Summary
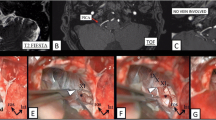
This report describes a case of delayed post-traumatic glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves palsy (i.e. dysphonia and swallowing dysfunction). A high resolution CT study of the cranial base detected a fracture rim encroaching on the left jugular foramen. Treatment consisted in supportive measures with incomplete recovery during a one-year follow-up period. Lower cranial nerves palsies after head trauma are rare and, should they occur, a thorough investigation in search of posterior cranial base and cranio-cervical lesions is warranted. The presumptive mechanism in our case is a fracture-related oedema and ischemic damage to the nerves leading to the delayed occurrence of the palsy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alberio, N., Cultrera, F., Antonelli, V. et al. Isolated glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves palsy due to fracture involving the left jugular foramen. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147, 791–794 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0547-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-005-0547-x