Abstract
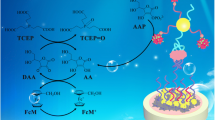
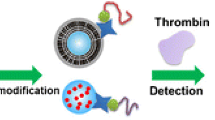
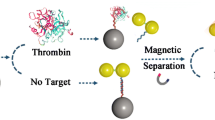
A method is described for the determination of proteins with LC-MS/MS enabled by a small molecule (adenosine) barcode and based on a double-recognition sandwich structure. The coagulation protein thrombin was chosen as the model analyte. Magnetic nanoparticles were functionalized with aptamer29 (MNP/apt29) and used to capture thrombin from the samples. MNP/apt29 forms a sandwich with functionalized gold nanoparticles modified with (a) aptamer15 acting as thrombin-recognizing element and (b) a large number of adenosine as mass barcodes. The sandwich formed (MNP/apt29-thrombin-apt15/AuNP/adenosine) can ben magnetically separated from the sample. Mass barcodes are subsequently released from the sandwiched structure for further analysis by adding 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid. Adenosine is then detected by LC-MS/MS as it reflects the level of thrombin with impressively amplified signal. Numerous adenosines introduced into the sandwich proportional to the target concentration further amplify the signal. Under optimized conditions, the response is linearly proportional to the thrombin concentration in the range of 0.02 nM to 10 nM, with a detection limit of 9 fM. The application of this method to the determination of thrombin in spiked plasma samples gave recoveries that ranged from 92.3% to 104.7%.

Schematic representation of a method for the determination of thrombin with LC-MS/MS. The method is based on a double-recognition sandwiched structure. With LC-MS/MS, mass barcodes (adenosine) are detected to quantify thrombin, which amplifies the detection signal impressively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Khalil DN, Smith EL, Brentjens RJ, Wolchok JD (2016) The future of cancer treatment: immunomodulation, CARs and combination immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 13(5):273–290. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2016.25
Benjamin Leader QJB, Golan DE (2008) Protein therapeutics: a summary and pharmacological classification. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:21–39
Lequin RM (2005) Enzyme immunoassay (EIA)/enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Clin Chem 51(12):2415–2418. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2005.051532
Giljohann DA, Mirkin CA (2009) Drivers of biodiagnostic development. Nature 462(7272):461–464. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08605
Yunlei Xianyu ZW, Jiang X (2014) A plasmonic nanosensor for immunoassay via enzyme-triggered click chemistry. ACS Nano 8(12):12741–12747
Ma X, Chen Z, Kannan P, Lin Z, Qiu B, Guo L (2016) Gold nanorods as colorful chromogenic substrates for semiquantitative detection of nucleic acids, proteins, and small molecules with the naked eye. Anal Chem 88(6):3227–3234. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b04621
Zhan L, Guo SZ, Song F, Gong Y, Xu F, Boulware DR, McAlpine MC, Chan WCW, Bischof JC (2017) The role of nanoparticle Design in Determining Analytical Performance of lateral flow immunoassays. Nano Lett 17(12):7207–7212. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b02302
Yu CC, Kuo YY, Liang CF, Chien WT, Wu HT, Chang TC, Jan FD, Lin CC (2012) Site-specific immobilization of enzymes on magnetic nanoparticles and their use in organic synthesis. Bioconjug Chem 23(4):714–724. https://doi.org/10.1021/bc200396r
Zhou J, Gan N, Li T, Zhou H, Li X, Cao Y, Wang L, Sang W, Hu F (2013) Ultratrace detection of C-reactive protein by a piezoelectric immunosensor based on Fe3O4@SiO2 magnetic capture nanoprobes and HRP-antibody co-immobilized nano gold as signal tags. Sensors Actuators B Chem 178:494–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.01.013
Zhao Q, Li XF, Le XC (2011) Aptamer capturing of enzymes on magnetic beads to enhance assay specificity and sensitivity. Anal Chem 83(24):9234–9236. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac203063z
Piella J, Bastús NG, Puntes V (2016) Size-controlled synthesis of Sub-10-nanometer citrate-stabilized gold nanoparticles and related optical properties. Chem Mater 28(4):1066–1075. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b04406
Schuetze B, Mayer C, Loza K, Gocyla M, Heggen M, Epple M (2016) Conjugation of thiol-terminated molecules to ultrasmall 2 nm-gold nanoparticles leads to remarkably complex 1H-NMR spectra. J Mater Chem B 4(12):2179–2189. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5tb02443a
Azubel M, Kornberg RD (2016) Synthesis of water-soluble, thiolate-protected gold nanoparticles uniform in size. Nano Lett 16(5):3348–3351. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00981
Zhou J, Rossi J (2017) Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: current potential and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(3):181–202. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2016.199
van den Kieboom CH, van der Beek SL, Mészáros T, Gyurcsányi RE, Ferwerda G, de Jonge MI (2015) Aptasensors for viral diagnostics. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 74:58–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2015.05.012
Liu Z, Liu H, Wang L, Su X (2016) A label-free fluorescence biosensor for highly sensitive detection of lectin based on carboxymethyl chitosan-quantum dots and gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 932:88–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.05.025
Wang L, Yang W, Li T, Li D, Cui Z, Wang Y, Ji S, Song Q, Shu C, Ding L (2017) Colorimetric determination of thrombin by exploiting a triple enzyme-mimetic activity and dual-aptamer strategy. Microchim Acta 184(9):3145–3151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2327-8
Meirinho SG, Dias LG, Peres AM, Rodrigues LR (2017) Electrochemical aptasensor for human osteopontin detection using a DNA aptamer selected by SELEX. Anal Chim Acta 987:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2017.07.071
Cheng Z, Choi N, Wang R, Lee S, Moon KC, Yoon SY, Chen L, Choo J (2017) Simultaneous detection of dual prostate specific antigens using surface-enhanced Raman scattering-based immunoassay for accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer. ACS Nano 11(5):4926–4933. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.7b01536
El-Said WA, Fouad DM, El-Safty SA (2016) Ultrasensitive label-free detection of cardiac biomarker myoglobin based on surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sensors Actuators B Chem 228:401–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.041
Jazayeri MH, Amani H, Pourfatollah AA, Avan A, Ferns GA, Pazoki-Toroudi H (2016) Enhanced detection sensitivity of prostate-specific antigen via PSA-conjugated gold nanoparticles based on localized surface plasmon resonance: GNP-coated anti-PSA/LSPR as a novel approach for the identification of prostate anomalies. Cancer Gene Ther 23(10):365–369. https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2016.42
Joanna Zheng JM, Yongxin Zhu BX, Olah T (2014) Application and challenges in using LC–MS assays for absolute quantitative analysis of therapeutic proteins in drug discovery. Bioanalysis 6(6):21
Li H, Ortiz R, Tran LT, Salimi-Moosavi H, Malella J, James CA, Lee JW (2013) Simultaneous analysis of multiple monoclonal antibody biotherapeutics by LC-MS/MS method in rat plasma following cassette-dosing. AAPS J 15(2):337–346. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-012-9435-5
An B, Zhang M, Johnson RW, Qu J (2015) Surfactant-aided precipitation/on-pellet-digestion (SOD) procedure provides robust and rapid sample preparation for reproducible, accurate and sensitive LC/MS quantification of therapeutic protein in plasma and tissues. Anal Chem 87(7):4023–4029. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00350
Liu J, Lu Y (2006) Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat Protoc 1(1):246–252. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.38
Sheng H, Ye BC (2009) Different strategies of covalent attachment of oligonucleotide probe onto glass beads and the hybridization properties. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 152(1):54–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-008-8245-9
Jwa-Min Nam CST, Mirkint CA (2003) Nanoparticle-based bio-bar codes for the ultrasensitive detection of proteins. Science 301(5641):3
Bernd Giese DM (2002) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic and density functional theory study of adenine adsorption to silver surfaces. J Phys Chem B 106:12
Kundu J, ON BGJ, Zhang D, Lal S, Barhoumi A, Scuseria GE, Halas NJ (2009) Adenine− and adenosine monophosphate (AMP)−gold binding interactions studied by surface-enhanced Raman and infrared spectroscopies. J Phys Chem C 113:8
Siriwardana K, Gadogbe M, Ansar SM, Vasquez ES, Collier WE, Zou S, Walters KB, Zhang D (2014) Ligand adsorption and exchange on Pegylated gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 118(20):11111–11119. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp501391x
Zhuo B, Li Y, Huang X, Lin Y, Chen Y, Gao W (2015) An electrochemiluminescence aptasensing platform based on ferrocene-graphene nanosheets for simple and rapid detection of thrombin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 208:518–524. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.11.064
Bai Y, Feng F, Zhao L, Wang C, Wang H, Tian M, Qin J, Duan Y, He X (2013) Aptamer/thrombin/aptamer-AuNPs sandwich enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensor for the detection of subnanomolar thrombin. Biosens Bioelectron 47:265–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.02.004
Liu X, Hua X, Fan Q, Chao J, Su S, Huang YQ, Wang L, Huang W (2015) Thioflavin T as an efficient G-quadruplex inducer for the highly sensitive detection of thrombin using a new foster resonance energy transfer system. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(30):16458–16465. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b03662
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81573387, No.81703472, No.81603072 and No.81560695). Also thanks for the support from the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. KYCX17_0683).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval was not required because the study is not on animals.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was not required for this study because the study is not on human subjects.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 399 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Li, T., Shu, C. et al. Non-enzymolytic adenosine barcode-mediated dual signal amplification strategy for ultrasensitive protein detection using LC-MS/MS. Microchim Acta 185, 293 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2832-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2832-4