Summary.
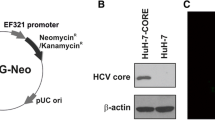
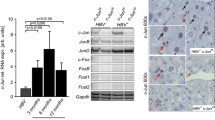
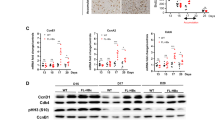
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is one of the major causes of chronic liver disease with the potential for development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The core protein of HCV has been shown to modulate expression of various cellular genes and to influence a number of cellular functions. We investigated the effect of constitutively expressed HCV core protein on cell cycle progression in HepG2 cell line, which is derived from a differentiated human hepatoblastoma and shows biosynthetic features similar to human hepatocytes. The results indicated that stable expression of the core protein in unsynchronized HepG2 cells induced a perturbation of the cell cycle with reduced cell doubling meantime and increased S phase fraction. Increase of c-myc protein above the basal expression level was demonstrated with a significant increase of c-myc stability, as revealed by its prolonged intracellular half-life, in HepG2 expressing HCV core protein. In contrast, p53 and p21 levels were unchanged. These results suggest that HCV core protein may promote cell cycle progression in HepG2 cells possibly through increasing stability of c-myc oncoprotein. These results are in support of important role played by HCV core protein in virus-mediated pathogenesis in persistently infected hosts and in hepatocarcinogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruggieri, A., Murdolo, M., Harada, T. et al. Cell cycle perturbation in a human hepatoblastoma cell line constitutively expressing Hepatitis C virus core protein. Arch Virol 149, 61–74 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-003-0202-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-003-0202-x