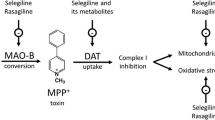
Abstract
MAO-B and COMT are both enzymes involved in dopamine breakdown and metabolism. Inhibitors of these enzymes are used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. This review article describes the scientific background to the localization and function of the enzymes, the physiological changes resulting from their inhibition, and the basic and clinical pharmacology of the various inhibitors and their role in treatment of Parkinson’s disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Tyramine is an endogenous trace amine produced by decarboxylation of tyrosine by AAADC and also occurs in foodstuff, such as yellow cheese, which is produced by a fermentation or maturation process.
Microdialysis is a system for perfusing a discrete brain area and determining the concentration of a neurotransmitter in extracellular fluid (ecf).
Systemic administration of L-DOPA is always accompanied by a peripherally acting inhibitor of AAADC, either carbidopa or benserazide which enhances the bio-availability of L-DOPA to the brain.
References
Abercrombie ED, Bonatz AE, Zigmond MJ (1990) Effects of l-DOPA on extracellular dopamine in striatum of normal and 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats. Brain Res 525(1):36–44
Adolfsson R, Gottfries CG, Oreland L, Wiberg A, Winblad B (1980) Increased activity of brain and platelet monoamine oxidase in dementia of Alzheimer type. Life Sci 27(12):1029–1034
Aluf Y, Vaya J, Khatib S, Finberg JP (2011) Alterations in striatal oxidative stress level produced by pharmacological manipulation of dopamine as shown by a novel synthetic marker molecule. Neuropharmacology 61(1–2):87–94
Aluf Y, Vaya J, Khatib S, Loboda Y, Finberg JP (2013) Selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase A or B reduces striatal oxidative stress in rats with partial depletion of the nigro-striatal dopaminergic pathway. Neuropharmacology 65:48–57
Apud JA, Mattay V, Chen J, Kolachana BS, Callicott JH, Rasetti R et al (2007) Tolcapone improves cognition and cortical information processing in normal human subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(5):1011–1020
Asanuma M, Miyazaki I, Ogawa N (2003) Dopamine- or l-DOPA-induced neurotoxicity: the role of dopamine quinone formation and tyrosinase in a model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotox Res 5(3):165–176
Asanuma M, Miyazaki I, Murakami S, Diaz-Corrales FJ, Ogawa N (2014) Striatal astrocytes act as a reservoir for l-DOPA. PLoS One 9(9):e106362
Bar Am O, Amit T, Youdim MB (2004) Contrasting neuroprotective and neurotoxic actions of respective metabolites of anti-Parkinson drugs rasagiline and selegiline. Neurosci Lett 355(3):169–172
Bar-Am O, Weinreb O, Amit T, Youdim MB (2010) The neuroprotective mechanism of 1-(R)-aminoindan, the major metabolite of the anti-parkinsonian drug rasagiline. J Neurochem 112(5):1131–1137
Bar-Am O, Gross A, Friedman R, Finberg JP (2012) Cardiovascular baroreceptor activity and selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase. Eur J Pharmacol 683(1–3):226–230
Bartl J, Muller T, Grunblatt E, Gerlach M, Riederer P (2014) Chronic monoamine oxidase-B inhibitor treatment blocks monoamine oxidase—a enzyme activity. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 121(4):379–383
Bhattacharya KF, Nouri S, Olanow CW, Yahr MD, Kaufmann H (2003) Selegiline in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: its impact on orthostatic hypotension. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 9(4):221–224
Birkmayer W, Riederer P, Youdim MB, Linauer W (1975) The potentiation of the anti akinetic effect after l-DOPA treatment by an inhibitor of MAO-B, deprenil. J Neural Transm 36(3–4):303–326
Borgohain R, Szasz J, Stanzione P, Meshram C, Bhatt MH, Chirilineau D et al (2014) Two-year, randomized, controlled study of safinamide as add-on to levodopa in mid to late Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 29(10):1273–1280
Brooks DJ (2008) Optimizing levodopa therapy for Parkinson’s disease with levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone: implications from a clinical and patient perspective. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 4(1):39–47
Butcher SP, Fairbrother IS, Kelly JS, Arbuthnott GW (1990) Effects of selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors on the in vivo release and metabolism of dopamine in the rat striatum. J Neurochem 55(3):981–988
Caccia C, Maj R, Calabresi M, Maestroni S, Faravelli L, Curatolo L et al (2006) Safinamide: from molecular targets to a new anti-Parkinson drug. Neurology 67(7 Suppl 2):S18–S23
Carlile GW, Chalmers-Redman RM, Tatton NA, Pong A, Borden KE, Tatton WG (2000) Reduced apoptosis after nerve growth factor and serum withdrawal: conversion of tetrameric glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase to a dimer. Mol Pharmacol 57(1):2–12
Cenci MA, Ohlin KE, Odin P (2011) Current options and future possibilities for the treatment of dyskinesia and motor fluctuations in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 10(6):670–684
Cereda E, Cilia R, Canesi M, Tesei S, Mariani CB, Zecchinelli AL et al (2017) Efficacy of rasagiline and selegiline in Parkinson’s disease: a head-to-head 3-year retrospective case-control study. J Neurol 264(6):1254–1263
Chang Y, Wang LB, Li D, Lei K, Liu SY (2017) Efficacy of rasagiline for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: an updated meta-analysis. Ann Med 49(5):421–434
Chen JJ, Swope DM, Dashtipour K (2007) Comprehensive review of rasagiline, a second-generation monoamine oxidase inhibitor, for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Clin Ther 29(9):1825–1849
Churchyard A, Mathias CJ, Boonkongchuen P, Lees AJ (1997) Autonomic effects of selegiline: possible cardiovascular toxicity in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63(2):228–234
Churchyard A, Mathias CJ, Lees AJ (1999) Selegiline-induced postural hypotension in Parkinson’s disease: a longitudinal study on the effects of drug withdrawal. Mov Disord 14(2):246–251
Culpepper L, Kovalick LJ (2008) A review of the literature on the selegiline transdermal system: an effective and well-tolerated monoamine oxidase inhibitor for the treatment of depression. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry 10(1):25–30
Daws LC (2009) Unfaithful neurotransmitter transporters: focus on serotonin uptake and implications for antidepressant efficacy. Pharmacol Ther 121(1):89–99
deMarcaida JA, Schwid SR, White WB, Blindauer K, Fahn S, Kieburtz K et al (2006) Effects of tyramine administration in Parkinson’s disease patients treated with selective MAO-B inhibitor rasagiline. Mov Disord 21(10):1716–1721
Denney RM, Denney CB (1985) An update on the identity crisis of monoamine oxidase: new and old evidence for the independence of MAO A and B. Pharmacol Ther 30(3):227–258
Diatchenko L, Slade GD, Nackley AG, Bhalang K, Sigurdsson A, Belfer I et al (2005) Genetic basis for individual variations in pain perception and the development of a chronic pain condition. Hum Mol Genet 14(1):135–143
Edmondson DE, Binda C (2018) Monoamine Oxidases. Sub Cell Biochem 87:117–139
Edmondson DE, Binda C, Wang J, Upadhyay AK, Mattevi A (2009) Molecular and mechanistic properties of the membrane-bound mitochondrial monoamine oxidases. Biochemistry 48(20):4220–4230
Eigeldinger-Berthou S, Meier C, Zulliger R, Lecaude S, Enzmann V, Sarra GM (2012) Rasagiline interferes with neurodegeneration in the Prph2/rds mouse. Retina 32(3):617–628
Eisenhofer G, Kopin IJ, Goldstein DS (2004) Catecholamine metabolism: a contemporary view with implications for physiology and medicine. Pharmacol Rev 56(3):331–349
Ekblom J, Jossan SS, Bergstrom M, Oreland L, Walum E, Aquilonius SM (1993) Monoamine oxidase-B in astrocytes. Glia 8(2):122–132
Ferreira JJ, Rocha JF, Falcao A, Santos A, Pinto R, Nunes T et al (2015) Effect of opicapone on levodopa pharmacokinetics, catechol-O-methyltransferase activity and motor fluctuations in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 22(5):815–825, e856
Ferreira JJ, Lees A, Rocha JF, Poewe W, Rascol O, Soares-da-Silva P et al (2016) Opicapone as an adjunct to levodopa in patients with Parkinson’s disease and end-of-dose motor fluctuations: a randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 15(2):154–165
Ferreira JJ, Lees AJ, Poewe W, Rascol O, Rocha JF, Keller B et al (2018) Effectiveness of opicapone and switching from entacapone in fluctuating Parkinson disease. Neurology 90(21):e1849–e1857
Finberg JP (2014) Update on the pharmacology of selective inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B: focus on modulation of CNS monoamine neurotransmitter release. Pharmacol Ther 143(2):133–152
Finberg JP, Gillman PK (2011) Selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase type B and the “cheese effect”. In: Youdim MB, Riederer P (eds) International review of neurobiology, vol 100. Academic Press, Burlington, pp 169–190
Finberg JP, Rabey JM (2016) Inhibitors of MAO-A and MAO-B in psychiatry and neurology. Front Pharmacol 7:340
Finberg JP, Tenne M (1982) Relationship between tyramine potentiation and selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase types A and B in the rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol 77(1):13–21
Finberg JP, Youdim MB (2002) Pharmacological properties of the anti-Parkinson drug rasagiline; modification of endogenous brain amines, reserpine reversal, serotonergic and dopaminergic behaviours. Neuropharmacology 43(7):1110–1118
Finberg JP, Wang J, Goldstein DS, Kopin IJ, Bankiewicz KS (1995) Influence of selective inhibition of monoamine oxidase A or B on striatal metabolism of l-DOPA in hemiparkinsonian rats. J Neurochem 65(3):1213–1220
Fox SH, Katzenschlager R, Lim SY, Barton B, de Bie RMA, Seppi K et al (2018) International Parkinson and movement disorder society evidence-based medicine review: update on treatments for the motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 33(8):1248–1266
Frakey LL, Friedman JH (2017) Cognitive effects of rasagiline in mild-to-moderate stage Parkinson’s disease without dementia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 29(1):22–25
Gallagher IM, Clow A, Glover V (1998) Long-term administration of (−)-deprenyl increases mortality in male Wistar rats. J Neural Transm Suppl 52:315–320
Gerlach M, van den Buuse M, Blaha C, Bremen D, Riederer P (2004) Entacapone increases and prolongs the central effects of l-DOPA in the 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 370(5):388–394
Giladi N, Asgharnejad M, Bauer L, Grieger F, Boroojerdi B (2016) Rotigotine in combination with the MAO-B inhibitor selegiline in early Parkinson’s disease: a post hoc analysis. J Parkinson’s Dis 6(2):401–411
Gillman PK (2011) Advances pertaining to the pharmacology and interactions of irreversible nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitors. J Clin Psychopharmacol 31(1):66–74
Glezer S, Finberg JP (2003) Pharmacological comparison between the actions of methamphetamine and 1-aminoindan stereoisomers on sympathetic nervous function in rat vas deferens. Eur J Pharmacol 472(3):173–177
Goldberg JF, Thase ME (2013) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors revisited: what you should know. J Clin Psychiatry 74(2):189–191
Goldstein DS, Sullivan P, Holmes C, Miller GW, Alter S, Strong R et al (2013) Determinants of buildup of the toxic dopamine metabolite DOPAL in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 126(5):591–603
Goldstein DS, Kopin IJ, Sharabi Y (2014) Catecholamine autotoxicity. Implications for pharmacology and therapeutics of Parkinson disease and related disorders. Pharmacol Ther 144(3):268–282
Goren T, Adar L, Sasson N, Weiss YM (2010) Clinical pharmacology tyramine challenge study to determine the selectivity of the monoamine oxidase type B (MAO-B) inhibitor rasagiline. J Clin Pharmacol 50(12):1420–1428
Guay DR (2006) Rasagiline (TVP-1012): a new selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor for Parkinson’s disease. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother 4(4):330–346
Jankovic J, Berkovich E, Eyal E, Tolosa E (2014) Symptomatic efficacy of rasagiline monotherapy in early Parkinson’s disease: post-hoc analyses from the ADAGIO trial. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 20(6):640–643
Jarrott B, Iversen LL (1971) Noradrenaline metabolizing enzymes in normal and sympathetically denervated vas deferens. J Neurochem 18(1):1–6
Jenner P, Langston JW (2011) Explaining ADAGIO: a critical review of the biological basis for the clinical effects of rasagiline. Mov Disord 26(13):2316–2323
Johnston JP (1968) Some observations upon a new inhibitor of monoamine oxidase in brain tissue. Biochem Pharmacol 17(7):1285–1297
Kaakkola S, Wurtman RJ (1993) Effects of catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors and l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine with or without carbidopa on extracellular dopamine in rat striatum. J Neurochem 60(1):137–144
Katsaiti I, Nixon J (2018) Are there benefits in adding catechol-O methyltransferase inhibitors in the pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease patients? A systematic review. J Parkinson’s Dis 8(2):217–231
Kieburtz K (2009) ADAGIO misses a beat? Lancet Neurol 8(12):1081–1082
Knoll J (1988) The striatal dopamine dependency of life span in male rats. Longevity study with (−)deprenyl. Mech Ageing Dev 46(1–3):237–262
Knoll J (1992) (−)Deprenyl-medication: a strategy to modulate the age-related decline of the striatal dopaminergic system. J Am Geriatr Soc 40(8):839–847
Knoll J (1998) (−)Deprenyl (selegiline), a catecholaminergic activity enhancer (CAE) substance acting in the brain. Pharmacol Toxicol 82(2):57–66
Knoll J, Magyar K (1972) Some puzzling pharmacological effects of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol 5:393–408
Knoll J, Miklya I (2016) Longevity study with low doses of selegiline/(−)-deprenyl and (2R)-1-(1-benzofuran-2-yl)-N-propylpentane-2-amine (BPAP). Life Sci 167:32–38
Knoll J, Ecseri Z, Kelemen K, Nievel J, Knoll B (1965) Phenylisopropylmethylpropinylamine (E-250), a new spectrum psychic energizer. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 155(1):154–164
Knoll J, Miklya I, Knoll B (2002) Stimulation of the catecholaminergic and serotoninergic neurons in the rat brain by R-(−)-1-(benzofuran-2-yl)-2-propylaminopentane, (−)-BPAP. Life Sci 71(18):2137–2144
Kumagae Y, Matsui Y, Iwata N (1991) Deamination of norepinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin by type A monoamine oxidase in discrete regions of the rat brain and inhibition by RS-8359. Jpn J Pharmacol 55(1):121–128
Kunugi H, Nanko S, Ueki A, Otsuka E, Hattori M, Hoda F et al (1997) High and low activity alleles of catechol-O-methyltransferase gene: ethnic difference and possible association with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 221(2–3):202–204
Kuoppamaki M, Korpela K, Marttila R, Kaasinen V, Hartikainen P, Lyytinen J et al (2009) Comparison of pharmacokinetic profile of levodopa throughout the day between levodopa/carbidopa/entacapone and levodopa/carbidopa when administered four or five times daily. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 65(5):443–455
Kuoppamaki M, Leinonen M, Poewe W (2015) Efficacy and safety of entacapone in levodopa/carbidopa versus levodopa/benserazide treated Parkinson’s disease patients with wearing-off. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 122(12):1709–1714
Lader MH, Sakalis G, Tansella M (1970) Interactions between sympathomimetic amines and a new monoamine oxidase inhibitor. Psychopharmacologia 18(1):118–123
Lamensdorf I, Youdim MB, Finberg JP (1996) Effect of long-term treatment with selective monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors on dopamine release from rat striatum in vivo. J Neurochem 67(4):1532–1539
Lang AE, Espay AJ (2018) Disease modification in Parkinson’s disease: current approaches, challenges, and future considerations. Mov Disord 33(5):660–677
Laux G (1993) Do MAO-B inhibitors have any role in the treatment of depression. In: Szelenyi I (ed) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase B. Birkhauser Verlag. Basel, pp 319–326
Lei D, Shao Z, Zhou X, Yuan H (2018) Synergistic neuroprotective effect of rasagiline and idebenone against retinal ischemia-reperfusion injury via the Lin28-let-7-Dicer pathway. Oncotarget 9(15):12137–12153
Levitt P, Pintar JE, Breakefield XO (1982) Immunocytochemical demonstration of monoamine oxidase B in brain astrocytes and serotonergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79(20):6385–6389
Levkovitch-Verbin H, Vander S, Melamed S (2011) Rasagiline-induced delay of retinal ganglion cell death in experimental glaucoma in rats. J Glaucoma 20(5):273–277
Lin CH, Fan JY, Lin HI, Chang CW, Wu YR (2018) Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) genetic variants are associated with cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 50:48–53
Lotufo-Neto F, Trivedi M, Thase ME (1999) Meta-analysis of the reversible inhibitors of monoamine oxidase type A moclobemide and brofaromine for the treatment of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 20(3):226–247
Mandel SA, Sagi Y, Amit T (2007) Rasagiline promotes regeneration of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons in post-MPTP-induced Parkinsonism via activation of tyrosine kinase receptor signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 32(10):1694–1699
Mann J, Gershon S (1980) l-Deprenyl, a selective monoamine oxidase type-B inhibitor in endogenous depression. Life Sci 26(11):877–882
Mann JJ, Aarons SF, Wilner PJ, Keilp JG, Sweeney JA, Pearlstein T et al (1989) A controlled study of the antidepressant efficacy and side effects of (−)-deprenyl. A selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46(1):45–50
Mannisto PT, Kaakkola S (1999) Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): biochemistry, molecular biology, pharmacology, and clinical efficacy of the new selective COMT inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev 51(4):593–628
Mannisto PT, Tuomainen P, Tuominen RK (1992) Different in vivo properties of three new inhibitors of catechol O-methyltransferase in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 105(3):569–574
Mannisto PT, Lang A, Rauhala P, Vasar E (1995) Beneficial effects of co-administration of catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors and l-dihydroxyphenylalanine in rat models of depression. Eur J Pharmacol 274(1–3):229–233
Marin C, Aguilar E, Bonastre M, Tolosa E, Obeso JA (2005) Early administration of entacapone prevents levodopa-induced motor fluctuations in hemiparkinsonian rats. Exp Neurol 192(1):184–193
Maruyama W, Akao Y, Youdim MB, Davis BA, Naoi M (2001) Transfection-enforced Bcl-2 overexpression and an anti-Parkinson drug, rasagiline, prevent nuclear accumulation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase induced by an endogenous dopaminergic neurotoxin, N-methyl(R)salsolinol. J Neurochem 78(4):727–735
Maruyama W, Akao Y, Carrillo MC, Kitani K, Youdium MB, Naoi M (2002) Neuroprotection by propargylamines in Parkinson’s disease: suppression of apoptosis and induction of prosurvival genes. Neurotoxicol Teratol 24(5):675–682
Mendis N, Pare CM, Sandler M, Glover V, Stern GM (1981) Is the failure of (−)deprenyl, a selective monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, to alleviate depression related to freedom from the cheese effect? Psychopharmacology 73(1):87–90
Montastruc JL, Chaumerliac C, Desboeuf K, Manika M, Bagheri H, Rascol O et al (2000) Adverse drug reactions to selegiline: a review of the French pharmacovigilance database. Clin Neuropharmacol 23(5):271–275
Moreau JL, Borgulya J, Jenck F, Martin JR (1994) Tolcapone: a potential new antidepressant detected in a novel animal model of depression. Behav Pharmacol 5(3):344–350
Mosnaim AD, Hudzik T, Wolf ME (2015) Behavioral effects of beta-phenylethylamine and various monomethylated and monohalogenated analogs in mice are mediated by catecholaminergic mechanisms. Am J Ther 22(6):412–422
Mostile G, Nicoletti A, Dibilio V, Luca A, Raciti L, Sciacca G et al (2017) Switching l-DOPA therapy from pulsatile to pulse administration reduces motor complications in Parkinson’s disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 40(1):6–10
Muller T (2015) Catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors in Parkinson’s disease. Drugs 75(2):157–174
Muller T, Hoffmann JA, Dimpfel W, Oehlwein C (2013) Switch from selegiline to rasagiline is beneficial in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 120(5):761–765
Muller T, Riederer P, Grunblatt E (2017) Determination of monoamine oxidase A and B activity in long-term treated patients with Parkinson disease. Clin Neuropharmacol 40(5):208–211
Murata M, Hasegawa K, Kanazawa I, Japan Zonisamide on PDSG (2007) Zonisamide improves motor function in Parkinson disease: a randomized, double-blind study. Neurology 68(1):45–50
Murata M, Odawara T, Hasegawa K, Iiyama S, Nakamura M, Tagawa M et al (2018) Adjunct zonisamide to levodopa for DLB parkinsonism: a randomized double-blind phase 2 study. Neurology 90(8):e664–e672
Navailles S, Bioulac B, Gross C, De Deurwaerdere P (2010) Serotonergic neurons mediate ectopic release of dopamine induced by l-DOPA in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 38(1):136–143
Navailles S, Bioulac B, Gross C, De Deurwaerdere P (2011) Chronic l-DOPA therapy alters central serotonergic function and l-DOPA-induced dopamine release in a region-dependent manner in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Dis 41(2):585–590
O’Carroll AM, Fowler CJ, Phillips JP, Tobbia I, Tipton KF (1983) The deamination of dopamine by human brain monoamine oxidase. Specificity for the two enzyme forms in seven brain regions. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 322(3):198–202
Olanow CW (2006) Rationale for considering that propargylamines might be neuroprotective in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 66(10 Suppl 4):S69–S79
Olanow CW, Myllyla VV, Sotaniemi KA, Larsen JP, Palhagen S, Przuntek H et al (1998) Effect of selegiline on mortality in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis. Neurology 51(3):825–830
Olanow CW, Schapira AH, LeWitt PA, Kieburtz K, Sauer D, Olivieri G et al (2006) TCH346 as a neuroprotective drug in Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 5(12):1013–1020
Olanow CW, Rascol O, Hauser R, Feigin PD, Jankovic J, Lang A et al (2009) A double-blind, delayed-start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson’s disease. N Engl J Med 361(13):1268–1278
Olanow CW, Kieburtz K, Rascol O, Poewe W, Schapira AH, Emre M et al (2013) Factors predictive of the development of levodopa-induced dyskinesia and wearing-off in Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 28(8):1064–1071
Olanow CW, Kieburtz K, Leinonen M, Elmer L, Giladi N, Hauser RA et al (2017) A randomized trial of a low-dose Rasagiline and Pramipexole combination (P2B001) in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 32(5):783–789
Petit GH, Berkovich E, Hickery M, Kallunki P, Fog K, Fitzer-Attas C et al (2013) Rasagiline ameliorates olfactory deficits in an alpha-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 8(4):e60691
Pursiainen V, Korpelainen TJ, Haapaniemi HT, Sotaniemi AK, Myllyla VV (2007) Selegiline and blood pressure in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 115(2):104–108
Rascol O, Brooks DJ, Melamed E, Oertel W, Poewe W, Stocchi F et al (2005) Rasagiline as an adjunct to levodopa in patients with Parkinson’s disease and motor fluctuations (LARGO, Lasting effect in Adjunct therapy with Rasagiline Given Once daily, study): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group trial. Lancet 365(9463):947–954
Rascol O, Fitzer-Attas CJ, Hauser R, Jankovic J, Lang A, Langston JW et al (2011) A double-blind, delayed-start trial of rasagiline in Parkinson’s disease (the ADAGIO study): prespecified and post-hoc analyses of the need for additional therapies, changes in UPDRS scores, and non-motor outcomes. Lancet Neurol 10(5):415–423
Rascol O, Hauser RA, Stocchi F, Fitzer-Attas CJ, Sidi Y, Abler V et al (2016) Long-term effects of rasagiline and the natural history of treated Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 31(10):1489–1496
Reilly DK, Rivera-Calimlim L, Van Dyke D (1980) Catechol-O-methyltransferase activity: a determinant of levodopa response. Clin Pharmacol Ther 28(2):278–286
Reynolds GP, Riederer P, Sandler M, Jellinger K, Seemann D (1978) Amphetamine and 2-phenylethylamine in post-mortem Parkinsonian brain after (−)deprenyl administration. J Neural Transm 43(3–4):271–277
Riederer P, Muller T (2018) Monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease: clinical-pharmacological aspects. J Neural Transm (Vienna). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1876-2
Rocha JF, Almeida L, Falcao A, Palma PN, Loureiro AI, Pinto R et al (2013) Opicapone: a short lived and very long acting novel catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitor following multiple dose administration in healthy subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 76(5):763–775
Rocha JF, Ferreira JJ, Falcao A, Santos A, Pinto R, Nunes T et al (2016) Effect of 3 single-dose regimens of opicapone on levodopa pharmacokinetics, catechol-O-methyltransferase activity and motor response in patients with parkinson disease. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev 5(3):232–240
Rodrigues FB, Ferreira JJ (2017) Opicapone for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother 18(4):445–453
Sader-Mazbar O, Loboda Y, Rabey MJ, Finberg JP (2013) Increased l-DOPA-derived dopamine following selective MAO-A or -B inhibition in rat striatum depleted of dopaminergic and serotonergic innervation. Br J Pharmacol 170(5):999–1013
Saura J, Bleuel Z, Ulrich J, Mendelowitsch A, Chen K, Shih JC et al (1996) Molecular neuroanatomy of human monoamine oxidases A and B revealed by quantitative enzyme radioautography and in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neuroscience 70(3):755–774
Saura J, Andres N, Andrade C, Ojuel J, Eriksson K, Mahy N (1997) Biphasic and region-specific MAO-B response to aging in normal human brain. Neurobiol Aging 18(5):497–507
Schrempf W, Fauser M, Wienecke M, Brown S, Maass A, Ossig C et al (2018) Rasagiline improves polysomnographic sleep parameters in patients with Parkinson’s disease: a double-blind, baseline-controlled trial. Eur J Neurol 25(4):672–679
Semkova I, Wolz P, Schilling M, Krieglstein J (1996) Selegiline enhances NGF synthesis and protects central nervous system neurons from excitotoxic and ischemic damage. Eur J Pharmacol 315(1):19–30
Shoulson I, Oakes D, Fahn S, Lang A, Langston JW, LeWitt P et al (2002) Impact of sustained deprenyl (selegiline) in levodopa-treated Parkinson’s disease: a randomized placebo-controlled extension of the deprenyl and tocopherol antioxidative therapy of parkinsonism trial. Ann Neurol 51(5):604–612
Smith LA, Jackson MJ, Al-Barghouthy G, Rose S, Kuoppamaki M, Olanow W et al (2005) Multiple small doses of levodopa plus entacapone produce continuous dopaminergic stimulation and reduce dyskinesia induction in MPTP-treated drug-naive primates. Mov Disord 20(3):306–314
Solla P, Cannas A, Marrosu F, Marrosu MG (2010) Therapeutic interventions and adjustments in the management of Parkinson disease: role of combined carbidopa/levodopa/entacapone (Stalevo). Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 6:483–490
Sonsalla PK, Wong LY, Winnik B, Buckley B (2010) The antiepileptic drug zonisamide inhibits MAO-B and attenuates MPTP toxicity in mice: clinical relevance. Exp Neurol 221(2):329–334
Stocchi F, Rabey JM (2011) Effect of rasagiline as adjunct therapy to levodopa on severity of OFF in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurol 18(12):1373–1378
Stocchi F, Rascol O, Kieburtz K, Poewe W, Jankovic J, Tolosa E et al (2010) Initiating levodopa/carbidopa therapy with and without entacapone in early Parkinson disease: the STRIDE-PD study. Ann Neurol 68(1):18–27
Stocchi F, Borgohain R, Onofrj M, Schapira AH, Bhatt M, Lucini V et al (2012) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of safinamide as add-on therapy in early Parkinson’s disease patients. Mov Disord 27(1):106–112
Szoko E, Tabi T, Riederer P, Vecsei L, Magyar K (2018) Pharmacological aspects of the neuroprotective effects of irreversible MAO-B inhibitors, selegiline and rasagiline, in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1853-9
Tatton W, Chalmers-Redman G RME (1996) Modulation of gene expression rather than monoamine oxidase inhibition: (−)-deprenyl-related compounds in controlling neurodegeneration. Neurology 47(Supplement 3):S171–S183
Thebault JJ, Guillaume M, Levy R (2004) Tolerability, safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of rasagiline: a potent, selective, and irreversible monoamine oxidase type B inhibitor. Pharmacotherapy 24(10):1295–1305
Tipton KF (2018) 90 years of monoamine oxidase: some progress and some confusion. J Neural Transm (Vienna). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1881-5
Vaya J, Aluf Y, Finberg JPM (2012) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. In: Gadoth N, Gobel HH (eds) Oxidative stress and free radical damage in neurology. Springer, New York, pp 191–224
Wachtel SR, Abercrombie ED (1994) l-3,4-Dihydroxyphenylalanine-induced dopamine release in the striatum of intact and 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats: differential effects of monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitors. J Neurochem 63(1):108–117
Weinreb O, Amit T, Bar-Am O, Chillag-Talmor O, Youdim MB (2005) Novel neuroprotective mechanism of action of rasagiline is associated with its propargyl moiety: interaction of Bcl-2 family members with PKC pathway. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1053:348–355
Westlund KN, Denney RM, Kochersperger LM, Rose RM, Abell CW (1985) Distinct monoamine oxidase A and B populations in primate brain. Science 230(4722):181–183
Westlund KN, Denney RM, Rose RM, Abell CW (1988) Localization of distinct monoamine oxidase A and monoamine oxidase B cell populations in human brainstem. Neuroscience 25(2):439–456
Yanagida O, Kanai Y, Chairoungdua A, Kim DK, Segawa H, Nii T et al (2001) Human l-type amino acid transporter 1 (LAT1): characterization of function and expression in tumor cell lines. Biochim Biophys Acta 1514(2):291–302
Youdim MB, Gross A, Finberg JP (2001a) Rasagiline [N-propargyl-1R(+)-aminoindan], a selective and potent inhibitor of mitochondrial monoamine oxidase B. Br J Pharmacol 132(2):500–506
Youdim MB, Wadia A, Tatton W, Weinstock M (2001b) The anti-Parkinson drug rasagiline and its cholinesterase inhibitor derivatives exert neuroprotection unrelated to MAO inhibition in cell culture and in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci 939:450–458
Youdim MB, Edmondson D, Tipton KF (2006) The therapeutic potential of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(4):295–309
Yu PH, Hertz L (1983) Type A and B monoamine oxidase in glial cells in long-term culture. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 7(4–6):687–690
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author was a developer of rasagiline and receives royalties from the sale of this drug. This financial connection with the pharmaceutical industry in no way affected his opinions in writing this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Finberg, J.P.M. Inhibitors of MAO-B and COMT: their effects on brain dopamine levels and uses in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 126, 433–448 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1952-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-018-1952-7