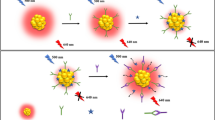
Abstract
Upconverting nanoparticles (UCNPs) are attractive reporters in immunoassays because of their outstanding detectability. However, non-specific binding of antibody-UCNP conjugates on protein coated solid support results in background, which limits the immunoassay sensitivity. Thus, the full potential of UCNPs as reporters cannot be fully exploited. The authors report here a method to improve the sensitivity of UCNP-based immunoassays by reducing the non-specific binding of antibody-UNCP conjugates on the protein coated solid support. In the assays studied here, poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) coated NaYF4:Yb3+,Er3+ type UCNPs were conjugated to two different antibodies against cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). The two-step heterogeneous sandwich immunoassays were performed in microtitration wells, and the green luminescence of antibody-UCNP conjugates was measured at 540 nm upon 980 nm excitation. Non-specific binding of antibody-UCNP conjugates was reduced by mixing free PAA with PAA coated UCNPs before adding the UCNPs to the wells. The free PAA in the buffer reduced the background in both cTnI and TSH immunoassays (compared to the control assay without free PAA). The limits of detection decreased from 2.1 ng·L−1 to 0.48 ng·L−1 in case of cTnI and from 0.070 mIU·L−1 to 0.020 mIU·L−1 in case of TSH if PAA is added to the buffer. Presumably, the effect of free PAA is due to blocking of the surface areas where PAA coated UCNP would bind proteins non-specifically. The method introduced here is likely to be applicable to other kinds of PAA-coated nanoparticles, and similar approaches conceivably work also with other nanoparticle coatings.

The presence of free poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) in a buffer solution prevents aggregation and non-specific protein binding of PAA-coated upconverting nanoparticles (UCNPs) in heterogeneous sandwich immunoassays. The decrease in non-specific binding enables distinctly more sensitive assays to be performed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Quinton J, Kolodych S, Chaumonet M, Bevilacqua V, Nevers MC, Volland H, Gabillet S, Thuéry P, Créminon C, Taran F (2012) Reaction discovery by using a sandwich immunoassay. Angew Chem Int Ed 124:6248–6252
Pei X, Zhang B, Tang J, Liu B, Lai W, Tang D (2013) Sandwich-type immunosensors and immunoassays exploiting nanostructure labels: a review. Anal Chim Acta 758:1–18
Farka Z, Juřík T, Kovář D, Trnková L, Skládal P (2017) Nanoparticle-based immunochemical biosensors and assays: recent advances and challenges. Chem Rev 117:9973–10042
Amaro M, Oaew S, Surareungchai W (2012) Scano-magneto immunoassay based on carbon nanotubes/gold nanoparticles nanocomposite for Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium detection. Biosens Bioelectron 38:157–162
Soukka T, Paukkunen J, Härmä H, Lönnberg S, Lindroos H, Lövgren T (2001) Supersensitive time-resolved immunofluorometric assay of free prostate-specific antigen with nanoparticle label technology. Clin Chem 47:1269–1278
Gorris HH, Resch-Genger U (2017) Perspectives and challenges of photon-upconversion nanoparticles-part II: bioanalytical applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:5875–5890
Haase M, Schäfer H (2011) Upconverting nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:5808–5829
Auzel F (2004) Upconversion and anti-stokes processes with f and d ions in solids. Chem Rev 104:139–174
Wilhelm S, Kaiser M, Würth C, Heiland J, Carrillo-Carrion C, Muhr V, Wolfbeis OS, Parak WJ, Resch-Genger U, Hirsch T (2015) Water dispersible upconverting nanoparticles: effects of surface modification on their luminescence and colloidal stability. Nano 7:1403–1410
Näreoja T, Rosenholm JM, Lamminmäki U, Hänninen PE (2017) Super-sensitive time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay for thyroid-stimulating hormone utilizing europium (III) nanoparticle labels achieved by protein corona stabilization, short binding time, and serum preprocessing. Anal Bioanal Chem 409:3407–3416
Jeyachandran Y, Mielczarski J, Mielczarski E, Rai B (2010) Efficiency of blocking of non-specific interaction of different proteins by BSA adsorbed on hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces. J Colloid Interface Sci 341:136–142
Trevino J, Calle A, Rodríguez-Frade J, Mellado M, Lechuga L (2009) Determination of human growth hormone in human serum samples by surface plasmon resonance immunoassay. Talanta 78:1011–1016
Bentzen EL, Tomlinson ID, Mason J, Gresch P, Warnement MR, Wright D, Sanders-Bush E, Blakely R, Rosenthal SJ (2005) Surface modification to reduce nonspecific binding of quantum dots in live cell assays. Bioconjug Chem 16:1488–1494
Sirkka N, Lyytikäinen A, Savukoski T, Soukka T (2016) Upconverting nanophosphors as reporters in a highly sensitive heterogeneous immunoassay for cardiac troponin I. Anal Chim Acta 925:82–87
Sedlmeier A, Gorris HH (2015) Surface modification and characterization of photon-upconverting nanoparticles for bioanalytical applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:1526–1560
Xiong L, Yang T, Yang Y, Xu C, Li F (2010) Long-term in vivo biodistribution imaging and toxicity of polyacrylic acid-coated upconversion nanophosphors. Biomaterials 31:7078–7085
Wang L, Zhang Y, Zhu Y (2010) One-pot synthesis and strong near-infrared upconversion luminescence of poly (acrylic acid)-functionalized YF3: Yb3+/Er3+ nanocrystals. Nano Res 3:317–325
Budijono SJ, Shan J, Yao N, Miura Y, Hoye T, Austin RH, Ju Y, Prud’homme RK (2010) Synthesis of stable block-copolymer-protected NaYF4: Yb3+, Er3+ up-converting phosphor nanoparticles. Chem Mater 22:311–318
Välimaa L, Pettersson K, Vehniäinen M, Karp M, Lövgren T (2003) A high-capacity streptavidin-coated microtitration plate. Bioconjug Chem 14:103–111
Ylikotila J, Hellström JL, Eriksson S, Vehniäinen M, Välimaa L, Takalo H, Bereznikova A, Pettersson K (2006) Utilization of recombinant fab fragments in a cTnI immunoassay conducted in spot wells. Clin Biochem 39:843–850
Eriksson S, Junikka M, Laitinen P, Majamaa-Voltti K, Alfthan H, Pettersson K (2003) Negative interference in cardiac troponin I immunoassays from a frequently occurring serum and plasma component. Clin Chem 49:1095–1104
Palo E, Tuomisto M, Hyppänen I, Swart HC, Hölsä J, Soukka T, Lastusaari M (2017) Highly uniform up-converting nanoparticles: why you should control your synthesis even more. J Lumin 185:125–131
Kuningas K, Rantanen T, Ukonaho T, Lövgren T, Soukka T (2005) Homogeneous assay technology based on upconverting phosphors. Anal Chem 77:7348–7355
Hyytiä H, Heikkilä T, Hedberg P, Puolakanaho T, Pettersson K (2015) Skeletal troponin I cross-reactivity in different cardiac troponin I assay versions. Clin Biochem 48:313–317
Soukka T, Kuningas K, Rantanen T, Haaslahti V, Lövgren T (2005) Photochemical characterization of up-converting inorganic lanthanide phosphors as potential labels. J Fluoresc 15:513–528
Liufu S, Xiao H, Li Y (2005) Adsorption of poly (acrylic acid) onto the surface of titanium dioxide and the colloidal stability of aqueous suspension. J Colloid Interface Sci 281:155–163
Lin CL, Lee CF, Chiu WY (2005) Preparation and properties of poly (acrylic acid) oligomer stabilized superparamagnetic ferrofluid. J Colloid Interface Sci 291:411–420
Naccache R, Vetrone F, Mahalingam V, Cuccia LA, Capobianco JA (2009) Controlled synthesis and water dispersibility of hexagonal phase NaGdF4: Ho3+/Yb3+ nanoparticles. Chem Mater 21:717–723
Ipe BI, Shukla A, Lu H, Zou B, Rehage H, Niemeyer CM (2006) Dynamic light-scattering analysis of the electrostatic interaction of hexahistidine-tagged cytochrome P450 enzyme with semiconductor quantum dots. Chem PhysChem 7:1112–1118
Gambinossi F, Mylon SE, Ferri JK (2015) Aggregation kinetics and colloidal stability of functionalized nanoparticles. Adv Colloid Interface 222:332–349
Apple FS, Sandoval Y, Jaffe AS, Ordonez-Llanos J (2017) Cardiac troponin assays: guide to understanding analytical characteristics and their impact on clinical care. Clin Chem 63:73–81
Kamimura M, Miyamoto D, Saito Y, Soga K, Nagasaki Y (2008) Design of poly (ethylene glycol)/streptavidin coimmobilized upconversion nanophosphors and their application to fluorescence biolabeling. Langmuir 24:8864–8870
Hilderbrand SA, Shao F, Salthouse C, Mahmood U, Weissleder R (2009) Upconverting luminescent nanomaterials: application to in vivo bioimaging. Chem Commun 28:4188–4190
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Tekes, the Finnish Funding Agency for Innovation and the Doctoral Programme of Molecular Life Sciences. The authors wish to thank Jessica Rosenholm from Åbo Akademi for assisting with the DLS measurements and Raili Kronström for the technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 381 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahtinen, S., Lyytikäinen, A., Sirkka, N. et al. Improving the sensitivity of immunoassays by reducing non-specific binding of poly(acrylic acid) coated upconverting nanoparticles by adding free poly(acrylic acid). Microchim Acta 185, 220 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2756-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2756-z