Abstract
The authors describe a method for the fluorometric determination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by exploiting target-triggered chain reactions and deoxyribonuclease I (DNase I)-aided target recycling. It is making use of a carboxy-fluorescein (FAM)-labeled single-stranded probe containing two sections. One is complementary to the 5′ terminus of the target, while the 3′ terminus of the other target is adsorbed on the surface of graphene oxide (GO) via π-stacking interactions without the target (16S rRNA). This adsorption results in quenching of the fluorescence of the label and protects it from being cleaved by DNase I. However, upon addition of the target, DNA/RNA hybrids are repelled by GO. This leads to fluorescence recovery as measured at excitation/emission wavelengths of 480/514 nm due to a chain reaction that is triggered by the target. The signal is strongly amplified by using DNase I-mediated target recycling. The 16S rRNA of MRSA can be detected by this method in the 1 to 30 nM concentration range, and the detection limit is 0.02 nM. The method was applied to analyze bacterial samples, and the detection limit is as low as 30 CFU . mL−1. The assay is highly sensitive and selective and in our percpetion has a large potential in diagnosis of drug-resistant bacteria.

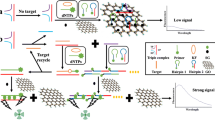
Schematic of the graphene oxide-based fluorescent bioassay for Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus detection by using target-triggered chain reaction and deoxyribonuclease I-aided signal amplification





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sowash MG, Uhlemann AC (2014) Community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus case studies. Methods Mol Biol 1085:25–69
Gordon RJ, Lowy FD (2008) Pathogenesis of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. Clin Infect Dis 46:S350–S359
Thurlow LR, Joshi GS, Richardson AR (2012) Virulence strategies of the dominant USA300 lineage of community associated methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA). FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 65:5–22
Jackson CR, Davis JA, Barrett JB (2013) Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from retail meat and humans in Georgia. J Clin Microbiol 51:1199–1207
Chuang CC, Hsiao CH, Tan HY, Ma HK, Lin KK, Chang CJ, Huang YC (2012) Staphylococcus aureus ocular infection: methicillin-resistance, clinical features, and antibiotic susceptibilities. PLoS One 8:e42437
Wolk DM, Struelens MJ, Pancholi P, Davis T, Dellalatta P (2009) Rapid detection of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-Resistant S. aureus (MRSA) in wound specimens and blood cultures: multicenter preclinical evaluation of the Cepheid Xpert MRSA/SA skin and soft tissue and blood culture assays. J Clin Microbiol 47:823–826
Park CE, Akhtar M, Rayman MK (1992) Nonspecific reactions of a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit (TECRA) for detection of staphylococcal enterotoxins in foods. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:2509–2512
Liu Y, Zhang J, Ji YD (2016) PCR-based approaches for the detection of clinical methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Open Microbiol J 10:45–56
Shi JY, Chan CY, Pang YT, Ye WW, Tian F, Lyu J, Zhang Y, Yang M (2015) A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) biosensor based on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for the detection of mecA gene sequence of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens Bioelectron 67:595–600
Watanabe K, Kuwata N, Sakamoto H, Amano Y, Satomura T, Suye S (2015) A smart DNA sensing system for detecting methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using modified nanoparticle probes. Biosens Bioelectron 67:419–423
Nawattanapaiboon K, Kiatpathomchai W, Santanirand P, Vongsakulyanon A, Amarit R, Somboonkaew A, Sutapun B, Srikhirin T (2015) SPR-DNA array for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in combination with loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 74:335–340
Kawanami T, Yatera K, Yamasaki K, Noguchi S, Fukuda K, Akata K, Naito K, Kido T, Ishimoto H, Taniguchi H, Mukae H (2016) Clinical impact of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus on bacterial pneumonia: cultivation and 16S ribosomal RNA gene analysis of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. BMC Infect Dis 16:155
Nasseri S, Ebrahimi S, Abtahi M, Saeedi R (2017) Synthesis and characterization of polysulfone/graphene oxide nano-composite membranes for removal of bisphenol a from water. J Environ Manag 205:174–182
Zhang Y, Zhang M, Jiang H, Shi J, Li F, Xia Y, Zhang G, Li H (2017) Bio-inspired layered chitosan/graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogels with high strength and pH-driven shape memory effect. Carbohydr Polym 177:116–125
Lv H, Li S, Liu YM, Wang GK, Li X, Lu Y, Wang JJ (2015) A reversible fluorescent INHIBIT logic gate for determination of silver and iodide based on the use of graphene oxide and a silver-selective probe DNA. Microchim Acta 182:2513–2520
Wu Q, Song DQ, Zhang D, Sun Y (2016) An enhanced SPR immunosensing platform for human IgG based on the use of silver nanocubes and carboxy-functionalized graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 183:2177–2184
Wang Y, Li ZH, Wang J, Li J, Yin Y (2011) Graphene and graphene oxide: biofunctionalization and applications in biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 29:205–212
Gurunathan S, Kim JH (2016) Synthesis, toxicity, biocompatibility, and biomedical applications of graphene and graphene-related materials. Int J Nanomedicine 11:1927–1945
Wang LJ, Tian JN, Huang Y, Lin XW, Yang W, Zhao YC, Zhao SL (2016) Homogenous fluorescence polarization assay for the DNA of HIV a T7 by exploiting exonuclease-assisted quadratic recycling amplification and the strong interaction between graphene oxide and ssDNA. Microchim Acta 183:2147–2153
Hu X, Liu Y, Qu X, Sun Q (2017) A quantum dot-labelled aptamer/graphene oxide system for the construction of a half-adder and half-subtractor with high resettability. Chem Commun (Camb) 53:11181–11184
Ning Y, Duan YF, Feng YY, Deng L (2014) Label-free fluorescent Aptasensor based on a graphene oxide self-assembled probe for the determination of adenosine triphosphate. Anal Lett 47:2350–2360
Wang Y, Li Z, Weber TJ, Hu D, Lin CT, Li J, Lin Y (2013) In situ live cell sensing of multiple nucleotides exploiting DNA/RNA aptamers and graphene oxide Nanosheets. Anal Chem 85:6775–6782
Chen F, Liu Y, Liao R, Gong H, Chen C, Chen X, Cai C (2017) Reduced graphene oxide as a resonance light-scattering probe for thrombin detection using dual-aptamer-based dsDNA. Anal Chim Acta 985:141–147
Ning Y, Wei K, Cheng LJ, Hu J, Xiang Q (2017) Fluorometric aptamer based determination of adenosine triphosphate based on deoxyribonuclease I-aided target recycling and signal amplification using graphene oxide as a quencher. Microchim Acta 184:1847–1854
Ning Y, Gao Q, Zhang XQ, Wei K, Chen LL (2016) A graphene oxide–based sensing platform for the determination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus based on strand-displacement polymerization recycling and synchronous fluorescent signal amplification. J Biomol Screen 21:851–857
Zhang YL, Tang LN, Yang F, Sun ZY, Zhang GJ (2015) Highly sensitive DNA-based fluorometric mercury(II) bioassay based on graphene oxide and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Microchim Acta 182:1535–1541
Ren X, Ma H, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Yan T, Du B, Wei Q (2017) A sulfur-doped graphene-based immunological biosensing platform for multianalysis of cancer biomarkers. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b13416
Liu KY, Yan X, Mao BY, Wang S, Deng L (2016) Aptamer-based detection of Salmonella enteritidis using double signal amplification by Klenow fragment and dual fluorescence. Microchim Acta 183:643–649
He QZ, Luo HQ, Tang L, Liu J, Chen KK, Zhang QF, Ning Y (2017) Nanographite-based fluorescent biosensing of Salmonella enteritidis by applying deoxyribonuclease-assisted recycling. Microchim Acta 184:3875–3882
Huang Y, Chen J, Zhao S, Shi M, Chen ZF, Liang H (2013) Label-free colorimetric Aptasensor based on nicking enzyme assisted signal amplification and DNAzyme amplification for highly sensitive detection of protein. Anal Chem 85:4423–4430
Hiremath N, Guntupalli R, Vodyanoy V, Chin AB, Park MK (2015) Detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus using novel lytic phage-based magnetoelastic biosensors. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 210:129–136
Xiong J, Wang WW, Zhou YL, Kong WJ, Wang ZX, Fu ZF (2016) Ultra-sensitive chemiluminescent detection of Staphylococcus aureus based on competitive binding of Staphylococcus protein A-modified magnetic beads to immunoglobulin G. Microchim Acta 183:1507–1512
Xiong J, Wang WX, Fu ZF (2017) Fluorimetric sandwich affinity assay for Staphylococcus aureus based on dual-peptide recognition on magnetic nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184:4197–4202
Yuan JL, Yu Y, Li C, Ma XY, Xia Y, Chen J, Wang ZP (2014) Visual detection and microplate assay for Staphylococcus aureus based on aptamer recognition coupled to tyramine signal amplification. Microchim Acta 181:321–327
Tawil N, Sacher E, Mandeville R, Meunier M (2012) Surface plasmon resonance detection of E. coli and methicillin-resistant S. aureus using bacteriophages. Biosens Bioelectron 37:24–29
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan province(2016JJ3098), Outstanding Youth Scientific Research Project Funded by Education department of Hunan Province (15B169), Key Project Funded by Hunan traditional Chinese medicine administration (201711), Science and Technology Innovation Team in Colleges and Universities in Hunan Province《Chinese traditional medicine for treatment of infectious diseases》(No: 15, Grxjb-7), Doctor start-up Foundation of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (9982-1001019), Key Subjects of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine《pathogenic biology》(NO.1) and Project Funded by Hunan Provincial Level Course《Immunology and pathogenic biology》(No. 48) for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 6661 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ning, Y., Zou, L., Gao, Q. et al. Graphene oxide-based fluorometric determination of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by using target-triggered chain reaction and deoxyribonuclease-assisted recycling. Microchim Acta 185, 183 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2702-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2702-0