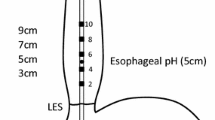
Abstract
Purpose
To identify the factors that affect laparoscopic fundoplication (LF) treatment efficacy in patients with erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease (e-GERD) esophagitis, based on the findings of multichannel intraluminal impedance pH (MII-pH) and high-resolution manometry (HRM).
Methods
The subjects were 102 patients with e-GERD diagnosed by endoscopy, who underwent LF as the initial surgery. To analyze the findings of MII-pH and HRM, the patients were divided into two groups: a cured group (CR), comprised of patients whose esophagitis was cured postoperatively; and a recurrence group (RE), comprised of patients who suffered recurrent esophagitis.
Results
There were 96 patients in the CR group and 6 in the RE group. MII-pH indicated that the acid reflux time, the longest reflux time, and the number of refluxes longer than 5 min, were significantly higher in the RE group than in the CR group (p = 0.0028, p = 0.0008, p = 0.012, respectively). The HRM indicated that only the distal contractile integral (DCI) was significantly lower in the RE group (p = 0.0109).
Conclusion
The results of this study indicate that esophageal clearance may affect the treatment outcome of LF. Based on the findings of MII-pH, the longest reflux time and the number of refluxes longer than 5 min were important factors influencing the therapeutic effect, whereas based on the HRM, the DCI value was most important.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, Blum AL, Armstrong D, Galmiche JP, et al. Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles classification. Gut. 1999;45(2):172–802.
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J, Jones R. The Montreal definition and classification of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006;101(8):1900–20.
Emerenziani S, Habib FI, Ribolsi M, Caviglia R, Guarino MP, Petitti T, et al. Effect of hiatal hernia on proximal oesophageal acid clearance in gastro-oesophageal reflux disease patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23(6):751–7.
Johnson LF, DeMeester TR. Twenty-four-hour pH monitoring of the distal esophagus. A quantitative measure of gastroesophageal reflux. Am J Gastroenterol. 1974;62(4):325–32.
Shay S, Tutuian R, Sifrim D, Vela M, Wise J, Balaji N, et al. Twenty-four hour ambulatory simultaneous impedance and pH monitoring: a multicenter report of normal values from 60 healthy volunteers. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99(6):1037–43.
Yano F, Omura N, Tsuboi K, Hoshino M, Yamamoto SR, Akimoto S, et al. Standard values of 24-h multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring for the Japanese. Esophagus. 2017;14(1):91–6.
Yadlapati R. High-resolution esophageal manometry: interpretation in clinical practice. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2017;33(4):311–9.
Hunter JG, Smith CD, Branum GD, Waring JP, Trus TL, Cornwell M, et al. Laparoscopic fundoplication failures: patterns of failure and response to fundoplication revision. Ann Surg. 1999;230(4):595–606.
Hoshino M, Omura N, Yano F, Tsuboi K, Yamamoto SR, Akimoto S, et al. Impact of reflux esophagitis on the esophageal function before and after laparoscopic fundoplication. Esophagus. 2018;15(4):224–30.
El-Selag HB, Sonnenberg A. Outcome of erosive reflux esophagitis after Nissen fundoplication. Am J Gastroenterol. 1999;94(7):1771–6.
Isolauri J, Luostarinen M, VilJakka M, Isolauri E, Keyrilainen O, Karvonen AL. Long-term comparison of antireflux surgery versus conservative therapy for reflux esophagitis. Ann Surg. 1997;225(3):295–9.
Omura N, Kashiwagi H, Yano F, Tsuboi K, Yanaga K. Characteristics of symptomatic GERD in Japanese patients based on 24-h pH monitoring. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:791–5.
Tsuboi K, Omura N, Yano F, Hoshino M, Yamamoto SR, Akimoto S, et al. Effect of preoperative balloon dilation on treatment outcomes of laparoscopic Heller-Dor surgery for achalasia: a propensity score matched study. Surg Today. 2018;48(12):1068–75.
Hoshino M, Omura N, Yano F, Tsuboi K, Yamamoto SR, Akimoto S, et al. Backflow prevention mechanism of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication using high-resolution manometry. Surg Endosc. 2016;30(7):2703–10.
Kahrilas PJ, Bredenoord AJ, Fox M, Gyawali CP, Roman S, Smout AJ, International High Resolution Manometry Working Group, et al. The Chicago classification of esophageal motility disorders, v3.0. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2015;27(2):160–74.
Hoshino M, Omura N, Yano F, Tsuboi K, Yamamoto SR, Akimoto S, et al. Comparison of the multichannel impedance pH and conventional pH for measuring esophageal acid exposure: a propensity score-matched analysis. Surg Endosc. 2017;31(12):5241–7.
Bancewicz J, Matthews HR, O’Hanrahan T, Adams I. A comparison of surgically treated reflux patients in two surgical centers. In: Little AG, Ferguson MK, Skinner DB, editors. Diseases of the esophagus. Mount Kisco: Oxford Academic; 1990. p. 177–80.
Ismail T, Bancewicz J, Barlow J. Yield pressure, anatomy of the cardia and gastro-oesophageal reflux. Br J Surg. 1995;82(7):943–7.
Omura N, Tsuboi K, Yano F. Minimally invasive surgery for large hiatal hernia. Ann Gastroenerol Surg. 2019;3(5):487–95.
Sandhu DS, Fass R. Current trends in the management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Gut Liver. 2018;12(1):7–16.
Tutuian R, Castell DO. Review article: complete gastro-oesophageal reflux monitoring combined pH and impedance. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24(2):27–37.
Sidhwa F, Moore A, Alligood E, Fisichella PM. Diagnosis and treatment of the extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Ann Surg. 2017;265(1):63–7.
Gyawali CP, Kahrilas PJ, Savarino E, Zerbib F, Mion F, Smout AJPM, et al. Modern diagnosis of GERD : the Lyon consensus. Gut. 2018;67(7):1351–62.
Garbarino S, Horton A, Patel A. The utility of esophageal motility testing in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019;21(8):37. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-019-0704-7.
Dallemagne B, Weerts JM, Jehaes C, Markiewicz S, Lombard R. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Endosc. 1991;1(3):138–43.
Omura N, Yano F, Tsuboi K, Hoshino M, Yamamoto SR, Akimoto S, et al. Surgical results of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease with special reference to recurrence. Esophagus. 2018;15(4):217–23.
Broeders JA, Rijnhart-de Jong HG, Draaisma WA, Bredenoord AJ, Smout AJ, Gooszen HG. Ten-year outcome of laparoscopic and conventional nissen fundoplication: randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg. 2009;250(5):698–706.
Mardani J, Lundell L, Engström C. Total or posterior partial fundoplication in the treatment of GERD: results of a randomized trial after 2 decades of follow-up. Ann Surg. 2011;253(5):875–8.
Engström C, Cai W, Irvine T, Devitt PG, Thompson SK, Game PA, et al. Twenty years of experience with laparoscopic antireflux surgery. Br J Surg. 2012;99(10):1415–21.
Rouphael C, Shakya S, Arora Z, Gabbard S, Rice T, Lopez R, et al. Esophageal dysmotility and other preoperative factors associated with acid suppressive therapy after fundoplication. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2020;55(1):1–8.
Siegal SR, Dunst CM, Robinson B, Dewey EN, Swanstrom LL, DeMeester SR. Preoperative High-resolution manometry criteria are associated with dysphagia after Nissen fundoplication. World J Surg. 2019;43(4):1062–7.
Kapadia S, Osler T, Lee A, Borrazzo E. The role of preoperative high resolution manometry in predicting dysphagia after laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. Surg Endosc. 2018;32(5):2365–72.
Ip S, Tatsioni A, Conant A, Karagozian R, Fu L, Chew P, et al. Predictors of clinical outcomes following fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease remain insufficiently defined: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(3):752–8.
Fibbe C, Layer P, Keller J, Strate U, Emmermann A, Zornig C. Esophageal motility in reflux disease before and after fundoplication: a prospective, randomized, clinical, and manometric study. Gastroenterol. 2001;121(1):5–14.
Herbella FAM, Tedesco P, Nipomnick I, Fiscichella PM, Patti MG. Effect of partial and total laparoscopic fundoplication on esophageal body motility. Surg Endosc. 2007;21(2):285–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsuboi, K., Yano, F., Omura, N. et al. Factors affecting the treatment outcomes of laparoscopic fundoplication for erosive reflux esophagitis: findings of esophageal pathological function tests. Surg Today 51, 1568–1576 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-021-02226-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-021-02226-4