Abstract
The authors describe an electrochemical assay for fast detection of Escherichia coli (E. coli). It is based on a dual signal amplification strategy and the use of a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) whose surface was modified with a polyaniline (PANI) film and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) via cyclic voltammetry (CV). In the next step, avidin was covalently immobilized on the PANI/AuNP composite on the SPCE surface. Subsequently, the biotinylated DNA capture probe was immobilized onto the PANI/AuNP/avidin-modified SPCE by biotin-avidin interaction. Then, DNA of E.coli, digoxigenin-labeled DNA detector probe and anti-digoxigenin-labeled horseradish peroxidase (HRP) were placed on the electrode. 3,3′,5,5′-Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) and H2O2 solution were added and the CV electrochemical signal was generated at a potential of −0.1 V (vs. Ag/AgCl) and a scan rate 50 mV.s−1. The assay can detect 4 × 106 to 4 CFU of E. coli without DNA amplification. The biosensor is highly specific over other pathogens including Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus haemolyticus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It can be concluded that this genosensor has an excellent potential for rapid and accurate diagnosis of E.coli inflicted infections.

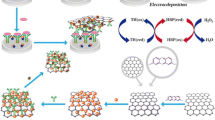
Schematic of an electrochemical E. coli genosensor based on sandwich assay on a polyaniline/gold nanoparticle-modified screen printed carbon electrode (SPCE). The biosensor can detect 4 × 106 to 4 CFU of E. coli without DNA amplification.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allocati N, Masulli M, Alexeyev MF, Di Ilio C (2013) Escherichia coli in Europe: an overview. Int J Environ Res Public Health 10(12):6235–6254
Tang H, Zhang W, Geng P, Wang Q, Jin L, Wu Z, Lou M (2006) A new amperometric method for rapid detection of Escherichia coli density using a self-assembled monolayer-based bienzyme biosensor. Anal Chim Acta 562(2):190–196
Li K, Lai Y, Zhang W, Jin L (2011) Fe 2 O 3@ Au core/shell nanoparticle-based electrochemical DNA biosensor for Escherichia coli detection. Talanta 84(3):607–613
Foxman B (2002) Epidemiology of urinary tract infections: incidence, morbidity, and economic costs. Am J Med 113(1):5–13
Ejrnæs K (2011) Bacterial characteristics of importance for recurrent urinary tract infections caused by Escherichia coli. Dan Med Bull 58(4):B4187
Mach KE, Wong PK, Liao JC (2011) Biosensor diagnosis of urinary tract infections: a path to better treatment? Trends Pharmacol Sci 32(6):330–336
Kumar M, Ghosh S, Nayak S, Das A (2016) Recent advances in biosensor based diagnosis of urinary tract infection. Biosens Bioelectron 80:497–510
Chen Y, Li Y, Yang Y, Wu F, Cao J, Bai L (2017) A polyaniline-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite as a redox nanoprobe in a voltammetric DNA biosensor for Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Microchim Acta 184(6):1801–1808
Setterington EB, Alocilja EC (2012) Electrochemical biosensor for rapid and sensitive detection of magnetically extracted bacterial pathogens. Biosensors 2(1):15–31
Azimzadeh M, Rahaie M, Nasirizadeh N, Daneshpour M, Naderi-Manesh H (2017) Electrochemical miRNA biosensors: the benefits of nanotechnology. Nanomedicine Res J 2(1):36–48
Kurundu Hewage EM, Spear D, Umstead TM, Hu S, Wang M, Wong PK, Chroneos ZC, Halstead ES, Thomas NJ (2017) An electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of pediatric bloodstream infections. SLAS Technology (Translating Life Sciences Innovation) 22(6):616–625
Ma X, Jiang Y, Jia F, Yu Y, Chen J, Wang Z (2014) An aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for the detection of Salmonella. J Microbiol Methods 98:94–98
Dhand C, Das M, Datta M, Malhotra B (2011) Recent advances in polyaniline based biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 26(6):2811–2821
Daneshpour M, Izadi P, Omidfar K (2016) Femtomolar level detection of RASSF1A tumor suppressor gene methylation by electrochemical nano-genosensor based on Fe3O4/TMC/Au nanocomposite and PT-modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 77:1095–1103
Saberi RS, Shahrokhian S, Marrazza G (2013) Amplified electrochemical DNA sensor based on polyaniline film and gold nanoparticles. Electroanalysis 25(6):1373–1380
Liu C, Jiang D, Xiang G, Liu L, Liu F, Pu X (2014) An electrochemical DNA biosensor for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, based on signal amplification of graphene and a gold nanoparticle–polyaniline nanocomposite. Analyst 139(21):5460–5465
Liao JC, Mastali M, Gau V, Suchard MA, Møller AK, Bruckner DA, Babbitt JT, Li Y, Gornbein J, Landaw EM (2006) Use of electrochemical DNA biosensors for rapid molecular identification of uropathogens in clinical urine specimens. J Clin Microbiol 44(2):561–570
Singh R, Verma R, Sumana G, Srivastava AK, Sood S, Gupta RK, Malhotra B (2012) Nanobiocomposite platform based on polyaniline-iron oxide-carbon nanotubes for bacterial detection. Bio Electro Chem 86:30–37
Paniel N, Baudart J (2013) Colorimetric and electrochemical genosensors for the detection of Escherichia coli DNA without amplification in seawater. Talanta 115:133–142
Heurich M, Kadir MKA, Tothill IE (2011) An electrochemical sensor based on carboxymethylated dextran modified gold surface for ochratoxin A analysis. Sensors Actuators B Chem 156(1):162–168
Arshak K, Velusamy V, Korostynska O, Oliwa-Stasiak K, Adley C (2009) Conducting polymers and their applications to biosensors: emphasizing on foodborne pathogen detection. IEEE Sensors J 9(12):1942–1951
Xu Q, Leng J, H-b L, Lu G-j, Wang Y, Hu X-Y (2010) The preparation of polyaniline/gold nanocomposites by self-assembly and their electrochemical applications. React Funct Polym 70(9):663–668
Zhu C, Yang G, Li H, Du D, Lin Y (2014) Electrochemical sensors and biosensors based on nanomaterials and nanostructures. Anal Chem 87(1):230–249
Syedmoradi L, Daneshpour M, Alvandipour M, Gomez FA, Hajghassem H, Omidfar K (2017) Point of care testing: the impact of nanotechnology. Biosens Bioelectron 87:373–387
Monošík R, Streďanský M, Šturdík E (2012) Biosensors-classification, characterization and new trends. Acta Chim Slov 5(1):109–120
Williams E, Pividori M, Merkoci A, Forster R, Alegret S (2003) Rapid electrochemical genosensor assay using a streptavidin carbon-polymer biocomposite electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 19(3):165–175
Prince S (2015) Characterization of electrodeposited polyaniline biosensor platform for Escherichia coli O157: H7 detection. M.S. thesis, Department of electrical and computer engineering of the college of engineering. Michigan Technological University
Lee AC, Liu G, Heng CK, Tan SN, Lim TM, Lin Y (2008) Sensitive electrochemical detection of horseradish peroxidase at disposable screen-printed carbon electrode. Electroanalysis 20(18):2040–2046
Saleh Ahammad A (2013) Hydrogen peroxide biosensors based on horseradish peroxidase and hemoglobin. The Journal of Biosensors and Bioelectronics (JBSBE) 9:2
Daneshpour M, Omidfar K, Ghanbarian H (2016) A novel electrochemical nanobiosensor for the ultrasensitive and specific detection of femtomolar-level gastric cancer biomarker miRNA-106a. Beilstein J Nanotechnol 7:2023
Fengqin Li ZY, Haichao Q, Zhang G, Yan H, Liu X, He X (2015) A highlysensitiveandspecific electrochemicalsensingmethod for robustdetectionof Escherichiacolilac Z genesequence. Biosens Bioelectron 68:78–82
Xu S, Zhang Y, Dong K, Wen J, Zheng C, Zhao S (2017) Electrochemical DNA biosensor based on graphene oxide-chitosan hybrid nanocomposites for detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:3443–3458
Hassan A-RHA-A, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Merkoçi A (2015) Highly sensitive and rapid determination of Escherichia coli O157: H7 in minced beef and water using electrocatalytic gold nanoparticle tags. Biosens Bioelectron 67:511–515
Luo C, Lei Y, Yan L, Yu T, Li Q, Zhang D, Ding S, Ju H (2012) A rapid and sensitive aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for direct detection of Escherichia coli O111. Electroanalysis 24(5):1186–1191
Zhang W, Luo C, Zhong L, Nie S, Cheng W, Zhao D, Ding S (2013) Sensitive detection of enteropathogenic E. coli using a bfpA gene-based electrochemical sensor. Microchim Acta 180(13–14):1233–1240
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a grant from Tarbiat Modares University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1639 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shoaie, N., Forouzandeh, M. & Omidfar, K. Voltammetric determination of the Escherichia coli DNA using a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with polyaniline and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185, 217 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2749-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2749-y