Abstract
The authors have synthesized molybdenum disulfide nanosheets (MoS2 nanosheets) by using a bottom-up hydrothermal method. The nanosheets display strong catalytic (enzyme mimetic) activity in catalyzing the oxidation of peroxidase substrate of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) in presence of H2O2 to produce a blue product. The peroxidase mimicking properties of MoS2 nanosheets depend on temperature, H2O2 concentration and pH value. A choline assay was worked out where choline was oxidized by choline oxidase in presence of oxygen to produce H2O2 which is colorimetrically detected, best at 652 nm. The method works in the 1 to 180 μM choline concentration range with a 0.4 μM detection limit. Color changes may also be detected visually. The assay is simple, highly sensitive, selective and rapid. It was applied in the determination of choline in (spiked) milk and serum.

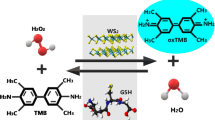
Basic principle of intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of MoS2 nanosheets, applied to design a rapid and selective colorimetric assay for choline detection based on the tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) color reaction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blusztajn JK (1998) Choline, a vital amine. Science (New York, NY) 281:794–795
Schebb NH, Fischer D, Hein EM, Hayen H, Krieglstein J, Klumpp S, Karst U (2008) Fast sample preparation and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for assaying cell lysate acetylcholine. J Chromatogr A 1183:100–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHROMA.2008.01.033
Koc H, Mar M-H, Ranasinghe A et al (2002) Quantitation of choline and its metabolites in tissues and foods by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 74:4734–4740. https://doi.org/10.1021/AC025624X
Szilagyi PIA, Schmidt DE, Green JP (1968) Microanalytical determination of acetylcholine, other choline esters, and choline by pyrolysis-gas chromatography. Anal Chem 40:2009–2013. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60269a001
Khan A, Ab Ghani S (2012) Multienzyme microbiosensor based on electropolymerized o-phenylenediamine for simultaneous in vitro determination of acetylcholine and choline. Biosens Bioelectron 31:433–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIOS.2011.11.007
Nasir M, Nawaz MH, Latif U, Yaqub M, Hayat A, Rahim A (2017) An overview on enzyme-mimicking nanomaterials for use in electrochemical and optical assays. Microchim Acta 184:323–342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2036-8
Otsuka H, Akiyama Y, Nagasaki Y, Kataoka K (2001) Quantitative and reversible lectin-induced association of gold nanoparticles modified with α-Lactosyl-ω-mercapto-poly(ethylene glycol). J Am Chem Soc 123:8226–8230. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja010437m
Rosi NL, Mirkin CA (2005) Nanostructures in biodiagnostics. Chem Rev 105:1547–1562. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr030067f
Li L, Li B, Cheng D, Mao L (2010) Visual detection of melamine in raw milk using gold nanoparticles as colorimetric probe. Food Chem 122:895–900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.03.032
Du J, Zhu B, Chen X (2013) Urine for plasmonic nanoparticle-based colorimetric detection of mercury ion. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 9:4104–11. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201300593
Du J, Shao Q, Yin S et al (2012) Colorimetric chemodosimeter based on diazonium-gold-nanoparticle complexes for sulfite ion detection in solution. Small (Weinheim an der Bergstrasse, Germany) 8:3412–6. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201201650
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Liu B, Liu J (2017) Molecular imprinting on inorganic nanozymes for hundred-fold enzyme specificity. J Am Chem Soc 139:5412–5419. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b00601
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu N, Wang T, Feng J, Yang D, Perrett S, Yan X (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.260
Asati A, Santra S, Kaittanis C, Nath S, Perez JM (2009) Oxidase-like activity of polymer-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 48:2308–2312. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200805279
Luo W, Zhu C, Su S, Li D, He Y, Huang Q, Fan C (2010) Self-catalyzed, self-limiting growth of glucose oxidase-mimicking gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano 4:7451–7458. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn102592h
Shi W, Wang Q, Long Y, Cheng Z, Chen S, Zheng H, Huang Y (2011) Carbon nanodots as peroxidase mimetics and their applications to glucose detection. Chem Commun (Camb) 47:6695–6697. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc11943e
Nirala NR, Abraham S, Kumar V, Bansal A, Srivastava A, Saxena PS (2015) Colorimetric detection of cholesterol based on highly efficient peroxidase mimetic activity of graphene quantum dots. Sensors Actuators B Chem 218:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.04.091
André R, Natálio F, Humanes M, Leppin J, Heinze K, Wever R, Schröder HC, Müller WEG, Tremel W (2011) V2O5 nanowires with an intrinsic peroxidase-like activity. Adv Funct Mater 21:501–509. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201001302
Salimi A, Kavosi B, Fathi F, Hallaj R (2013) Highly sensitive immunosensing of prostate-specific antigen based on ionic liquid-carbon nanotubes modified electrode: application as cancer biomarker for prostatebiopsies. Biosens Bioelectron 42:439–446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.10.053
Qu F, Li T, Yang M (2011) Colorimetric platform for visual detection of cancer biomarker based on intrinsic peroxidase activity of graphene oxide. Biosens Bioelectron 26:3927–3931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.03.013
Chen J, Ge J, Zhang L, Li Z, Li J, Sun Y, Qu L (2016) Reduced graphene oxide nanosheets functionalized with poly(styrene sulfonate) as a peroxidase mimetic in a colorimetric assay for ascorbic acid. Microchim Acta 183:1847–1853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1826-3
Wang B, Ju P, Zhang D, Han X, Zheng L, Yin X, Sun C (2016) Colorimetric detection of H2O2 using flower-like Fe2(MoO4)3 microparticles as a peroxidase mimic. Microchim Acta 183:3025–3033. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1955-8
Lin T, Zhong L, Guo L, Fu F, Chen G (2014) Seeing diabetes: visual detection of glucose based on the intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of MoS2 nanosheets. Nano 6:11856–11862. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr03393k
Matte HSSR, Gomathi A, Manna AK et al (2010) MoS2 and WS2 analogues of graphene. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 49:4059–4062. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201000009
Wang T, Zhu H, Zhuo J, Zhu Z, Papakonstantinou P, Lubarsky G, Lin J, Li M (2013) Biosensor based on ultrasmall MoS2 nanoparticles for electrochemical detection of H2O2 released by cells at the nanomolar level. Anal Chem 85:10289–10295. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac402114c
Haldar D, Dinda D, Saha SK et al (2016) High selectivity in water soluble MoS 2 quantum dots for sensing nitro explosives. J Mater Chem C 4:6321–6326. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6TC01811D
Pumera M, Sofer Z, Ambrosi A et al (2014) Layered transition metal dichalcogenides for electrochemical energy generation and storage. J Mater Chem A 2:8981–8987. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TA00652F
Cao H, Wang H, Huang Y, Sun Y, Shi S, Tang M (2017) Quantification of gold(III) in solution and with a test stripe via the quenching of the fluorescence of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots. Microchim Acta 184:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1988-z
Lu Y, Yu J, Ye W, Yao X, Zhou P, Zhang H, Zhao S, Jia L (2016) Spectrophotometric determination of mercury(II) ions based on their stimulation effect on the peroxidase-like activity of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. Microchim Acta 183:2481–2489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1886-4
Lin T, Zhong L, Chen H, Li Z, Song Z, Guo L, Fu F (2017) A sensitive colorimetric assay for cholesterol based on the peroxidase-like activity of MoS2 nanosheets. Microchim Acta 184:1233–1237. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2147-x
Pati S, Quinto M, Palmisano F, Zambonin PG (2004) Determination of choline in milk, milk powder, and soy lecithin hydrolysates by flow injection analysis and amperometric detection with a choline oxidase based biosensor. J Agric Food Chem 52:4638–4642. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf049835+
Liu N, Kim P, Kim JH, Ye JH, Kim S, Lee CJ (2014) Large-area atomically thin MoS 2 Nanosheets prepared using electrochemical exfoliation. ACS Nano 8:6902–6910. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn5016242
Tuteja SK, Duffield T, Neethirajan S (2017) Liquid exfoliation of 2D MoS2 nanosheets and their utilization as a label-free electrochemical immunoassay for subclinical ketosis. Nano 9:10886–10896. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr04307d
Acknowledgements
The first author is grateful to SERB N-PDF (PDF/2016/000243) for fellowship. The authors are also thankful to CIF, IIT (BHU) Varanasi for providing characterization facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests. Narsingh R. Nirala and Vinita have been carried out experiments and responsible for raw data if required.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 2.73 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nirala, N.R., Vinita & Prakash, R. Quick colorimetric determination of choline in milk and serum based on the use of MoS2 nanosheets as a highly active enzyme mimetic. Microchim Acta 185, 224 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2753-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2753-2