Abstract
Background
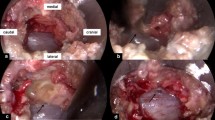
With the advancement of minimally invasive spinal surgery, endoscopic lumbar decompression has been widely used for the treatment of degenerative lumbar spinal diseases. Iatrogenic dural tear is a relatively common complication in endoscopic lumbar spinal surgery. The golden standard of treatment for iatrogenic dural tear is immediate open conversion and direct repair under microscopic visualization. Recently, most of endoscopic spinal surgery is performed under local anesthesia. So, conversion to open surgery is very embarrassing situation because of the need of additional general anesthesia. But, direct endoscopic dural repair is very difficult procedure due to the limitation of manipulation. No report showed direct dural suture under full endoscopic situation.
Purpose
The purpose of this surgical technique is to provide a method of full endoscopic dural suture repair without conversion to open surgery.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Epstein NE (2007) The frequency and etiology of intraoperative dural tears in 110 predominantly geriatric patients undergoing multilevel laminectomy with noninstrumented fusions. J Spinal Disord Tech 20(5):380–386
Bosacco SJ, Gardner HJ, Guille JT (2001) Evaluation and treatment of dural tears in lumbar spine surgery: a review. Clin Orthop Relat Res 389:238–247
Jones AA, Stambough JL, Balderston RA, Rothman RH, Booth RE Jr (1989) Long-term results of lumbar spine surgery complicated by unintended incidental durotomy. Spine 14:443–446
Khan MH, Rihn J, Steele G, Davis R, Donaldson WF 3rd, Kang JD, Lee JY (2006) Postoperative management protocol for incidental dural tears during degenerative lumbar spine surgery: a review of 3,183 consecutive degenerative lumbar cases. Spine 31:2609–2613
Dafford EE, Anderson PA (2015) Comparison of dural repair techniques. Spine J 15:1099–1105
Epstein NE (2010) Dural repair with four spinal sealants: focused review of the manufacturers’ inserts and the current literature. Spine J 10:1065–1068
Grannum S, Patel MS, Attar F, Newey M (2014) Dural tears in primary decompressive lumbar surgery. Is primary repair necessary for a good outcome? Eur Spine J 23(4):904–908
Guerin P, El Fegoun AB, Obeid I, Gille O et al (2012) Incidental durotomy during spine surgery: incidence, management and complications. A retrospective review. Injury 43(4):397–401
Epstein NE (2013) A review article on the diagnosis and treatment of cerebrospinal fluid fistulas and dural tears occurring during spinal surgery. Surg Neurol Int 4(Suppl 5):S301–S317
Wang JC, Bohlman HH, Riew KD (1998) Dural tears secondary to operations on the lumbar spine: management and results after a two-year-minimum follow-up of eighty-eight patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80(12):1728–1732
Miller PR, Elder FW Jr (1968) Meningeal pseudocysts (meningocele spurius) following laminectomy. Report of ten cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am 50(2):268–276
Karaeminogullari O, Atalay B, Sahin O, Ozalay M et al (2005) Remote cerebellar hemorrhage after a spinal surgery complicated by dural tear: case report and literature review. Neurosurgery 57(1 Suppl):E215
Shaffrey CI, Spotnitz WD, Shaffrey ME, Jane JA (1990) Neurosurgical applications of fibrin glue: augmentation of dural closure in 134 patients. Neurosurgery 26(2):207–210
Oertel JM, Burkhardt BW (2017) Full endoscopic treatment of dural tears in lumbar spine surgery. Eur Spine J 26(10):2496–2503
Sun MJ, Gao SM, Wang YH (2011) Simultaneous intra-operative repair for inadvertent dural tear under posterior lumbar disk scope. Orthop Surg 3(3):188–192
Shibayama M, Mizutani J, Takahashi I, Nagao S et al (2008) Patch technique for repair of a dural tear in microendoscopic spinal surgery. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(8):1066–1067
Chou D, Wang VY, Khan AS (2009) Primary dural repair during minimally invasive microdiscectomy using standard operating room instruments. Neurosurgery 64(5 Suppl 2):356–358
Than KD, Wang AC, Etame AB, La Marca F et al (2008) Postoperative management of incidental durotomy in minimally invasive lumbar spinal surgery. Minim Invas Neurosurg 51(5):263–266
Galarza M, Gazzeri R, Alfaro R, de la Rosa P et al (2018) Evaluation and management of small dural tears in primary lumbar spinal decompression and discectomy surgery. J Clin Neurosci 50:177–182
Ahn Y, Lee HY, Lee SH, Lee JH (2011) Dural tears in percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy. Eur Spine J 20(1):58–64
Guerin P, El Fegoun AB, Obeid I, Gille O et al (2012) Incidental durotomy during spine surgery: incidence, management and complications. A retrospective review. Injury 43(4):397–401
Papavero L, Engler N, Kothe R (2015) Incidental durotomy in spine surgery: first aid in ten steps. Eur Spine J 24(9):2077–2084
Tafazal SI, Sell PJ (2005) Incidental durotomy in lumbar spine surgery: incidence and management. Eur Spine J 14(3):287–290
Gautschi OP, Stienen MN, Smoll NR, Corniola MV et al (2014) Incidental durotomy in lumbar spine surgery–a three-nation survey to evaluate its management. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 156(9):1813–1820
Hodges SD, Humphreys SC, Eck JC, Covington LA (1999) Management of incidental durotomy without mandatory bed rest. A retrospective review of 20 cases. Spine 24(19):2062–2064
Narotam PK, Jose S, Nathoo N, Taylon C, Vora Y (2004) Collagen matrix (DuraGen) in dural repair: analysis of a new modified technique. Spine 29(24):2861–2867
Cammisa FP Jr, Girardi FP, Sangani PK et al (2000) Incidental durotomy in spine surgery. Spine 25:2663–2667
Jankowitz BT, Atteberry DS, Gerszten PC, Karausky P et al (2009) Effect of fibrin glue on the prevention of persistent cerebral spinal fluid leakage after incidental durotomy during lumbar spinal surgery. Eur Spine J 18(8):1169–1174
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any potential conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, J.K., Youn, M.S., Seong, Y.J. et al. Iatrogenic dural tear in endoscopic lumbar spinal surgery: full endoscopic dural suture repair (Youn’s technique). Eur Spine J 27 (Suppl 3), 544–548 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-018-5637-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-018-5637-6