Abstract
Background
Surgical access to the second (V2, maxillary) and third (V3, mandibular) branches of the trigeminal nerve (V) has been classically through a transoral approach. Increasing expertise with endoscopic anatomy has achieved less invasive, more efficient access to skull base structures. The authors present a surgical technique using an endoscopic endonasal approach for the treatment of painful V2 neuropathy.
Methods
Endoscopic endonasal dissections using a transmaxillary approach were performed in four formalin-fixed cadaver heads to expose the V2 branch of the trigeminal nerve. Relevant surgical anatomy was evaluated and anatomic parameters for neurectomy were identified.
Results
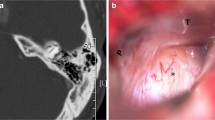
Endoscopic endonasal transmaxillary approaches completed bilaterally to the pterygopalatine and pterygomaxillary fossae exposed the V2 branch where it emerged from the foramen rotundum. The anatomy defined for the location of neurectomy was determined to be the point where V2 emerged from the foramen rotundum into the pterygopalatine fossa. The technique was then performed in 3 patients with intractable painful V2 neuropathy.
Conclusions
In our cadaveric study and clinical cases, the endoscopic endonasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa achieved effective exposure and treatment of isolated V2 painful neuropathy. Important surgical steps to visualize the maxillary nerve and its branches and key landmarks of the pterygopalatine fossa are discussed. This minimally invasive approach appears to be a valid alternative for select patients with painful V2 trigeminal neuropathy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfieri A, Jho HD, Schettino R, Tschabitscher M (2003) Endoscopic endonasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa: anatomic study. Neurosurgery 52:374–380
Amin SM, Nasr AY, Saleh HA, Foad MM, Herzallah IR (2010) Endoscopic orientation of the parasellar region in sphenoid sinus with ill-defined bony landmarks: an anatomic study. Skull Base 20(6):421–428
Bao S, Ni S, Zhang J, Li L, Mo D, Guo C, Zhang J, Yu G, You Y (2006) Treatment of lesions involving both the infratemporal fossa and middle skull base. Surg Neurol 66(Suppl 1):S10–S17
Braun TW, Sotereanos GC (1977) Transantral maxillary neurectomy for intractable neuralgia. J Oral Surg 35(7):583–584
Cavallo LM, Messina A, Gardner P, Esposito F, Kassam AB, Cappabianca P, de Divitiis E, Tschabitscher M (2005) Extend endoscopic endonasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa: anatomical study and clinical considerations. Neurosurg Focus 19(1):E5
Elhadi AM, Almefty KK, Mendes GAC, Kalani MY, Nakaji P, Dru A, Preul MC, Little AS (2014) Comparison of surgical freedom and area of exposure in three endoscopic transmaxillary approaches to the anterolateral cranial base. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 75(5):346–353
Falcon RT, Rivera-Serrano CM, Miranda JF, Prevedello DM, Snyderman CH, Kassam AB, Carrau RL (2011) Endoscopic endonasal dissection of the infratemporal fossa: anatomic relationships and importance of eustachian tube in the endoscopic skull base surgery. Laryngoscope 121:31–41
Fortes FS, Sennes LU, Carrau RL, Brito R, Ribas GC, Yasuda A, Rodrigues AJ Jr, Snyderman CH, Kassam AB (2008) Endoscopic anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa and the transpterygoid approach: development of a surgical instruction model. Laryngoscope 118(1):44–49
Gandhi D, Gujar S, Mukherji SK (2004) Magnetic resonance imaging of perineural spread of head and neck malignances. Top Magn Reson Imaging 15:79–85
Ginsberg LE (1999) Imaging of perineural tumor spread in head and neck câncer. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 20:175–186
Grewal SS, Kurbanov AA, Keller JT, Theodosopoulos PV, Zimmer LA (2014) Endoscopic endonasal approach to the maxillary strut: anatomical review and case series. Laryngoscope 124:1739–1743
Guo J, Huang D, Chen S, Zhu S, Rong Q (2015) Treatment of a subtype of trigeminal neuralgia with descending palatine neurotomy in the pterygopalatine fossa via the greater palatine foramen-pterygopalatine canal approach. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 43(1):97–101
Kassam AB, Prevedello DM, Carrau RL, Snyderman CH, Gardner P, Osawa S, Seker A, Rhoton AL Jr (2009) The front door to Meckel’s cave: an anteromedial corridor via expanded endoscopic endonasal approach-technical considerations and clinical series. Neurosurgery 64(3 suppl):71–82
Keller JT, Theodosopoulos PV, Zimmer LA (2012) Approach to the infratemporal fossa: correlation of endoscopic and multiplanar CT anatomy. Head Neck 34(3):313–320
Lodge WO (1950) Transantral neurotomy and sealing of the foramen rotundum for neuralgia. J Laryngol Otol 64(12):776–777
Ma Y, Tan G, Zhao Z, Li W, Huang L, Liu G (2014) Therapeutic effectiveness of endoscopic vidian neurectomy for the treatment of vasomotor rhinitis. Acta Otolaryngol 134(3):260–267
Marshak T, Yun WK, Hazout C, Sacks R, Harvey RJ (2016) A systematic review of the evidence base for vidian neurectomy in managing rhinitis. J Laryngol Otol 130(Suppl 4):S7–S28
Mellema JW, Tami TA (2004) An endoscopic study of the greater palatine nerve. Am J Rhinol 18(2):99–103
Morse LM (1953) Transantral excision of the sphenopalatine ganglion and maxillarynerve for facial pain. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 62(1):220–228
Pasquini E, Sciarreta V, Farneti G, Ippolito A, Mazzatenta D, Frank G (2002) Endoscopic endonasal approach for the treatment of benign schwannoma of the sinonasal tract and pterygopalatine fossa. Am J Rhinol 16:113–118
Pinheiro-Neto CD, Fernandez-Miranda JC, Prevedello DM, Carrau RL, Gardner PA, Snyderman CH (2013) Transposition of the pterygopalatine fossa during endoscopic endonasal transpterygoid approaches. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base 74(5):266–270
Prevedello DM, Pinheiro-Neto CD, Fernandez-Miranda LC et al (2010) Vidian nerve transposition for endoscopic endonasal middle fossa approaches. Neurosurgery 67(2,suppl operative):478–484
Solari D, Magro F, Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Samii A, Esposito F, Paternò V, De Divitiis E, Samii M (2007) Anatomical study of the pterygopalatina fossa using an endoscopic endonasal approach: spatial relations and distances between surgical landmarks. J Neurosurg 106(1):157–163
Theodosopoulos PV, Guthikonda B, Brescia A, Keller JT, Zimmer LA (2010) Endoscopic approach to the infratemporal fossa: anatomic sudy. Neurosurgery 66(1):196–202 discussion 202-203
Zhang H, Micomonaco DC, Dziegielewski PT, Sowerby LJ, Weis E, Wright ED (2015) Endoscopic vidian neurectomy: a prospective case series. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol 5(5):423–430
Zhou B, Huang Q, Shen PH, Cui SJ, Wang CS, Li YC, Yu ZK, Chen XH, Ye T (2016) The intranasal endoscopic removal of schwannoma of the pterygopalatine and infratemporal fossae via the prelacrimal recess approach. J Neurosurg 124(4):1068–1073
Zhu S, Rong Q, Chen S, Li X (2013) Pterygopalatine fossa segment neurectomy of maxillary nerve through maxillary sinus route in treating trigeminal neuralgia. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 41(7):652–656
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This retrospective study of patients was approved by the University of Cincinnati Institutional Review Board.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Neurosurgical technique evaluation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima, F., Andaluz, N. & Zimmer, L.A. Endoscopic endonasal treatment of maxillary nerve (V2) painful neuropathy: cadaveric study with clinical correlation. Acta Neurochir 162, 223–229 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04126-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-04126-6