Abstract
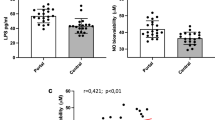
The role of circulating endothelin-1, a potent vasoconstricting peptide, in liver cirrhosis is still controversial. It has been postulated that endothelin-1 may play a role in the circulatory derangement occurring in cirrhotic subjects, and increased plasma endothelin-1 levels have been reported in these patients. In this study we looked for a relationship between the severity of the liver disease according to Child’s classification and plasma endothelin-1 concentrations in a group of cirrhotic patients compared with a healthy control group. Twenty-two cirrhotic patients and 10 healthy controls, matched for sex and age, were selected for study after informed consent. The etiology of cirrhosis was posthepatitis B in 8 of 22 cases, posthepatitis C in 13 of 22 cases, and alcoholism in 1 patient. According to Child’s classification, 6 patients were in class A, 6 in class B, and 10 in class C. Plasma endothelin-1 was measured by a commercial RIA kit (Amersham UK). Mean±SD plasma endothelin-1 levels were 8.8±0.9 pg/ml in controls and 9.2±1.1 pg/ml in all cirrhotic patients (P>0.05). In each subgroup of cirrhotics, plasma endothelin-1 was 8.6±1.2 pg/ml in Child A, 8.9±1.9 pg/ml in Child B, and 10.6±1.5 pg/ml in Child C groups, respectively. There were no statistical differences between control subjects and Child A and B cirrhotic patients (P>0.05). A significant increase in endothelinl was observed only in the Child C group versus either group A or B (P=0.004). Our results show that alterations of circulating endothelin-1 do not occur in all cirrhotic patients; higher plasma levels than controls are only detectable in patients with more-severe hepatic failure. We do not know whether increased endothelin-1 levels are a consequence of hemodynamic disorders occurring in the advanced phase of liver cirrhosis or play a pathogenic role.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sherlock S. Vasodilatation associated with hepatocellular disease: relation to functional organ failure. Gut 1990; 31:365.
Lewis FW, Adair O, Rector WG Jr. Arterial vasodilatation is not the cause of increased cardiac output in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1992; 102:1024.
Schrier RW, Arroyo V, Bernardi M, et al. Peripheral vasodilatation hypothesis: a proposal for the initiation of renal sodium and water retention in cirrhosis. Hepatology 1988; 8:1151.
Blendis LM, Bomzon A. The cardiovascular complications of cirrhosis. In: Bomzon A, Blendis LM, eds. Cardiovascular complications of liver disease. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 1990:1–7.
Lagi A, Laffi G, Cencetti S, Gentilini P. L’autoregolazione cerebrale nel cirrotico ascitico: superamento delle problematiche attuali. In: Gentilini P, ed. Aggiornamenti di Fisiopatologia Epatica. Scientific Press; 1998: 119–127.
Ring-Larsen H. Hepatic nephropathy related to haemodynamics. Liver 1983; 3:265.
Sacerdoti D, Bolognesi M, Merkel C, et al. Renal vasoconstriction in cirrhosis evaluated by duplex Doppler ultrasonography. Hepatology 1993; 17:219.
Laffi G, La Villa G, Gentilini P. Pathogenesis and management of the hepatorenal syndrome. Semin Liver Dis 1994; 14:71.
Bank ER, Thrall JH, Dantzker DR. Radionuclide demonstration of intrapulmonary shunting in cirrhosis. AJR 1983; 140:967.
Krowka MJ, Cortese DA. Hepatopulmonary syndrome: an evolving perspective in the era of the liver transplantation. Hepatology 1990; 11:138.
Bernardi M, Trevisani F, Santini C, et al. Plasma norepinephrine, weak neurotransmitters, and renin activity during active tilting in liver cirrhosis: relationship with cardiovascular homeostasis and renal function. Hepatology 1983; 3:56.
Murray BM, Paller MS. Decreased pressor reactivity to angiotensin II in cirrhotic rats. Evidence for a postreceptor defect in angiotensin action. Circ Res 1985; 57:424.
Vallance P, Moncada S. Hyperdynamic circulation in cirrhosis: a role for nitric oxide. Lancet 1991; 337:776.
Hartleb M, Moreau R, Cailmail S, et al. Vascular hyporesponsiveness to endothelin-1 in rats with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1994; 107:1085.
Tsai YT, Lin HC, Yang MC, et al. Plasma endothelin levels in patients with cirrhosis and their relationships to the severity of cirrhosis and renal function. J Hepatol 1995; 23:681.
Moore K, Wendon J, Frazer M, Karani J, Williams R, Badr K. Plasma endothelin immunoreactivity in liver disease and the hepatorenal syndrome. N Engl J Med 1992; 327:174.
Uchihara M, Izumi N, Sato C, Marumo F. Clinical significance of elevated plasma endothelin concentration in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1992; 16:95.
Bernardi M, Gulberg V, Colantoni A, Trevisani F, Gasbarrini A, Gerbes AL. Plasma endothelin-1 and -3 in cirrhosis: relationship with systemic hemodynamics, renal function and neurohumoral systems. J Hepatol 1996; 24:161.
Pugh RNH, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the esophagus for bleeding esophageal varices. Br J Surg 1973; 60:646.
Sherwin R, Joshi P, Hendler R, et al. Hyperglucagonemia in Laennec’s cirrhosis: the role of portal-systemic shunting. N Engl J Med 1974; 290:239.
Silva G, Navasa M, Bosh J, et al. Hemodynamic effects of glucagon in portal hypertension. Hepatology 1990; 11:668.
Sieber CC, Groszmann RJ. Nitric oxide mediates in vitro hyporeactivity to vasopressor in mesenteric vessels of portal hypertensive rats. Gastroenterology 1992; 103:235.
Moore K, Ward PS, Taylor GW, Williams R. Systemic and renal production of thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin in decompensated liver disease and hepatorenal syndrome. Gastroenterology 1991; 100:1069.
Schrier RW, Niederberger M, Weigert A, Gines P. Peripheral arterial vasodilation: determinant of functional spectrum of cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis 1994; 14:14.
Laffi G, La Villa G, Pinzani M, et al. Alterated renal and platelet arachidonic acid metabolism in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1986; 90:274.
Gentilini P, Laffi G. Pathophysiology and treatment of ascites and the hepatorenal syndrome. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol 1992; 6:581.
Pinzani M, Milani S, De Franco R, et al. Endothelin 1 is over-expressed in human cirrhotic liver and exerts multiple effects on activated hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology 1996; 110:534.
Rockey D. The cellular pathogenesis of portal hypertension: stellate cell contractility, endothelin and nitric oxide. Hepatology 1997; 25:2.
Petrowsky H, Schmandra T, Lorey T, Hanisch E, Herrmann G. Endothelin-induced contraction of the portal vein in cirrhosis. Eur Surg Res 1999; 31:289.
Kojima H, Yamao J, Tsujimoto T, Uemura M, Takaya A, Fukui H. Mixed endothelin receptor antagonist, SB 209670, decreases portal pressure in biliary cirrhotic rats in vivo by reducing portal venous system resistance. J Hepatol 2000; 32:43.
Badr KF, Murray JJ, Breyer MD, Takahashi K, Inagami T, Harris RC. Mesangial cells, glomerular and renal vascular responses to endothelin in the kidney. J Clin Invest 1989; 83:326.
Hocher B, Brause M, Mendes U, Berger D, Buhler H, Gross P. Impact of the endothelin system on water and sodium excretion in patients with liver cirrhosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 1999; 14:1133.
Veglio F, Pinna G, Melchio R, et al. Plasma endothelin levels in cirrhotic subjects. J Hepatol 1992; 15:85.
Zoja C, Orisio S, Perico N, et al. Constitutive expression of endothelin gene in cultured human mesangial cells and its modulation by transforming growth factor-beta, thombin and a thrombaxane A2 analogue. Lab Invest 1991; 64:16.
Kuchan MJ, Frangos JA. Shear stress regulates endothelin-1 release via protein kinase C and cGMP in cultured endothelial cells. Am J Physiol 1993; 264:H150.
Kohno M, Yasunari K, Yokokawa K, Murakawa K, Horio T, Takeda T. Inhibition by atrial natriuretic peptides of endothelin-1 secretion after stimulation with angiotensin II and thrombin of cultured human endothelial cells. J Clin Invest 1991; 87:1999.
Gerbes AL, Moller S, Gulberg V, Henriksen JH. Endothelin-1 and -3 plasma concentrations in patients with cirrhosis: role of splanchnic and renal passage and liver function. Hepatology 1995; 21:735.
Bruno CM, D’Amico R, Ierna D, Neri S. Does endothelin-1 play a role in the renal function of cirrhotic patients? Panminerva Med 1998; 40:196.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bruno, C.M., Neri, S., Sciacca, C. et al. Plasma endothelin-1 levels in liver cirrhosis. Int J Clin Lab Res 30, 169–172 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005990070002
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005990070002