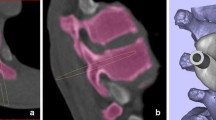
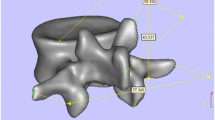
Abstract
Purpose
Accurate implantation of pedicle screw in spinal deformity correction surgeries is always challenging. We have developed a method of pedicle screw placement in severe and rigid scoliosis with a multi-level 3D printing drill guide template.
Methods
From November 2011 to March 2015, ten patients (4 males and 6 females) with severe and rigid scoliosis (Cobb angle >70° and flexibility <30%)were included. Multi-level template was designed and manufactured according to the part (two or three levels) of the most severe deformity. The drill template was then placed on the corresponding vertebral surface. Then, pedicle screws were carefully inserted along the trajectories. The other screws were placed in free hand. After surgery, the positions of the pedicle screws were evaluated by CT scan and graded for validation.
Results
48 screws were implanted using templates, other 104 screws in free hand, and the accuracies were 93.8 and 78.8%, respectively, with significant difference. The deformity correction ratio was 67.1 and 41.2% in coronal and sagittal plane post-operatively, respectively. The average operation time was 234.0 ± 34.1 min, and average blood loss was 557 ± 67.4 ml.
Conclusions
With the application of multi-level template, the incidence of cortex perforation in severe and rigid scoliosis decreased and this technology is, therefore, potentially applicable in clinical practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li M, Ni J, Li Y, Fang X, Gu S, Zhang Z, Zhu X (2009) Single-staged anterior and posterior spinal fusion: a safe and effective alternative for severe and rigid adolescent idiopathic scoliosis in China. J Paediatr Child Health 45(5):246–253
Liljenqvist UR, Halm HF, Link TM (1997) Pedicle screw instrumentation of the thoracic spine in idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 22(19):2239–2245
Clin J, Aubin CÉ, Lalonde N, Parent S, Labelle H (2011) A new method to include the gravitational forces in a finite element model of the scoliotic spine. Med Biol Eng Comput 49(8):967–977
Lonner BS, Auerbach JD, Estreicher MB, Kean KE (2009) Thoracic pedicle screw instrumentation: the learning curve and evolution in technique in the treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 34(20):2158–2164
Sarlak AY, Tosun B, Atmaca H, Sarisoy HT, Buluç L (2009) Evaluation of thoracic pedicle screw placement in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J 18(12):1892–1897
Rajasekaran S, Kanna PR, Shetty TA (2010) Intra-operative computer navigation guided cervical pedicle screw insertion in thirty-three complex cervical spine deformities. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine 1(1):38–43
Larson AN, Polly DW Jr, Guidera KJ, Mielke CH, Santos ER, Ledonio CG, Sembrano JN (2012) The accuracy of navigation and 3D image-guided placement for the placement of pedicle screws in congenital spine deformity. J Pediatr Orthop 32(6):e23–e29
Ma T, Xu YQ, Cheng YB, Jiang MY, Xu XM, Xie L, Lu S (2012) A novel computer-assisted drill guide template for thoracic pedicle screw placement: a cadaveric study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 132(1):65–72
Pettersson A, Kero T, Gillot L, Cannas B, Fäldt J, Söderberg R, Näsström K (2010) Accuracy of CAD/CAM-guided surgical template implant surgery on human cadavers: part I. J Prosthet Dent 103(6):334–342
Dandekeri SS, Sowmya MK, Bhandary S (2013) Stereolithographic surgical template: a review. J Clin Diagn Res 7(9):2093–2095
Seres L, Varga E Jr, Kocsis A, Rasko Z, Bago B, Varga E, Piffko J (2014) Correction of a severe facial asymmetry with computerized planning and with the use of a rapid prototyped surgical template: a case report/technique article. Head Face Med 11:10–27
Ciocca L, Fantini M, De Crescenzio F, Persiani F, Scotti R (2011) Computer-aided design and manufacturing construction of a surgical template for craniofacial implant positioning to support a definitive nasal prosthesis. Clin Oral Implants Res 22(8):850–856
Ferrari V, Parchi P, Condino S, Carbone M, Baluganti A, Ferrari M, Mosca F, Lisanti M (2013) An optimal design for patient-specific templates for pedicle spine screws placement. Int J Med Robot 9(3):298–304
Merc M, Drstvensek I, Vogrin M, Brajlih T, Recnik G (2013) A multi-level rapid prototyping drill guide template reduces the perforation risk of pedicle screw placement in the lumbar and sacral spine. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 133(7):893–899
Lu S, Xu YQ, Chen GP, Zhang YZ, Lu D, Chen YB, Shi JH, Xu XM (2011) Efficacy and accuracy of a novel rapid prototyping drill template for cervical pedicle screw placement. Comput Aided Surg 16(5):240–248
Bai G, He D, Yang C, Lu C, Huang D, Chen M, Yuan J (2014) Effect of digital template in the assistant of a giant condylar osteochondroma resection. J Craniofac Surg 25(3):e301–e304
Gan Y, Xu D, Lu S, Ding J (2011) Novel patient-specific navigational template for total knee arthroplasty. Comput Aided Surg 16(6):288–297
Owen BD, Christensen GE, Reinhardt JM, Ryken TC (2007) Rapid prototype patient-specific drill template for cervical pedicle screw placement. Comput Aided Surg 12(5):303–308
Lu S, Zhang YZ, Wang Z, Shi JH, Chen YB, Xu XM, Xu YQ (2012) Accuracy and efficacy of thoracic pedicle screws in scoliosis with patient-specific drill template. Med Biol Eng Comput 50(7):751–758
Seres L, Varga E Jr, Kocsis A, Rasko Z, Bago B, Varga E, Piffko J (1999) Complications associated with pedicle screws. J Bone Joint Surg Am 81(11):1519–1528
Zhang Y, Xie J, Wang Y, Bi N, Zhao Z, Li T (2014) Thoracic pedicle classification determined by inner cortical width of pedicles on computed tomography images: its clinical significance for posterior vertebral column resection to treat rigid and severe spinal deformities-a retrospective review of cases. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 15:278
Facanha-Filho FA, Winter RB, Lonstein JE, Koop S, Novacheck T, L’Heureux EA Jr, Noren CA (2001) Measurement accuracy in congenital scoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83-A(1):42–45
Mao K, Wang Y, Xiao S, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Wang Z, Lu N, Shourong Z, Xifeng Z, Geng C, Baowei L (2010) Clinical application of computer-designed polystyrene models in complex severe spinal deformities: a pilot study. Eur Spine J 19(5):797–802
Samdani AF, Ranade A, Sciubba DM, Cahill PJ, Antonacci MD, Clements DH, Betz RR (2010) Accuracy of free-hand placement of thoracic pedicle screws in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: how much of a difference does surgeon experience make? Eur Spine J 19(1):91–95
Puvanesarajah V, Liauw JA, Lo SF, Lina IA, Witham TF (2014) Techniques and accuracy of thoracolumbar pedicle screw placement. World J Orthop 5(2):112–123
Qi DB, Wang JM, Zhang YG, Zheng GQ, Zhang XS, Wang Y (2014) Positioning thoracic pedicle screw entry point using a new landmark: a study based on 3-dimensional computed tomographic scan. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 39(16):E980–E988
Berry E, Cuppone M, Porada S, Millner PA, Rao A, Chiverton N, Seedhom BB (2005) Personalised image-based templates for intra-operative guidance. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 219(2):111–118
Acknowledgements
We give special thanks to the technical support of Electromechanical Engineering College, Beijing University of Technology. We also thank Drs. Zhi B Lv, Tao Cui and other members of Department of Radiology, Beijing Ditan Hospital Capital Medical University for their excellent support in supplying CT image material.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no funding or conflicts of interest to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, K., Zhang, Q., Li, X. et al. Preliminary application of a multi-level 3D printing drill guide template for pedicle screw placement in severe and rigid scoliosis. Eur Spine J 26, 1684–1689 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4926-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-016-4926-1