Abstract
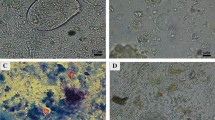
Laboratory animals, especially mice and rats, are commonly used in biomedical researches. This study was designed to evaluate the status of gastrointestinal parasites in Wistar rats using parasitological methods. Sixty Wistar rats in different ages which were being maintained conventionally were selected randomly from laboratory animal house. The contents of the gastrointestinal tract of the rats were examined by parasitological methods. All of the rats under study were infected with at least one parasite. Twelve genera of parasites were detected in the rats, the six of which were protozoa including Giardia muris, Entamoeba muris, Blastocystis spp., Eimeria spp., Tritrichomonas muris, and Cryptosporidium spp., and the six other ones were helminths including Hymenolepis nana, Syphacia muris, Syphacia obvelata, Strongyloides ratti, Trichosomoides crassicauda (bladder parasite), and Aspiculuris tetraptera. G. muris showed the highest prevalence rate (96%) followed by T. muris (95%). In addition, the lowest prevalence rate observed in this study was related to S. obvelata, S. ratti, T. crassicauda, and A. tetraptera, all with 1.5% prevalence. Consequently, it is crucial for researchers to monitor laboratory animals by health surveillance programs, essentially emphasizing the good laboratory practice (GLP) to ensure the quality, consistency, and reproducibility of data in their research.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker DG (1998) Natural pathogens of laboratory mice, rats, and rabbits and their effects on research. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:231–266
Bicalho KA, Araujo FTM, Rocha R, Carvalho ODS (2007) Sanitary profile in mice and rat colonies in laboratory animal houses in Minas Gerais: endo and ectoparasites. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 59:1478–1484
Casebolt D, Lindsey J, Cassell G (1988) Prevalence rates of infectious agents among commercial breeding populations of rats and mice. Lab Anim Sci 38:327–329
Chen XQ, Singh M, Ho LC, Moe KT, Tan SW, Yap EH (1997) A survey of Blastocystis sp. in rodents. Lab Anim Sci 47:91–94
Clark PR, Ward WT, Lang SA, Saghbini A, Kristan DM (2013) Order of inoculation during Heligmosomoides bakeri and Hymenolepis microstoma coinfection alters parasite life history and host responses. PathoGenetics 2:130–152
Daniels C, Belosevic M (1992) Disaccharidase activity in the small intestine of susceptible and resistant mice after primary and challenge infections with Giardia muris. Am J Trop Med Hyg 46:382–390
Daniels C, Belosevic M (1995) Disaccharidase activity in male and female C57BL/6 mice infected with Giardia muris. Parasitol Res 81:143–147
De Carneri I, Trane F, Mandelli V (1977) Giardia muris: oral infection with one trophozoite and generation time in mice. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 71:438
Duda A, Kosik-Bogacka D, Lanocha N, Szymanski S (2013) Blastocystis hominis-parasites or commensals? Ann Acad Med Stetin 1:23–28
Easterbrook JD, Kaplan J, Glass G, Watson J, Klein S (2008) A survey of rodent-borne pathogens carried by wild-caught Norway rats: a potential threat to laboratory rodent colonies. Lab Anim 42:92–98
Feng Y, Xiao L (2011) Zoonotic potential and molecular epidemiology of Giardia species and giardiasis. Clin Microbiol Rev 24:110–140
Gilioli R, Andrade L, Passos L, Silva F, Rodrigues D, Guaraldo A (2000) Parasite survey in mouse and rat colonies of Brazilian laboratory animal houses kept under different sanitary barrier conditions. Arq Bras Med Vet Zootec 52:33–37
Kalani H, Fakhar M, Sharif M, Faridnia R (2013) Survey on intestinal parasites in Swiss Webster mice. J Mazand Univ Med Sci 23:64–69
Harter S (2003) Implication de la Paléoparasitologie dans l'étude des populations anciennes de la vallée du Nil et de proche-orient: étude de cas. PhD dissertation Université de Reims-Champagne Ardenne
Held N, Hedrich H, Bleich A (2011) Successful sanitation of an EDIM-infected mouse colony by breeding cessation. Lab Anim 45:276–279
Hosseinzadeh S, Jamshidian Ghalesefidi M, Azami M, Mohaghegh MA, Hejazi SH, Ghomashlooyan M (2016) In vitro and in vivo anthelmintic activity of seed extract of Coriandrum sativum compared to Niclosamid against Hymenolepis nana infection. J Parasit Dis 40:1307–1310
Huq MMKM, Sheikh H (1985) Helminth parasites of rats, house mouse and moles in Bangladesh Pakistan. Vet J 5:143–144
Katsumata T, Hosea D, Ranuh IG, Uga S, Yanagi T, Kohno S (2000) Short report: possible Cryptosporidium muris infection in humans. Am J Trop Med Hyg 62:70–72
Lee LI, Chye TT, Karmacharya BM, Govind SK (2012) Blastocystis sp.: waterborne zoonotic organism, a possibility? Parasit Vectors 5:130
Lipman NS, Lampen N, Nguyen HT (1999) Identification of pseudocysts of Trichomonas muris in Armenian hamsters and their transmission to mice. Lab Anim Sci 49:313–315
Lv C, Zhang L, Wang R, Jian F, Zhang S, Ning C, Wang H, Feng C, Wang X, Ren X, Qi M, Xiao L (2009) Cryptosporidium spp. in wild, laboratory, and pet rodents in China: prevalence and molecular characterization. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7692–7699
Mohaghegh MA, Jafari R, Ghomashlooyan M, Mirzaei F, Azami M, Falahati M, Salehi F (2015) Soil contamination with oocysts of Cryptosporidium spp. in Isfahan, Central Iran. Int J Enteric Pathol 3:e29105
Mohaghegh MA, Hejazi SH, Ghomashlooyan M, Kalani H, Mirzaei F, Azami M (2017) Prevalence and clinical features of Cryptosporidium infection in hemodialysis patients. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench 10:137-142
Mohebali M, Zarei Z, Khanaliha K, Kia EB, Motavalli-Haghi A, Davoodi J, Rezaeian T, Tarighi F, Rezaeian M (2017) Natural intestinal protozoa in rodents (Rodentia: Gerbillinae, Murinae, Cricetinae) in Northwestern Iran. Iran J Parasitol 12:382–388
Motamedi G, Moharami M, Paykari H (2014) A survey on the gastrointestinal parasites of rabbit and Guinea pig in a laboratory animal house. Arch Razi Ins 69:77–81
Ozkul IA, Aydin Y (1994) Natural Cryptosporidium muris infection of the stomach in laboratory mice. Vet Parasitol 55:129–132
Parkinson CM, O’Brien A, Albers TM, Simon MA, Clifford CB, Pritchett-Corning KR (2011) Diagnosis of ecto- and endoparasites in laboratory rats and mice. J Vis Exp 2011:e2767
Perec-Matysiak A, Okulewicz A, Hildebrand J, Zalesny G (2006) Helminth parasites of laboratory mice and rats. Wiad Parazytol 52:99–102
Palmer CJ, Xiao L, Terashima A, Guerra H, Gotuzzo E, Saldías G, Bonilla JA, Zhou L, Lindquist A, Upton SJ (2003) Cryptosporidium muris, a rodent pathogen, recovered from a human in Peru. Emerg Infect Dis 9:1174–1176
Roberts-Thomson IC (1993) Genetic studies of human and murine giardiasis. Clin Infect Dis 16:S98–S104
Souza MVD, Sianto L, Chame M, Ferreira LF, Araujo A (2012) Syphacia sp.(Nematoda: Oxyuridae) in coprolites of Kerodon rupestris Wied, 1820 (Rodentia: Caviidae) from 5,300 years BP in northeastern Brazil. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 107:539–542
Stone WB, Manwell RD (1966) Potential helminth infections in humans from pet or laboratory mice and hamsters. Public Health Rep 81:647–653
Tan KS, Mirza H, Teo JD, Wu B, MacAry PA (2010) Current views on the clinical relevance of Blastocystis spp. Curr Infect Dis Rep 12:28–35
Taylor M, Marshall R, Green J, Catchpole J (1999) The pathogenesis of experimental infections of Cryptosporidium muris (strain RN 66) in outbred nude mice. Vet Parasitol 86:41–48
Thompson RC (2004) The zoonotic significance and molecular epidemiology of Giardia and giardiasis. Vet Parasitol 126:15–35
Thompson RA (2015) Neglected zoonotic helminths: Hymenolepis nana, Echinococcus canadensis and Ancylostoma ceylanicum. Clin Microbiol Infect 21:426–432
Treuting PM, Clifford CB, Sellers RS, Brayton CF (2012) Of mice and microflora: considerations for genetically ngineered mice. Vet Pathol 49:44–63
WA R (1919) A mouse oxyurid, Syphacia obvelata, as a parasite of man. J Parasitol 6:89–93
Wawrzyniak I, Poirier P, Viscogliosi E, Dionigia M, Texier C, Delbac F, El Alaoui H (2013) Blastocystis, an unrecognized parasite: an overview of pathogenesis and diagnosis. Ther Adv Infect Dis 1:167–178
Weigler BJ, Di Giacomo RF, Alexander S (2005) A national survey of laboratory animal workers concerning occupational risks for zoonotic diseases. Comp Med 55:183–191
Zenner L (1998) Effective eradication of pinworms (Syphacia muris, Syphacia obvelata and Aspiculuris tetraptera) from a rodent breeding colony by oral anthelmintic therapy. Lab Anim 32:337–342
Acknowledgments
We thank the Department of Parasitology and Mycology, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human subjects. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the studies were conducted.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohaghegh, M.A., Kalani, H., Azami, M. et al. Gastrointestinal parasitic infection in laboratory rats: a challenge for researchers. Comp Clin Pathol 27, 1237–1240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2727-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2727-0