Abstract
Background
Primary decompressive craniectomy (DC) is considered for traumatic brain injury (TBI) patients with clinical deterioration, presenting large amounts of high-density lesions on computed tomography (CT). Postoperative CT findings may be suitable for prognostic evaluation. This study evaluated the radiographic predictors of clinical outcome and survival using pre- and postoperative CT scans of such patients.
Methods
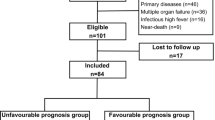
We enrolled 150 patients with moderate to severe TBI who underwent primary DC. They were divided into two groups based on the 6-month postoperative Glasgow Outcome Scale Extended scores (1–4, unfavorable; 5–8, favorable). Radiographic parameters, including hemorrhage type, location, presence of skull fracture, midline shifting, hemispheric diameter, effacement of cisterns, parenchymal hypodensity, and craniectomy size, were reviewed. Stepwise logistic regression analysis was used to identify the prognostic factors of clinical outcome and 6-month mortality.
Results
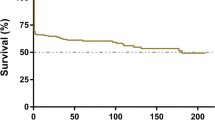
Multivariable logistic regression analysis revealed that age (odds ratio [OR] = 1.09; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.032–1.151; p = 0.002), postoperative low density (OR = 12.58; 95% CI 1.247–126.829; p = 0.032), and postoperative effacement of the ambient cistern (OR = 14.52; 95% CI 2.234–94.351; p = 0.005) and the crural cistern (OR = 4.90; 95% CI 1.359–17.678; p = 0.015) were associated with unfavorable outcomes. Postoperative effacement of the crural cistern was the strongest predictor of 6-month mortality (OR = 8.93; 95% CI 2.747–29.054; p = 0.000).
Conclusions
Hemispheric hypodensity and effacement of the crural and ambient cisterns on postoperative CT after primary DC seems to associate with poor outcome in patients with TBI.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarabi B, Hesdorffer DC, Ahn ES, Aresco C, Scalea TM, Eisenberg HM (2006) Outcome following decompressive craniectomy for malignant swelling due to severe head injury. J Neurosurg 104:469–479. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.104.4.469
Al-Jishi A, Saluja RS, Al-Jehani H, Lamoureux J, Maleki M, Marcoux J (2011) Primary or secondary decompressive craniectomy: different indication and outcome. Can J Neurol Sci 38:612–620. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0317167100012154
Azian A, Nurulazman A, Shuaib I, Mahayidin M, Ariff A, Naing N, Abdullah J (2001) Computed tomography of the brain in predicting outcome of traumatic intracranial haemorrhage in Malaysian patients. Acta Neurochir 143:711–720
Bao YH, Liang YM, Gao GY, Pan YH, Luo QZ, Jiang JY (2010) Bilateral decompressive craniectomy for patients with malignant diffuse brain swelling after severe traumatic brain injury: a 37-case study. J Neurotrauma 27:341–347. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2009.1040
Barthélemy EJ, Melis M, Gordon E, Ullman JS, Germano IM (2016) decompressive craniectomy for severe traumatic brain injury: a systematic review. World Neurosurg 88:411–420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.12.044
Carney N, Totten AM, O'Reilly C, Ullman JS, Hawryluk GW, Bell MJ, Bratton SL, Chesnut R, Harris OA, Kissoon N, Rubiano AM, Shutter L, Tasker RC, Vavilala MS, Wilberger J, Wright DW, Ghajar J (2017) Guidelines for the management of severe traumatic brain injury, Fourth Edition. Neurosurgery 80:6–15. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001432
Charry JD, Tejada JH, Pinzon MA, Tejada WA, Ochoa JD, Falla M, Tovar JH, Cuellar-Bahamon AM, Solano JP (2017) Predicted unfavorable neurologic outcome is overestimated by the Marshall computed tomography score, corticosteroid randomization after significant head injury (CRASH), and international mission for prognosis and analysis of clinical trials in traumatic brain injury (IMPACT) models in patients with severe traumatic brain injury managed with early decompressive craniectomy. World Neurosurg 101:554–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.02.051
Cooper DJ, Rosenfeld JV, Murray L, Arabi YM, Davies AR, D’Urso P, Kossmann T, Ponsford J, Seppelt I, Reilly P, Wolfe R, Investigators DT, Australian, New Zealand Intensive Care Society Clinical Trials G (2011) Decompressive craniectomy in diffuse traumatic brain injury. N Engl J Med 364:1493–1502. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1102077
Dekompresyon ŞKTTK, Çalışma BÖ (2014) Controlled decompression for the treatment of severe head injury: a preliminary study. Turk Neurosurg 24:214–220
Dewan MC, Rattani A, Gupta S, Baticulon RE, Hung YC, Punchak M, Agrawal A, Adeleye AO, Shrime MG, Rubiano AM, Rosenfeld JV, Park KB (2018) Estimating the global incidence of traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg:1–18. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.10.Jns17352
Dunisch P, Walter J, Sakr Y, Kalff R, Waschke A, Ewald C (2013) Risk factors of aseptic bone resorption: a study after autologous bone flap reinsertion due to decompressive craniotomy. J Neurosurg 118:1141–1147. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.1.JNS12860
Eisenberg HM, Gary HE Jr, Aldrich EF, Saydjari C, Turner B, Foulkes MA, Jane JA, Marmarou A, Marshall LF, Young HF (1990) Initial CT findings in 753 patients with severe head injury. A report from the NIH Traumatic Coma Data Bank. J Neurosurg 73:688–698. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1990.73.5.0688
Fatima N, Mohamed ME, De Leon A, El Beltagi A, Shuaib A, Saqqur M (2020) Comparative radiographic factors predicting functional outcome after decompressive craniectomy in severe traumatic brain injury. World Neurosurg 138:e876–e882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2020.03.118
Faul M, National Center for Injury P, Control (2010) Traumatic brain injury in the United States : emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and deaths, 2002-2006
Finkelstein EA, Corso PS, Miller TR (2006) The incidence and economic burden of injuries in the United States. The incidence and economic burden of injuries in the United States. Oxford University Press, New York. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195179484.001.0001
Furuya Y, Hlatky R, Valadka AB, Diaz P, Robertson CS (2003) Comparison of cerebral blood flow in computed tomographic hypodense areas of the brain in head-injured patients. Neurosurgery 52:340–345; discussion 345-346. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000043931.83041.aa
Guerra WK, Piek J, Gaab MR (1999) Decompressive craniectomy to treat intracranial hypertension in head injury patients. Intensive Care Med 25:1327–1329. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001340051068
Howard JL, Cipolle MD, Anderson M, Sabella V, Shollenberger D, Li PM, Pasquale MD (2008) Outcome after decompressive craniectomy for the treatment of severe traumatic brain injury. J Trauma 65:380–385; discussion 385-386. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31817c50d4
Huang YH, Lee TC, Lee TH, Liao CC, Sheehan J, Kwan AL (2013) Thirty-day mortality in traumatically brain-injured patients undergoing decompressive craniectomy. J Neurosurg 118:1329–1335. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.1.JNS121775
Hukkelhoven CW, Steyerberg EW, Habbema JD, Farace E, Marmarou A, Murray GD, Marshall LF, Maas AI (2005) Predicting outcome after traumatic brain injury: development and validation of a prognostic score based on admission characteristics. J Neurotrauma 22:1025–1039. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2005.22.1025
Jüttler E, Schwab S, Schmiedek P, Unterberg A, Hennerici M, Woitzik J, Witte S, Jenetzky E, Hacke W (2007) Decompressive surgery for the treatment of malignant infarction of the middle cerebral artery (DESTINY) a randomized, controlled trial. Stroke 38:2518–2525
Kakarieka A, Braakman R, Schakel E (1995) Classification of head injuries based on computerized tomography: prognostic value. Neurologia (Barcelona, Spain) 10:159
Krieger DW, Demchuk AM, Kasner SE, Jauss M, Hantson L (1999) Early clinical and radiological predictors of fatal brain swelling in ischemic stroke. Stroke 30:287–292
Lietke S, Zausinger S, Patzig M, Holtmanspotter M, Kunz M (2020) CT-based classification of acute cerebral edema: association with intracranial pressure and outcome. J Neuroimaging 30:640–647. https://doi.org/10.1111/jon.12736
Lobato RD, Cordobes F, Rivas JJ, de la Fuente M, Montero A, Barcena A, Perez C, Cabrera A, Lamas E (1983) Outcome from severe head injury related to the type of intracranial lesion. A computerized tomography study. J Neurosurg 59:762–774. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1983.59.5.0762
Maas AI, Hukkelhoven CW, Marshall LF, Steyerberg EW (2005) Prediction of outcome in traumatic brain injury with computed tomographic characteristics: a comparison between the computed tomographic classification and combinations of computed tomographic predictors. Neurosurgery 57:1173–1182
Maas AI, Steyerberg EW, Butcher I, Dammers R, Lu J, Marmarou A, Mushkudiani NA, McHugh GS, Murray GD (2007) Prognostic value of computerized tomography scan characteristics in traumatic brain injury: results from the IMPACT study. J Neurotrauma 24:303–314
Marks MP, Holmgren EB, Fox AJ, Patel S, von Kummer R, Froehlich J (1999) Evaluation of early computed tomographic findings in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 30:389–392
Marmarou A, Lu J, Butcher I, McHugh GS, Murray GD, Steyerberg EW, Mushkudiani NA, Choi S, Maas AI (2007) Prognostic value of the Glasgow Coma Scale and pupil reactivity in traumatic brain injury assessed pre-hospital and on enrollment: an IMPACT analysis. J Neurotrauma 24:270–280
Marshall LF, Marshall SB, Klauber MR, Clark MB, Eisenberg HM, Jane JA, Luerssen TG, Marmarou A, Foulkes MA (1991) A new classification of head injury based on computerized tomography. 75:S14. https://doi.org/10.3171/sup.1991.75.1s.0s14
Moein H, Sanati MA, Fard SA, Moein P, Hasheminasab SM (2012) Outcome of decompressive craniectomy in patients with severe head injury: a pilot randomized clinical trial. Neurosurg Q 22:149–152
Munch E, Horn P, Schurer L, Piepgras A, Paul T, Schmiedek P (2000) Management of severe traumatic brain injury by decompressive craniectomy. Neurosurgery 47:315–322; discussion 322-313. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200008000-00009
Murray GD, Butcher I, McHugh GS, Lu J, Mushkudiani NA, Maas AI, Marmarou A, Steyerberg EW (2007) Multivariable prognostic analysis in traumatic brain injury: results from the IMPACT study. J Neurotrauma 24:329–337
Nambiar M, MacIsaac C, Grabinski R, Liew D, Kavar B (2015) Outcomes of decompressive craniectomy in patients after traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Resusc 17:67–72
Park JH, Park JE, Kim SH, Lim YC, You NK, Ahn YH, Choi HY, Cho JM (2014) Outcomes of ultra-early decompressive craniectomy after severe traumatic brain injury-treatment outcomes after severe TBI. Korean J Neurotrauma 10:112–118. https://doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.112
Pillai S, Kolluri V, Praharaj S (2003) Outcome prediction model for severe diffuse brain injuries: development and evaluation. Neurol India 51:345
Pompucci A, De Bonis P, Pettorini B, Petrella G, Di Chirico A, Anile C (2007) Decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury: patient age and outcome. J Neurotrauma 24:1182–1188
Puffer RC, Yue JK, Mesley M, Billigen JB, Sharpless J, Fetzick AL, Puccio A, Diaz-Arrastia R, Okonkwo DO (2018) Long-term outcome in traumatic brain injury patients with midline shift: a secondary analysis of the Phase 3 COBRIT clinical trial. J Neurosurg 131:596–603. https://doi.org/10.3171/2018.2.JNS173138
Sauvigny T, Gottsche J, Vettorazzi E, Westphal M, Regelsberger J (2016) New radiologic parameters predict clinical outcome after decompressive craniectomy. World Neurosurg 88:519–525 e511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2015.10.072
Scott J, Buchan A, Sevick R (1999) Correlation of neurologic dysfunction with CT findings in early acute stroke. Can J Neurol Sci 26:182–189
Servadei F, Murray GD, Penny K, Teasdale GM, Dearden M, Iannotti F, Lapierre F, Maas AJ, Karimi A, Ohman J, Persson L, Stocchetti N, Trojanowski T, Unterberg A (2000) The value of the “worst” computed tomographic scan in clinical studies of moderate and severe head injury. Eur Brain Inj Consortium Neurosurg 46:70–75; discussion 75-77. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006123-200001000-00014
Stiver SI (2009) Complications of decompressive craniectomy for traumatic brain injury. Neurosurg Focus 26:E7. https://doi.org/10.3171/2009.4.FOCUS0965
Tang Z, Yang K, Zhong M, Yang R, Zhang J, Jiang Q, Liu H (2020) Predictors of 30-day mortality in traumatic brain-injured patients after primary decompressive craniectomy. World Neurosurg 134:e298–e305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.10.053
Vahedi K, Vicaut E, Mateo J, Kurtz A, Orabi M, Guichard J-P, Boutron C, Couvreur G, Rouanet F, Touzé E (2007) Sequential-design, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of early decompressive craniectomy in malignant middle cerebral artery infarction (DECIMAL Trial). Stroke 38:2506–2517
van Dongen KJ, Braakman R, Gelpke GJ (1983) The prognostic value of computerized tomography in comatose head-injured patients. J Neurosurg 59:951–957. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1983.59.6.0951
Zhao J, Su YY, Zhang Y, Zhang YZ, Zhao R, Wang L, Gao R, Chen W, Gao D (2012) Decompressive hemicraniectomy in malignant middle cerebral artery infarct: a randomized controlled trial enrolling patients up to 80 years old. Neurocrit Care 17:161–171
Funding
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korea Government (NRF-2019M3E5D1A02068142)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standard. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Brain trauma
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, J.H., Jeon, I., Seo, Y. et al. Radiographic predictors of clinical outcome in traumatic brain injury after decompressive craniectomy. Acta Neurochir 163, 1371–1381 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04679-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-020-04679-x