Abstract
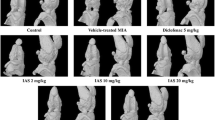
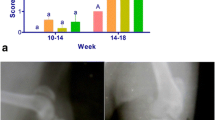
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a worldwide joint disease with clinically loss of motion and pain in human. The conventional treatments are associated with essential side effects. In folk medicine, Shilajit is applied for treatment of arthritis and bone fractures. The present study evaluated effect of Shilajit on the osteoarthritis in rat model. Thirty-six adult male rats were randomly divided into two groups including OA and treated with Shilajit groups. OA was induced by injection of monosodium iodoacetate in the articular space of femorotibial joint. Aqueous extract of Shilajit was given to the treatment group by gavage as daily during experimental course until 21 days. The joint samples were investigated 7, 14, and 21 days post induction. The main macroscopic changes in the affected joints were swelling and congestion at early stages. Histopathologic study showed surface irregularity, erosion and fissures, necrotic chondrocytes, depletion of toluidine blue staining, and lysis of subchondral bone in both OA and Shilajit groups after 7 and 14 days. Synovium revealed synovial cells hyperplasia and inflammatory cells infiltration. Moderate to advanced OA was seen in both groups without significant difference. After 21 days, histopathologic scores of destructive damages and synovitis were reduced in the Shilajit group and showed significant difference in compare to OA group. The present study shows that aqueous extract of Shilajit decreased cartilage degenerative changes in knee osteoarthritis. Also, it reduced inflammatory reactions in synovial membrane.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abshenas J, Kheirandish R, Salary AR (2014) Gastroprotective effect of mummy on induced gastric ulcer in rats. Comp Clin Pathol 23(2):305–309
Acharya SB, Frotan MH, Goel RK, Tripathi SK, Das PK (1988) Pharmacological actions of Shilajit. Indian J Exp Biol 26:775–777
Adatia A, Rainsford KD, Kean WF (2012) Osteoarthritis of the knee and hip. Part I: aetiology and pathogenesis as a basis for pharmacotherapy. J Pharm Pharmacol 64(5):617–625
Aeschbacher M, Graf C, Schwarzenbach RP, Sander M (2012) Antioxidant properties of humic substances. Environ Sci Technol 46(9):4916–4925
Agarwal SP, Khanna R, Karmarkar R, Anwer MK, Khar RK (2007) Shilajit: a review. Phytother Res 21:401–405
Bhattacharya SK, Sen A (1995) Effects of Shilajit on biogenic free radicals. Phytother Res 9:56–59
Carrasco-Gallardo C, Farıas GA, Fuentes P, Crespo F, Maccionia RB (2012) Can nutraceuticals prevent Alzheimer’s disease? Potential therapeutic role of a formulation containing Shilajit and complex B vitamins. Arch Med Res 43:699–704
Cheng DS, Visco CJ (2012) Pharmaceutical therapy for osteoarthritis. PM R 4:S82–S88
Cornejo A, Jimenez JM, Caballero L, Melo F, Maccioni RB (2011) Fulvic acid inhibits aggregation and promotes disassembly of tau fibrils associated with Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 27:143–153
Cournil C, Liagre B, Grosin L, Vol C, Abid A (2001) Overexpression and induction of heat shock protein (Hsp) 70 protects in vitro and in vivo from mono-iodoacetate (MIA)-induced chondrocytes death. Arthritis Res 3(Suppl 1):P41
Dehghan M, Sharifi Faradonbeh A (2012) The effect of mummy on the healing of bone fractures. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol 6(5):305–309
Di Paola R, Cuzzocrea S (2008) Autoimmunity of animal model of arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 8:73–75
Franceschi RT, Wilson JX, Dixon SJ (1995) Requirement for Na (+)-dependent ascorbic acid transport in osteoblast function. Am J Phys 268:C1430–C1439
Frolova LN, Kiseleva TL (1996) Chemical composition of mumie and methods for determination of its authenticity and quality. Chem Pharm J 8:49–53
Gaikwad NS, Panat AV, Deshpande MS, Ramya K, Khalid PU, Augustine P (2012) Effect of shilajit on the heart of Daphnia: a preliminary study. J Ayurveda Integr Med 3(1):3–5
Ghosal S, Lal J, Singh SK, Goel RK, Jaiswal AK, Bhattacharya SK (1991) The need for formulation of Shilajit by its isolated active constituents. Phytother Res 5:211–216
Ghosal S, Baumik S, Chattopadhyay S (1995) Shilajit induced morphometric and functional changes in mouse peritoneal macrophages. Phytother Res 9:194–198
Goel RK, Banerjee RS, Acharya SB (1990) Antiulcerogenic and anti-inflammatory studies with Shilajit. J Ethnopharmacol 29:95–103
Goldring MB, Otero M (2011) Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23(5):471–478
Guzman RE, Evans MG, Bove S, Morenko B, Kilgore K (2003) Mono-iodoacetate-induced histologic changes in subchondral bone and articular cartilage of rat femorotibial joints: an animal model of osteoarthritis. Toxicol Pathol 31:619–624
Hinton R, Moody RL, Davis AW, Thomas SF (2002) Osteoarthritis: diagnosis and therapeutic considerations. Am Fam Physician 65:841–848
Iannone F, Lapadula G (2010) Obesity and inflammation-targets for OA therapy. Curr Drug Targets 11(5):586–598
Ismailova VN (1965) To a question about the dosage of mumie and special features of the healing of the fractures of the bones during its application. Med J Uzbekistan 9:69–70
Jaiswal N, Haynesworth SE, Caplan AI, Bruder SP (1997) Osteogenic differentiation of purified, culture expanded human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. J Cell Biochem 64:295–312
Joone GK, van Rensburg CEJ (2004) An in vitro investigation of the anti-inflammatory properties of potassium humate. Inflammation 28(3):169–117
Junec R, Morrow R, Schoenherr JI, Schubert R, Kallmeyer R, Phull S, Klöcking R (2009) Bimodal effect of humic acids on the LPS-induced TNF-α release from differentiated U937 cells. Phytomedicine 16(5):470–476
Jung CR, Schepetkin IA, Woo SB, Khlebnikov AI, Kwon BS (2002) Osteoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by mumie extract. Drug Develop Res 57:122–133
Kelginbaev NS, Sorokina VA, Stefanidu AG, Ismailova VN (1973) Treatment of long tubular bone fractures with mumie asil preparations in experiments and clinical conditions. Exp Surg Anesthes 4:31–35
Kobayashi K, Imaizumi R, Sumichika H, Tanaka H, Goda M, Fukunari A, Komatsu H (2003) Sodium iodoacetate-induced experimental osteoarthritis and associated pain model in rats. J Vet Med Sci 65:1195–1199
Korago AA. (1992). Introduction in biominerology. Nauka St. Petersburg. p 280
Krenn V, Morawietz L, Häupl T, Neidel J, Petersen I, König A (2002) Grading of chronic synovitis—a histopathological grading system for molecular and diagnostic pathology. Pathol Res Pract 198(5):317–325
Kučerík J, Bakajová B, Pekař M (2008) Antioxidant effect of lignite humic acids and its salts on the thermo-oxidative stability/degradation of polyvinyl alcohol blends. Environ Chem Lett 6(4):241–245
Labban NY (2013) Shilajit, a novel regulator of bone/cartilage healing. Submitted to the faculty of the University Graduate School in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree. Doctor of Philosophy in the School of Dentistry, Indiana University
Le Graverand-Gastineau MP (2010) Disease modifying osteoarthritis drugs: facing development challenges and choosing molecular targets. Curr Drug Targets 11:528–535
Maccioni RB, Farías GA, Rojo LE, Jiménez JM (2012) In search of therapeutic solutions for Alzheimer’s disease. In: Mantamadiotis T (ed) Brain WTGW-DaDotH, pp 125–150
Mankin HJ, Dorfman H, Lippiello L, Zarins A (1971) Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteoarthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J Bone Joint Surg 53(3):523–537
Naveen SV, Ahmad RE, Hui WJ, Suhaeb AM, Murali MR, Shanmugam R, Kamarul T (2014) Histology, glycosaminoglycan level and cartilage stiffness in monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis: comparative analysis with anterior cruciate ligament transection in rat model and human osteoarthritis. Int J Med Sci 11(1):97–105
Neogi T (2013) The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 21(9):1145–1153
Patrignani P, Tacconelli S, Bruno A, Sostres C, Lanas A (2011) Managing the adverse effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Exp Rev Clin Pharm 4:605–621
Qutob S, Dixon SJ, Wilson JX (1998) Insulin stimulates vitamin C recycling and ascorbate accumulation in osteoblastic cells. Endocrinol 139:51–56
Rege AAA, Chowdhary AS (2014) Evaluation of Shilajit as putative HIV-protease inhibitor. Intern J Adv Res 2:154–157
Rosenberg A (2002) Bones, joints, soft tissue tumors. In: Cotran R, Kuman V, Collins T (eds) Pathologic basis of disease. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1215–1268
Schepetkin I, Khlebnikov A, Kwon BS (2002) Medical drugs from humus matter: focus on mumie. Drug Dev Res 57:140–159
Schepetkin IA, Khlebnikov AI, Ah SY, Woo SB, Jeong CS, Klubachuk ON, Kwon BS (2003) Characterization and biological activities of humic substances from mumie. J Agric Food Chem 51(18):5245–5254
Tripathi YB, Shukla S, Chaurasia S (1996) Antilipid peroxidative property of Shilajit. Phytother Res 10:269–270
van Rensburg CE, Naude PJ (2009) Potassium humate inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines and complement activation in vitro. Inflammation 32(4):270–276
Vašková J, Veliká B, Pilátová M, Kron I, Vaško L, Vaško L (2011) Effects of humic acid in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 47:376–382
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank from Mr. Saeed Hassanzadeh for providing tissue sections.
Funding
This study was funded by grant number (AZ-91-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All animals received human care in compliance with the Guide for Care and use of Laboratory. Animals published by the National Institutes of Health (NIH publication No. 85-23, revised 1985). The study was approved by the local ethics committee of our veterinary school.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azizi, S., Kheirandiah, R., Azari, O. et al. Potential pharmaceutic effect of Shilajit (mumie) on experimental osteoarthritis in rat. Comp Clin Pathol 27, 755–764 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2662-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-018-2662-0