Abstract
An ultrasensitive immunosensor for the direct detection of the illegally used livestock feed clebuterol (CLB) is described. It is based on the use of a glassy carbon electrode modified with an MoS2-AuPt nanocomposite and on biotin-streptavidin interaction. The use of MoS2-AuPt accelerates electron transfer, and this leads to a sharp increase in the electrochemical signal for the electrochemical probe hydrogen peroxide. Differential pulse voltammetry was used to record the current signal at a peak potential of −0.18 V (vs SCE). Under optimal conditions, the electrode has a linear response in the 10 pg·mL−1 to 100 ng·mL−1 CLB concentration range and a 6.9 pg·mL−1 detection limit (based on the 3σ criterium). This immunosensor is sensitive, highly specific and acceptably reproducible, and thus represents a valuable tool for the determination of CLB in pork.

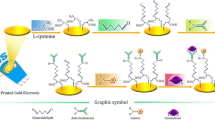
Schematic of a voltammetric immunosensor for the determination of clenbuterol (CLB) based on the use of a nanocomposite prepared from molybdenum disulfide and a gold-platinum alloy (MoS2-AuPt), and making use of the biotin-streptavidin system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu Y, Lu Q, Hu X, Wang H, Li H, Zhang Y, Yao S (2017) A Nanosensor based on carbon dots for recovered fluorescence detection Clenbuterol in pork samples. J Fluoresc 27(5):1847–1853
Lv CZ, Xun Y, Cao Z, Xie JL, Li D, Liu G, Yu L, Feng ZM, Yin YL, Tan SZ (2017) Sensitive determination of toxic Clenbuterol in pig meat and pig liver based on a carbon nanopolymer composite. Food Anal Methods 10(7):1–10
Li Y, Qi P, Ma X, Zhong J (2014) Quick detection technique for clenbuterol hydrochloride by using surface plasmon resonance biosensor. Eur Food Res Technol 239(2):195–201
Yan F, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Zhao J, Liu S, He L, Feng X, Zhang H, Zhang Z (2015) Carboxyl-modified graphene for use in an immunoassay for the illegal feed additive clenbuterol using surface plasmon resonance and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Microchim Acta 182(3–4):855–862
Yang Y, Zhang H, Huang C, Yang D, Jia N (2016) Electrochemical non-enzyme sensor for detecting clenbuterol (CLB) based on MoS 2 -Au-PEI-hemin layered nanocomposite. Biosens Bioelectron 89(Pt 1):461
Chen XB, Wu YL, Yang T (2011) Simultaneous determination of clenbuterol, chloramphenicol and diethylstilbestrol in bovine milk by isotope dilution ultraperformance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Instrum Anal 879(11):799–803
He L, Su Y, Zeng Z, Liu Y, Huang X (2007) Determination of ractopamine and clenbuterol in feeds by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anim Feed Sci Technol 132(3–4):316–323
Liu B, Yan H, Qiao F, Geng Y (2011) Determination of clenbuterol in porcine tissues using solid-phase extraction combined with ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and HPLC-UV detection. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879(1):90
Shelver WL, Smith DJ (2004) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay development for the beta-adrenergic agonist zilpaterol. J Agric Food Chem 52(8):2159–2166
Liu Q, Yang Y, Hui L, Zhu R, Qian S, Yang S, Xu J (2015) NiO nanoparticles modified with 5,10,15,20-tetrakis(4-carboxyl pheyl)-porphyrin: promising peroxidase mimetics for H 2 O 2 and glucose detection. Biosens Bioelectron 64:147–153
Liu Q, Yang Y, Lv X, Ding Y, Zhang Y, Jing J, Xu C (2016) One-step synthesis of uniform nanoparticles of porphyrin functionalized ceria with promising peroxidase mimetics for H 2 O 2 and glucose colorimetric detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:726–734
Liu Q, Chen P, Xu Z, Chen M, Ding Y, Yue K, Xu J (2017) A facile strategy to prepare porphyrin functionalized ZnS nanoparticles and their peroxidase-like catalytic activity for colorimetric sensor of hydrogen peroxide and glucose. Sensors Actuators B Chem 251:339–348
Ji H, Yan F, Lei J, Ju H (2012) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of nucleic acids by template enhanced hybridization followed with rolling circle amplification. Anal Chem 84(16):7166–7171
Jin H, Yanrong W, Yan C, Zhi Z, Xiaohai Y, Chaoyong James Y, Kemin W, Weihong T (2011) Pyrene-excimer probes based on the hybridization chain reaction for the detection of nucleic acids in complex biological fluids. Angew Chem Int Ed 50(2):401
Lee JU, Jeong JH, Lee DS, Sim SJ (2014) Signal enhancement strategy for a micro-arrayed polydiacetylene (PDA) immunosensor using enzyme-catalyzed precipitation. Biosens Bioelectron 61(6):314–320
Yan M, Bai W, Chao Z, Huang Y, Jiao Y, Chen A (2015) Design of nuclease-based target recycling signal amplification in aptasensors. Biosens Bioelectron 77:613
Tang D, Su B, Tang J, Ren J, Chen G (2010) Nanoparticle-based sandwich electrochemical immunoassay for carbohydrate antigen 125 with signal enhancement using enzyme-coated nanometer-sized enzyme-doped silica beads. Anal Chem 82(4):1527–1534
Li Y, Lin H, Peng H, Qi R, Luo C (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with MoS 2 nanosheets and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Microchim Acta 183(9):1–7
Cao X, Wang N, Jia S, Guo L, Li K (2013) Bimetallic AuPt nanochains: synthesis and their application in electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Biosens Bioelectron 39(1):226–230
Shi H, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Zhu Q, Song W (2011) Bimetallic nano-structured glucose sensing electrode composed of copper atoms deposited on gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 173(1–2):85–94
Zhou H, Liu Q, Liu W, Ge J, Lan M, Wang C, Geng J, Wang P (2014) Template-Free Preparation of Volvox-like CdxZn1−xS Nanospheres with Cubic Phase for Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production. Chem Asian J 9(3):811–818
Wang X, Nan F, Zhao J, Yang T, Ge T, Jiao K (2015) A label-free ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA sensor based on thin-layer MoS2 nanosheets with high electrochemical activity. Biosens Bioelectron 64:386–391
Zhu L, Zhang Y, Xu P, Wen W, Li X, Xu J (2016) PtW/MoS2 hybrid nanocomposite for electrochemical sensing of H2O2 released from living cells. Biosens Bioelectron 80:601–606
Pan N, Wang LY, Wu LL, Peng CF, Xie ZJ (2017) Colorimetric determination of cysteine by exploiting its inhibitory action on the peroxidase-like activity of Au@Pt core-shell nanohybrids. Microchim Acta 184(1):65–72
Ding Y, Yang B, Liu H, Liu Z, Zhang X, Zheng X, Liu Q (2018) FePt-Au ternary metallic nanoparticles with the enhanced peroxidase-like activity for ultrafast colorimetric detection of H2O2. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:775–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.115
Chen J, Yu C, Zhao Y, Niu Y, Zhang L, Yu Y, Wu J, He J (2017) A novel non-invasive detection method for the FGFR3 gene mutation in maternal plasma for a fetal achondroplasia diagnosis based on signal amplification by hemin-MOFs/PtNPs. Biosens Bioelectron 91:892–899
Jiang X, Chen K, Han H (2011) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of Bacillus thuringiensis transgenic sequence based on in situ Ag nanoparticles aggregates induced by biotin-streptavidin system. Biosens Bioelectron 28(1):464–468
Zhu Q, Chai Y, Zhuo Y, Yuan R (2015) Ultrasensitive simultaneous detection of four biomarkers based on hybridization chain reaction and biotin-streptavidin signal amplification strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 68(68):42–48
Liu N, Nie D, Tan Y, Zhao Z, Liao Y, Wang H, Sun C, Wu A (2016) An ultrasensitive amperometric immunosensor for zearalenones based on oriented antibody immobilization on a glassy carbon electrode modified with MWCNTs and AuPt nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(1):1–7
Chen B, Wang L, Gao S (2016) Development of a disposable label-free impedance Immunosensor for direct and sensitive Clenbuterol determination in pork. Food Anal Methods 9(6):1781–1788
Gan X, Zhao H, Quan X (2017) Two-dimensional MoS2: A promising building block for biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 89(Pt 1):56
Liu N, Nie D, Tan Y, Zhao Z, Liao Y, Wang H, Sun C, Wu A (2017) An ultrasensitive amperometric immunosensor for zearalenones based on oriented antibody immobilization on a glassy carbon electrode modified with MWCNTs and AuPt nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(1):1–7
Chen Q, Yu C, Gao R, Gao L, Li Q, Yuan G, He J (2016) A novel electrochemical immunosensor based on the rGO-TEPA-PTC-NH2 and AuPt modified C60 bimetallic nanoclusters for the detection of Vangl1, a potential biomarker for dysontogenesis. Biosens Bioelectron 79:364–370
Yang T, Chen M, Kong Q, Luo X, Jiao K (2016) Toward DNA electrochemical sensing by free-standing ZnO nanosheets grown on 2D thin-layered MoS2. Biosens Bioelectron 89(Pt 1):538–544
Zhang X, Zhao H, Xue Y, Wu Z, Zhang Y, He Y, Li X, Yuan Z (2012) Colorimetric sensing of clenbuterol using gold nanoparticles in the presence of melamine. Biosens Bioelectron 34(1):112–117
Liu G, Chen H, Peng H, Song S, Gao J, Lu J, Ding M, Li L, Ren S, Zou Z (2011) A carbon nanotube-based high-sensitivity electrochemical immunosensor for rapid and portable detection of clenbuterol. Biosens Bioelectron 28(1):308–313
Zhang Z, Duan F, He L, Peng D, Yan F, Wang M, Zong W, Jia C (2016) Electrochemical clenbuterol immunosensor based on a gold electrode modified with zinc sulfide quantum dots and polyaniline. Microchim Acta 183(3):1089–1097
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31071093, 31170129, and 31200064) and the Science and Technology Planning Project of Yuzhong District of Chongqing City, China (No. 20140119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2558 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, R., Chen, S., Xu, W. et al. A voltammetric immunosensor for clenbuterol based on the use of a MoS2-AuPt nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 185, 209 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2746-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2746-1