Abstract
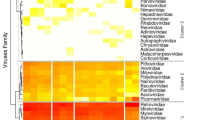
In a comprehensive research project on bat viruses, we successfully isolated a novel herpesvirus from the spleen of a greater horseshoe bat (Rhinolophus ferrumequinum) in Japan using a cell line established from the kidney of the same bat. This herpesvirus was a novel gammaherpesvirus (Rhinolophus gammaherpesvirus 1; RGHV-1), which belonged to the genus Percavirus. The whole RGHV-1 genome (147,790 bp) showed that 12 of the 84 genes predicted to contain open reading frames did not show any homology to those of other herpesviruses.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davison AJ, Eberle R, Ehlers B, Hayward GS et al (2009) The order Herpesvirales. Arch Virol. 154:171–177
Maeda K, Hondo E, Terakawa J, Kiso Y, Nakaichi N et al (2008) Isolation of novel adenovirus from fruit bat (Pteropus dasymallus yayeyamae). Emerg Infect Dis 14:347–349
Mizutani T, Endoh D, Okamoto M, Shirato K et al (2007) Rapid genome sequencing of RNA viruses. Emerg Infect Dis. 13:322–324
Agius CT, Nagesha HS, Studdert MJ (1992) Equine herpesvirus 5: comparisons with EHV2 (equine cytomegalovirus), cloning, and mapping of a new equine herpesvirus with a novel genome structure. Virology 191:176–186
Hirokawa T, Boon-Chieng S, Mitaku S (1998) SOSUI: classification and secondary structure prediction system for membrane proteins. Bioinformatics 14:378–379
Lehner PJ, Hoer S, Dodd R, Duncan LM (2005) Downregulation of cell surface receptors by the K3 family of viral and cellular ubiquitin E3 ligases. Immunol Rev. 207:112–125
Wu Z, Ren X, Yang L, Hu Y, Yang J et al (2012) Virome analysis for identification of novel mammalian viruses in bat species from Chinese provinces. J Virol. 86:10999–11012
Host KM, Damania B (2016) Discovery of a novel bat gammaherpesvirus. mSphere 1(1):e00016-16
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants for the Science and Technology Research Partnership for Sustainable Development (SATREPS) project from Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) and Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
A greater horseshoe bat was captured with permission from Yamaguchi Prefecture in 2006. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Diego G. Diel.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noguchi, K., Kuwata, R., Shimoda, H. et al. The complete genomic sequence of Rhinolophus gammaherpesvirus 1 isolated from a greater horseshoe bat. Arch Virol 164, 317–319 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-4040-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-018-4040-2