zea mays L.) by modulating polyamine and protein metabolism. J Plant Growth Regul 35:518–533
Thompson JF (1980) 10–arginine synthesis, proline synthesis, and related processes. Amino Acids Derivatives 1:375–402
Upreti KK, Sharma M (2016) Role of plant growth regulators in abiotic stress tolerance. In: Rao NKS et al (eds) Abiotic stress physiology of horticultural crops. Springer, India, pp 19–46
Vaseva I, Akiscan Y, Demirevska K, Anders I, Feller U (2011) Drought stress tolerance of red and white clover-comparative analysis of some chaperonins and dehydrins. Sci Hort 130:653–659
Vaseva I, Akiscan Y, Simova-Stoilova L, Kostadinova A, Nenkova R, Anders I, Feller U, Demirevska K (2012) Antioxidant response to drought in red and white clover. Acta Physiol Plant 34:1689–1699
Verma V, Ravindran P, Kumar PP (2016) Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. BMC Plant Biol 16:1–10
Wang N, Jing Z, He X, Sun H, Zhang G, Wu F (2015) Comparative proteomic analysis of drought tolerance in the two contrasting Tibetan wild genotypes and cultivated genotype. BMC Genomics 16:432
Wei S, Hu W, Deng X, Zhang Y, Liu X, Zhao X, Luo Q, Jin Z, Li Y, Zhou S (2014) A rice calcium-dependent protein kinase OsCPK9 positively regulates drought stress tolerance and spikelet fertility. BMC Plant Biol 14:133
Wen XP, Ban Y, Inoue H, Matsuda N, Kita M, Moriguchi T (2011) Antisense inhibition of a spermidine synthase gene highlights the role of polyamines for stress alleviation in pear shoots subjected to salinity and cadmium. Environ Exp Bot 72:157–166
Xia A, Zhang J, Dai L, Deng G, Liao Y, Liu L, Wang B, Peng D (2016) Isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ)-based comparative proteome analysis of the response of ramie under drought stress. Int J Mol Sci 17:1607
Xia XJ, Wang YJ, Zhou YH, Tao Y, Mao WH, Shi K, Asami T, Chen Z, Yu JQ (2009) Reactive oxygen species are involved in brassinosteroid-induced stress tolerance in cucumber. Plant Physiol 150:801–814
Xie H, Yang DH, Yao H, Bai G, Zhang YH, Xiao BG (2016) iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomic analysis reveals proteomic changes in leaves of cultivated tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) in response to drought stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 469:768–775
Xoconostlecázares B, Ramírezortega FA, Floreselenes L, Ruizmedrano R (2010) Drought tolerance in crop plants. Amer J Plant Physiol 5:241–256
Xu ZS, Li ZY, Chen Y, Chen M, Li LC, Ma YZ (2012) Heat shock protein 90 in plants: molecular mechanisms and roles in stress responses. Int J Mol Sci 13:15706–15723
Yamamoto A, Shim IS, Fujihara S (2016) Inhibition of putrescine biosynthesis enhanced salt stress sensitivity and decreased spermidine content in rice seedlings. Biol Plant 61:385–388
Yang LM, Jiang TB, Fountain JC, Scully BT, Lee RD, Kemerait RC, Chen SX, Guo BZ (2014) Protein profiles reveal diverse responsive signaling pathways in kernels of two maize inbred lines with contrasting drought sensitivity. Int J Mol Sci 15:18892–18918
Yang XL, Yu J, Dacosta M, Huang B (2013) Changes in carbohydrate metabolism in two Kentucky bluegrass cultivars during drought stress and recovery. J Amer Soc Hort Sci 138:1639–1644
Yang J, Zhang J, Liu K, Wang Z, Liu L (2007) Involvement of polyamines in the drought resistance of rice. J Exp Bot 58:1545–1555
Ye Z, Sangireddy S, Okekeogbu I, Zhou S, Yu CL, Hui D, Howe KJ, Fish T, Thannhauser TW (2016) Drought-induced leaf proteome changes in switchgrass seedlings. Int J Mol Sci 17:1251
Yin ZP, Li S, Ren J, Song XS (2014) Role of spermidine and spermine in alleviation of drought-induced oxidative stress and photosynthetic inhibition in Chinese dwarf cherry (Cerasus humilis) seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 74:209–218
Youssefian S, Nakamura M, Orudgev E, Kondo N (2001) Increased cysteine biosynthesis capacity of transgenic tobacco overexpressing an O-acetylserine(thiol) lyase modifies plant responses to oxidative stress. Plant Physiol 126:1001–1011
Zhang CM, Zou ZR, Huang Z, Zhang ZX (2010) Effects of exogenous spermidine on photosynthesis of tomato seedlings under drought stress. Agr Res Arid Areas 28:182–187
Zhao Y, Wang Y, Yang H, Wang W, Wu J, Hu X (2016) Quantitative proteomic analyses identify ABA-related proteins and signal pathways in maize leaves under drought conditions. Front Plant Sci 7:1827
Zhou Q, Yu B (2010) Changes in content of free, conjugated and bound polyamines and osmotic adjustment in adaptation of vetiver grass to water deficit. Plant Physiol Biochem Ppb 48:417–425
Zieske LR (2006) A perspective on the use of iTRAQ reagent technology for protein complex and profiling studies. J Exp Bot 57:1501–1508
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31372371), Modern Agro-industry Technology Research System (No.CARS-35-05), and Sichuan Province Support Project (No. 2013NZ0013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Prof. Yan Peng designed the experiments and provided materials and funding; Dr. Zhou Li performed experiments and wrote the manuscript; Dr. Zhou Li, Yan Zhang, and Dandan Peng analyzed the data; Prof. Xinquan Zhang and Xiao Ma provided reagents and materials; Prof. Linkai Huang and Yanhong Yan improved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Handling Editor: Bhumi Nath Tripathi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Peng, D. et al. The inhibition of polyamine biosynthesis weakens the drought tolerance in white clover (Trifolium repens) associated with the alteration of extensive proteins. Protoplasma 255, 803–817 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1186-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1186-9