Abstract
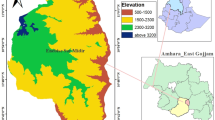
Climate variability has been a threat to the socio-economic development of Ethiopia. This paper examined the changes in rainfall, minimum, and maximum temperature extremes of Jemma Sub-Basin of the Upper Blue Nile Basin for the period of 1981 to 2014. The nonparametric Mann-Kendall, seasonal Mann-Kendall, and Sen’s slope estimator were used to estimate annual trends. Ten rainfall and 12 temperature indices were used to study changes in rainfall and temperature extremes. The results showed an increasing trend of annual and summer rainfall in more than 78% of the stations and a decreasing trend of spring rainfall in most of the stations. An increase in rainfall extreme events was detected in the majority of the stations. Several rainfall extreme indices showed wetting trends in the sub-basin, whereas limited indices indicated dryness in most of the stations. Annual maximum and minimum temperature and extreme temperature indices showed warming trend in the sub-basin. Presence of extreme rainfall and a warming trend of extreme temperature indices may suggest signs of climate change in the Jemma Sub-Basin. This study, therefore, recommended the need for exploring climate induced risks and implementing appropriate climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemayehu A, Bewket W (2016) Local climate variability and crop production in the central highlands of Ethiopia. Environ Dev 19:36–48
Alexander L, Zhang X, Peterson T, Caesar J, Gleason B, Tank K, Haylock M, Collins D, Trewin B, Rahimzadeh F, Tagipour A, Rupa Kumar K, Revadekar J, Griffiths G, Vincent L, Stephenson D, Burn J, Aguilar E, Brunet M, Taylor M, New M, Zhai P, Rusticucci M, Vazquez-Aguirre J (2006) Global observed changes in daily climate extremes of temperature and rainfall. J Geophys Res 111:D05109. https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JD006290
Alexander L, Hope P, Collins D, Trewin B, Lynch A, Nicholls N (2007) Trends in Australia’s climate means and extremes: a global context. Aust Meteorol Mag 56:1–18
Ali Y, Crosato A, Mohamed Y, Abdalla, S. And Wright, N. (2014) Sediment balances in the Blue Nile River Basin. Int J Sediment Res 29:1–13
Baldassarre G, Elshamy M, van Griensven A, Soliman E, Kigobe M, Ndomba P, Mutemi J, Mutua F, Moges S, Xuan Y, Solomatine D, Uhlenbrook S (2011) Future hydrology and climate in the River Nile basin: a review. Hydrol Sci J 56(2):199–211
Betrie G, Mohamed Y, van Griensven A, Srinivasan R (2011) Sediment management modelling in the Blue Nile Basinusing SWAT model. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:807–818
Beniston M (2003) Climatic change in mountain regions: a review of possible impacts. Clim Chang 59:5–3
Bewket W, Conway D (2007) A note on the temporal and spatial variability of rainfall in the drought-prone Amhara region of Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 27:1467–1477
Buuren S, Groothuis-Oudshoorn K, Robitzsch A, Vink G, Doove L, Jolani S (2015) Package ‘mice’ version 2.25; title multivariate imputation by chained equations.
Cama M, Schillaci C, Kropáˇcek J, Hochschild V, Maerker M (2017) Modelling soil erosion in a head catchment of Jemma Basin on the Ethiopian highlands. Geophys Res Abstr 19:EGU2017–EGU1458
Cheung W, Senay G, Singh A (2008) Trends and spatial distributionof annual and seasonal rainfall in Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 28:1723–1734
Conway D, Hulme M (1993) Recent fluctuations in precipitation and runoff over the Nile sub-basins and their impact on main Nile discharge. Clim Chang 25:127–151
Conway D, Schipper L (2011) Adaptation to climate change in Africa: challenges and opportunities identified from Ethiopia. Glob Environ Chang 21:227–237
CSA (Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia) (2007) Summary and Statistical Report of the 2007 Population and Housing Census Results
CSA (Central Statistical Agency of Ethiopia) (2013) Population projection of Ethiopia for all regions at Wereda level from 2014–2017
EPCC (Ethiopian Panel on Climate Change) (2015) First assessment report, Working Group II Agriculture and Food Security, Published by the Ethiopian Academy of Sciences
Folland C, Karl T, Salinge M (2002) Observed climate variability and change. W eather 57:269–278
Funk C, Rowland J, Eilerts G, Kebebe E, Biru N, White E, Galu G (2012) A climate trend analysis of Ethiopia, US Geological Survey, Fact Sheet 3053 USGS
Hirsch R, Slack J, Smith R (1982) Techniques for trend assessment for monthly water quality data. Water Resour Res 18:107–121
IPCC (2001) Climate change 2001: the scientific basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
IPCC (2012) Managing the risks of extreme events and disasters to advance climate change adaptation [field, C.B., V. Barros, T.F. Stocker, D. Qin, D.J. Dokken, K.L. Ebi, M.D. Mastrandrea, K.J. Mach, G.-K. Plattner, S.K. Allen, M. Tignor, and P.M. Midgley (eds.)]. A special report of working groups I and II of the intergovernmental panel on climate change (IPCC). Cambridge University press, Cambridge, UK, and New York, NY, USA, pp. 555–564
IPCC (2013) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. Contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change [stocker, T.F., D. Qin, G.-K. Plattner, M. Tignor, S.K. Allen, J. Boschung, A. Nauels, Y. Xia, V. Bex and P.M. Midgley (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, 1535 pp
Keggenhoff I, Elizbarashvili M, Amiri-Farahani A, King L (2014) Trends in daily temperature and rainfall extremes over Georgia, 1971–2010. Weather Clim Extremes 4:75–85
Kendall M (1975) Rank correlation measures. Charles Griffin, London
Maidment R, Allan R, Black E (2015) Recent observed and simulated changes in rainfall over Africa. Geophys Res Lett 42:8155–8164. https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL065765
Mann H (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13(3):245–259
Mekasha, A., Tesfaye, K. and Duncan, A. (2013) Trends in daily observed temperature and rainfall extremes over three Ethiopian eco-environments. Int. J. Climatol. wileyonlinelibrary.com. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.3816.
Mengistu D, Bewket W, Lal R (2013) Recent spatiotemporal temperature and rainfall variability and trends over the upper Blue Nile River basin, Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 34:2278–2292
MoA (Ministry of Agriculture of Ethiopia) (2000) Agroecological zonations of Ethiopia. Addis Ababa
MoWR (Ministry of Water Resources) (1998) Abay River Basin Integrated Dev Master Plan. McSweeney, C., New, M., Lizcano, G. and UNDP. (2008) Climate change country profiles: Ethiopia. http://country-profiles.geog.ox.ac.uk.
MRI (Mountain research Intiative) (2015) Elevation-dependent warming in mountain regions of the world mountain research initiative. Nat Clim Chang 5:424–430
NMSA (National Meteorological Services Agency) (1996) Climatic and agroclimatic resources of Ethiopia. Meteorological research report series, no. 1, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
NMA (National Meteorological Agency) (2007) Climate change national adaptation programme of action (NAPA) of Ethiopia. Ministry of Water Resources
Peterson T, Manton M (2008) Monitoring changes in climate extremes: a tale of international collaboration. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 89:1266–1271. https://doi.org/10.1175/2008BAMS2501.1
Pohlert, T. (2016) Package ‘trend’; Title Non-Parametric Trend Tests and Change-Point Detection
R Development Core Team (2015) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna
Revadekar J, Hameed S, Collins D, Manton M, Sheikh M, Borgaonkar H, Kothawale D, Adnan M, Ahmed A, Ashraf J, Baidya S, Islam N, Jayasinghearachchi D, Manzoor N, Premalal, K. And. L. Shreshta, M. (2013) Impact of altitude and latitude on changes in temperature extremes over South Asia during 1971–2000. Int J Climatol 33:199–209
Seleshi Y, Zanke U (2004) Recent changes in rainfall and rainy days in Ethiopia. Int J Climatol 24:973–983
Seleshi Y, Camberlin P (2006) Recent changes in dry spell and extreme rainfall events in Ethiopia. Theor Appl Climatol 83:181–191
Sen P (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63:1379–1389
Shah S, Rehman A, Rashid T, Karim J, Shah S (2016) A comparative study of ordinary least squares regression and Theil-Sen regression through simulation in the presence of outliers. Lasbela, U. J Sci Technol V:137–142
Shang H, Yan J, Gebremichael M, Ayalew S (2011) Trend analysis of extreme precipitation in the Northwestern Highlands of Ethiopia with a case study of Debremarkos. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:1937–1944
Shanko D, Camberlin P (1998) The effects of the southwest Indian Ocean tropical cyclones on Ethiopian drought. Int J Climatol 18:1373–1388
Sutcliffe JV, Parks YP (1999) The hydrology of the Nile. IAHS special publication no. 5. IAHS Press, Wallingford 179p
Tank K, Peterson T, Quadir D, Dorji S, Zou X, Tang H, Santhosh C, Joshi U, Jaswal K, Kolli RK, Sikder A, Deshpande N, Revadekar J, Yeleuova K, Vandasheva S, Faleyeva M, Gomboluudev P, Budhathoki K, Hussain A, Afzaal M, Chandrapala L, Anvar H, Amanmurad D, Asanova V, Jones P, New M, Spektorman T (2006) Changes in daily temperature and precipitation extremes in central and south Asia. J Geophys Res 111:D16105
Taye M, Willems P (2012) Temporal variability of hydroclimatic extremes in the Blue Nile basin. Water Resour Res 48:W03513. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR011466
Tesemma Z, Mohamed A, Steenhuis T (2010) Trends in rainfall and runoff in the Blue Nile Basin: 1964–2003. Hydrol Process 24(25):3747–3758. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.7893
Tesso G, Emana B, Ketema M (2012) A time series analysis of climate variability and its impacts on food production in North Shewa zone in Ethiopia. Afr Crop Sci J 20(2):261–274
Thiel, H. (1950) A rank-invariant method of linear and polynomial regression analysis.
Tierney J, Smerdon J, Anchukaitis K, Seager R (2013) Multidecadal variability in East African hydroclimate controlled by the Indian Ocean. Nature 493:389–392. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11785
Turrado C, López M, Lasheras F, Gómez B, Rollé J, Juez F (2014) Missing data imputation of solar radiation data under different atmospheric conditions. Sensors 14:20382–20399. https://doi.org/10.3390/s141120382
Viste E, Sorteberg A (2011) Moisture transport into the Ethiopian highlands. Int. J, Climatol
WMO (World Meteorological Organization) (2009) Guidelines on: analysis of extremes in a changing climate in support of informed decisions for adaptation Climate Data and Monitoring WCDMP-No 72
World Bank (2006) Managing water resources to maximise sustainable growth: a country water resources assistance strategy for Ethiopia. World Bank, Washington, DC
Yilma A, Awulachew S (2009) Characterization and atlas of the Blue Nile Basin and its sub-basins. International Water Management Institute
Zhang X, Yang F (2004) RClimDex (1.0) user guide. Climate research branch Environment Canada, Downsview (Ontario)
Zhang X, Alexander L, Hegerl G, Klein-Tank A, Peterson T, Trewin B, Zwiers F (2011) Indices for monitoring changes in extremes based on daily temperature and rainfall data. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Clim Chang 2:851–870. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcc.147
Acknowledgments
This study would not have been possible without the financial support given to the first author from the Water and Land Resources Center (WLC), Addis Ababa University, and Debretabor University. We are especially indebted to the Ethiopian Meteorological Agency that kindly provides the daily weather data of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Worku, G., Teferi, E., Bantider, A. et al. Observed changes in extremes of daily rainfall and temperature in Jemma Sub-Basin, Upper Blue Nile Basin, Ethiopia. Theor Appl Climatol 135, 839–854 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2412-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2412-x