Abstract
Background
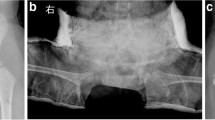
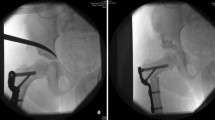
Closed reduction and spica cast is still the preferred treatment option for children presenting with developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) after the age of 6 months. This study aims to investigate the outcomes of patients with DDH treated by closed reduction and dynamic cast immobilization.
Methods
In total, 159 patients (mean age 15.6 ± 4.2 months; 172 hips) were treated with a dynamic cast immobilization for 3 months, followed by an abduction brace until a stable concentric reduction was achieved. Radiological examination was performed at each follow-up visit to assess reduction, redislocation rate and presence of avascular necrosis (AVN) of the femoral epiphysis. Final radiographic results were evaluated with the Severin classification.
Results
The redislocation rate was 4.1% (7/172); the overall AVN rate was 14.5% (grade II: 16 hips; grade III: 5 hips; grade IV: 3 hips). At last follow-up visit, the mean age of patients was 61.6 ± 21.3 months (range 30.8–141), and the mean acetabular index was 22.6° ± 5.6°; 67.3% of the hips had Severin type I radiographic criteria, 8.5% had type II, 23.6% had type III, and 0.6% had type IV.
Conclusions
Dynamic cast is an alternative to spica cast immobilization in DDH patients undergoing closed reduction. It has similar redislocation and AVN rates compared to standard spica cast immobilization, as reported by previous studies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cooper AP, Doddabasappa SN, Mulpuri K (2014) Evidence-based management of developmental dysplasia of the hip. Orthop Clin N Am 45(3):341–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ocl.2014.03.005
Kotlarsky P, Haber R, Bialik V, Eidelman M (2015) Developmental dysplasia of the hip: What has changed in the last 20 years? World J Orthop 6(11):886–901. https://doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v6.i11.886
Noordin S, Umer M, Hafeez K, Nawaz H (2010) Developmental dysplasia of the hip. Orthop Rev 2(2):e19. https://doi.org/10.4081/or.2010.e19
Tennant SJ, Eastwood DM, Calder P, Hashemi-Nejad A, Catterall A (2016) A protocol for the use of closed reduction in children with developmental dysplasia of the hip incorporating open psoas and adductor releases and a short-leg cast: mid-term outcomes in 113 hips. Bone Jt J 98-b(11):1548–1553. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.98b11.36606
Leeprakobboon D, Kaewpornsawan K, Eamsobhana P (2014) Four-point molding: a new cast molding technique for closed reduction treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Med Assoc Thail 97(Suppl 9):S29–S33
Keren Y, Sadia S, Eidelman M (2011) The use of the lotus position during spica cast application for the treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a technical note. Orthopedics 34(9):708–709. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20110714-12
Fettweis E (1990) Treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip in a squatting position, Fettweis method. Acta Orthop Belgica 56(1):155–165
Yamada N, Maeda S, Fujii G, Kita A, Funayama K, Kokubun S (2003) Closed reduction of developmental dislocation of the hip by prolonged traction. J Bone Jt Surg Br 85(8):1173–1177
Pospischill R, Weninger J, Ganger R, Altenhuber J, Grill F (2012) Does open reduction of the developmental dislocated hip increase the risk of osteonecrosis? Clin Orthop Relat Res 470(1):250–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-011-1929-4
Sankar WN, Gornitzky AL, Clarke NM, Herrera-Soto JA, Kelley SP, Matheney T, Mulpuri K, Schaeffer EK, Upasani VV, Williams N, Price CT (2016) Closed reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip: early-term results from a prospective, multicenter cohort. J Pediatr Orthop. https://doi.org/10.1097/bpo.0000000000000895
Crego CH Jr, Schwartzmann JR (1948) Follow-up study of the early treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Am 30a(2):428–442
Esteve R (1960) Congenital dislocation of the hip: a review and assessment of results of treatment with special reference to frame reduction as compared with manipulative reduction. J Bone Jt Surg Br 42-b:253–263
Tiderius C, Jaramillo D, Connolly S, Griffey M, Rodriguez DP, Kasser JR, Millis MB, Zurakowski D, Kim YJ (2009) Post-closed reduction perfusion magnetic resonance imaging as a predictor of avascular necrosis in developmental hip dysplasia: a preliminary report. J Pediatr Orthop 29(1):14–20. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181926c40
Bao Q, Bao S (1996) Long-term investigation of closed reduction of congenital hip dislocation in children with modified frog-leg cast. Zhonghua wai ke za zhi [Chinese journal of surgery] 34(4):212–214
Cai Z, Li L, Zhang L, Ji S, Zhao Q (2017) Dynamic long leg casting fixation for treating 12- to 18-month-old infants with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Int Med Res 45(1):272–281. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300060516675110
Kalamchi A, MacEwen GD (1980) Avascular necrosis following treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Am 62(6):876–888
Severin E (1941) Contribution to the knowledge of congenital dislocation of the hip joint: late results of closed reduction and arthrographic studies of recent cases. Acta Chir Scand 84(Suppl 63):53–54
Gage JR, Winter RB (1972) Avascular necrosis of the capital femoral epiphysis as a complication of closed reduction of congenital dislocation of the hip: a critical review of twenty years’ experience at Gillette Children’s Hospital. J Bone Jt Surg Am 54(2):373–388
Terjesen T, Halvorsen V (2007) Long-term results after closed reduction of latedetected hip dislocation: 60 patients followed up to skeletal maturity. Acta Orthop 78(2):236–246. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453670710013744
Murray T, Cooperman DR, Thompson GH, Ballock T (2007) Closed reduction for treatment of development dysplasia of the hip in children. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead, NJ) 36(2):82–84
Kaneko H, Kitoh H, Mishima K, Matsushita M, Ishiguro N (2013) Long-term outcome of gradual reduction using overhead traction for developmental dysplasia of the hip over 6 months of age. J Pediatr Orthop 33(6):628–634. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e31829b2d8b
Aksoy MC, Ozkoc G, Alanay A, Yazici M, Ozdemir N, Surat A (2002) Treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip before walking: results of closed reduction and immobilization in hip spica cast. Turk J Pediatr 44(2):122–127
Rampal V, Sabourin M, Erdeneshoo E, Koureas G, Seringe R, Wicart P (2008) Closed reduction with traction for developmental dysplasia of the hip in children aged between one and five years. J Bone Jt Surg Br 90(7):858–863. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620x.90b7.20041
Kitoh H, Kitakoji T, Katoh M, Ishiguro N (2006) Prediction of acetabular development after closed reduction by overhead traction in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Orthop Sci 11(5):473–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00776-006-1049-2
Gogus MT, Aksoy MC, Atay OA, Acaroglu RE, Surat A (1997) Treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. Results of closed reduction and immobilization in the hip spica cast. Turk J Pediatr 39(4):499–503
Sibinski M, Murnaghan C, Synder M (2006) The value of preliminary overhead traction in the closed management of DDH. Int Orthop 30(4):268–271. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-006-0080-4
Shin CH, Yoo WJ, Park MS, Kim JH, Choi IH, Cho TJ (2016) Acetabular remodeling and role of osteotomy after closed reduction of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Am 98(11):952–957. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.15.00992
Herold HZ (1980) Avascular necrosis of the femoral head in congenital dislocation of the hip. Isr J Med Sci 16(4):295–300
Gregosiewicz A, Wosko I (1988) Risk factors of avascular necrosis in the treatment of congenital dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 8(1):17–19
Kruczynski J (1996) Avascular necrosis of the proximal femur in developmental dislocation of the hip. Incidence, risk factors, sequelae and MR imaging for diagnosis and prognosis. Acta Orthop Scand Suppl 268:1–48
Brougham DI, Broughton NS, Cole WG, Menelaus MB (1990) Avascular necrosis following closed reduction of congenital dislocation of the hip: review of influencing factors and long-term follow-up. J Bone Jt Surg Br 72(4):557–562
Sibinski M, Synder M, Domzalski M, Grzegorzewski A (2004) Risk factors for avascular necrosis after closed hip reduction in developmental dysplasia of the hip. Ortop Traumatol Rehabil 6(1):60–66
Burgos J, Gonzalez-Herranz P, Ocete G, Rapariz JM (1995) Secondary avascular necrosis after treatment for congenital dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B 4(2):188–193
Schur MD, Lee C, Arkader A, Catalano A, Choi PD (2016) Risk factors for avascular necrosis after closed reduction for developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Child Orthop 10(3):185–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11832-016-0743-7
Barakat AS, Zein AB, Arafa AS, Azab MA, Reda W, Hegazy MM, Al Barbary HM, Kaddah MA (2017) Closed reduction with or without adductor tenotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip presenting at walking age. Curr Orthop Pract 28(2):195–199. https://doi.org/10.1097/bco.0000000000000478
Sucato DJ, De La Rocha A, Lau K, Ramo BA (2017) Overhead Bryant’s traction does not improve the success of closed reduction or limit AVN in developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 37(2):e108–e113. https://doi.org/10.1097/bpo.0000000000000747
Li LY, Zhang LJ, Jia JY, Zhao Q, Wang EB, Li QW (2013) Does dynamic immobilization reduce chondrocyte apoptosis and disturbance to the femoral head perfusion? Int J Clin Exp Pathol 6(2):212–223
Bhaskar A, Desai H, Jain G (2016) Risk factors for early redislocation after primary treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip: Is there a protective influence of the ossific nucleus? Indian J Orthop 50(5):479–485. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.189610
Kim NH, Park BM, Lee HM (1990) Congenital dislocation of the hip: a long-term follow-up in Korea. Yonsei Med J 31(2):134–143. https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.1990.31.2.134
Quinn RH, Renshaw TS, DeLuca PA (1994) Preliminary traction in the treatment of developmental dislocation of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop 14(5):636–642
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
No patients were involved. This is a retrospective study of patient’s data, and an IRB approval was obtained.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Zhou, Q., Liu, Y. et al. Closed reduction and dynamic cast immobilization in patients with developmental dysplasia of the hip between 6 and 24 months of age. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 29, 51–57 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-018-2289-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-018-2289-5