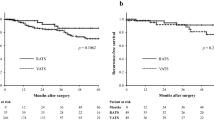
Abstract
The robotic surgical system was designed to overcome the drawbacks of conventional endoscopic surgery. Since national health insurance in Japan began covering robotic-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS) for malignant lung and mediastinal tumors in 2018, the number of RATS procedures being performed domestically has increased rapidly. This review evaluates the advantages and disadvantages of RATS for patients with lung cancers, based on an electronic literature search of PubMed. The main advantages of RATS are its ability to achieve excellent lymph-node removal with low morbidity and mortality, and minimal postoperative pain. Conversely, its disadvantages include a long operation time and the need for specialized instruments. However, the learning curve for RATS is reported to be shorter than that for VATS: some studies recommend that a surgeon needs to perform 18–22 robotic operations to attain sufficient skill. RATS for lung cancer is more expensive than VATS and the cost of training is high. Although the main disadvantage of RATS is that it reduces operator’s tactile senses, the endoscope, which is directly manipulated by the surgeon at the console, using various magnifications, and 3D HD images on the monitor, may compensate for this. Ultimately, RATS offers better maneuverability, accuracy, and stability over VATS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Storz P, Buess GF, Kunert W, Kirschniak A. 3D HD versus 2D HD: surgical task efficiency in standardised phantom tasks. Surg Endosc. 2012;26:1454–60.
Brooks P. Robotic-assisted thoracic surgery for early-stage lung cancer: a review. AORN J. 2015;102:40–9.
McLachlan G. From 2D to 3D: the future of surgery? Lancet. 2011;378:1368.
Moore LJ, Wilson MR, Waine E, Masters RS, McGrath JS, Vine SJ. Robotic technology results in faster and more robust surgical skill acquisition than traditional laparoscopy. J Robot Surg. 2015;9:67–73.
Park BJ, Flores RM, Rusch VW. Robotic assistance for video-assisted thoracic surgical lobectomy: technique and initial results. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2006;131:54–9.
Veronesi G, Galetta D, Maisonneuve P, Melfi F, Schmid RA, Borri A, et al. Four-arm robotic lobectomy for the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;140:19–25.
Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS, Skylizard L, Minnich DJ. Initial consecutive experience of completely portal robotic pulmonary resection with 4 arms. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;142:740–6.
Gharagozloo F, Margolis M, Tempesta B, Strother E, Najam F. Robot- assisted lobectomy for early-stage lung cancer: report of 100 consecutive cases. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:380–4.
Dylewski MR, Ohaeto AC, Pereira JF. Pulmonary resection using a total endoscopic robotic video-assisted approach mark. Semin Thoracic Surg. 2011;23:36–42.
Nakamura H, Suda T, Ikeda N, Okada M, Date H, Oda M, et al. Initial results of robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery in Japan. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;62:720–5.
Jang HJ, Lee HS, Park SY, Zo JI. Comparison of the early robot-assisted lobectomy experience to video-assisted thoracic surgery lobectomy for lung cancer: a single-institution case series matching study. Innovations. 2011;6:305–10.
Louie BE, Farivar AS, Aye RW, Vallières E. Early experience with robotic lung resection results in similar operative outcomes and morbidity when compared with matched video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery cases. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;93:1598–604 (discussion 1604–5).
Veronesi G. Robotic surgery for the treatment of early-stage lung cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2013;25:107–14.
Louie BE, Wilson JL, Kim S, Cerfolio RJ, Park BJ, Farivar AS, et al. Comparison of video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery and robotic approaches for clinical stage I and stage II non-small cell lung cancer using the society of thoracic surgeons database. Ann Thorac Surg. 2016;102:917–24.
Kent M, Wang T, Whyte R, Curran T, Flores R, Gangadharan S. Open, video-assisted thoracic surgery, and robotic lobectomy: review of a national database. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97:236–42. (discussion 242-4).
Nasir BS, Bryant AS, Minnich DJ, Wei B, Cerfolio RJ. Performing robotic lobectomy and segmentectomy: Cost, profitability, and outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;98:203–9.
Nakamura H. Systematic review of published studies on safety and efficacy of thoracoscopic and robot-assisted lobectomy for lung cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;20:93–8.
Veronesi G. Robotic lobectomy and segmentectomy for lung cancer: results and operating technique. J Thorac Dis. 2015;7:122–30.
Giulianotti PC, Buchs NC, Caravaglios G, Bianco FM. Robot-assisted lung resection: outcomes and technical details. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;11:388–92.
Mungo B, Hooker CM, Ho JSY, Yang SC, Battafarano RJ, Brock MV, et al. Robotic versus thoracoscopic resection for lung cancer: early results of a new robotic program. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2016;26:243–8.
Novellis P, Bottoni E, Voulaz E, Cariboni U, Testori A, Bertolaccini L, et al. Robotic surgery, video-assisted thoracic surgery, and open surgery for early stage lung cancer: comparison of costs and outcomes at a single institute. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10:790–8.
Liang H, Liang W, Zhao L, Chen D, Zhang J, Zhang Y. et al. Robotic versus video-assisted lobectomy/segmentectomy for lung cancer. Ann Surg. 2018;268:254–9.
Veronesi G, Novellis P, Difrancesco O, Dylewski M. Robotic assisted lobectomy for locally advanced lung cancer. J Vis Surg. 2017;3:78.
Cerfolio RJ. Total port approach for robotic lobectomy. Thorac Surg Clin. 2014;24:151–6.
Melfi FM, Mussi A. Robotically assisted lobectomy: learning curve and complications. Thorac Surg Clin. 2008;18:289–95. vi-vii.
Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS, Minnich DJ. Starting a robotic program in general thoracic surgery: why, how, and lessons learned. Ann Thorac Surg. 2011;91:1729–36.
Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS. How to teach robotic pulmonary resection. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2013;25:76–82.
Meyer M, Gharagozloo F, Tempesta B, Margolis M, Strother E, Christenson D. The learning curve of robotic lobectomy. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg. 2012;8:448–52.
Hernandez JD, Bann S, Munz K, Moorthy K, Datta V, Martin S, et al. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of the learning curve of a simulated task on the da Vinci system. Surg Endosc. 2004;18:372–8.
Hernandez JM, Humphries LA, Keeling WB, Golkar F, Dimou F, Garrett J, et al. Robotic lobectomy: flattening the learning curve. J Robot Surg. 2012;6:41–5.
Veronesi G, Agoglia BG, Melfi F, Maisonneuve P, Raffaella Bertolotti R, Bianchi PP, et al. Experience with robotic lobectomy for lung cancer. Innovations. 2011;6:355–60.
Arnold BN, Thomas DC, Bhatnager V, Blasberg JD, Wang Z, Boffa DJ, et al. Defining the learning curve in robot-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy. Surgery. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2018.06.011.
Wei B, Eldaif SM, Cerfolio RJ. Robotic lung resection for non-small cell lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25:515–31.
Park BJ, Flores RM. Cost comparison of robotic, video-assisted thoracic surgery and thoracotomy approaches to pulmonary lobectomy. Thorac Surg Clin. 2008;18:297–300.
Swanson SJ, Miller DL, McKenna RJ, Howington J, Marshall MB, Yoo AC, et al. Comparing robot-assisted thoracic surgical lobectomy with conventional video-assisted thoracic surgical lobectomy and wedge resection: Results from a multihospital database (Premier). J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2014;147:929–37.
Paul S, Jalbert J, Isaacs AJ, et al. Comparative effectiveness of robotic- assisted vs thoracoscopic lobectomy. Chest. 2014;146:1505–12.
Deen SA, Wilson JL, Wilshire CL, Vallières E, Farivar AS, Aye RW, et al. Defining the cost of care for lobectomy and segmentectomy: a comparison of open, video-assisted thoracoscopic, and robotic approaches. Ann Thorac Surg. 2014;97:1000–7.
Dylewski MR, Lazzaro RS. Robotics—the answer to the Achilles’ heel of VATS pulmonary resection. Chin J Cancer Res. 2012;24:259–60.
Kajiwara N, Kato Y, Hagiwara M, Kakihana M, Ohira T, Kawate N, et al. Robot-assisted thoracic surgery as required for financial viability under the 2016 revised reimbursement paradigm of the Japanese National Health Insurance System. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;24:73–80.
McKenna RJ. Lobectomy by video assisted thoracic surgery with mediastinal node sampling for lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1994;107:879–82.
Gharagozloo F, Margolis M, Tempesta B. Robot-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy for early-stage lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85:1880–6.
Suda T. Transition from video-assisted thoracic surgery to robotic pulmonary surgery. J Vis Surg. 2017;3:55.
Huang J, Li J, Li H, Lin H, Lu P, Luo Q. Continuous 389 cases of Da Vinci robot-assisted thoracoscopic lobectomy in treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: experience in Shanghai Chest Hospital. J Thorac Dis. 2018;10:3776–82.
Veronesi G, Park B, Cerfolio R, Dylewski M, Toker A, Fontaine JP, et al. Robotic resection of Stage III lung cancer: an international retrospective study. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;54:912–9.
Cao C, Manganas C, Ang SC, Yan TD. A systematic review and meta-analysis on pulmonary resections by robotic video-assisted thoracic surgery. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;1:3–10.
Demmy TL, Yendamuri S, D’Amico TA, Burfeind WR. Oncologic equivalence of minimally invasive lobectomy: the scientific and practical arguments. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018;106:609–17.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
I have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanzaki, M. Current status of robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for lung cancer. Surg Today 49, 795–802 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-019-01793-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00595-019-01793-x