Abstract
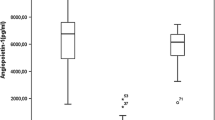
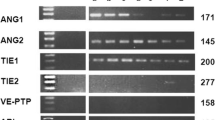
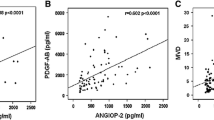
The angiogenic-related factors, angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 and their receptor Tie-2, have wide-ranging effects on tumor behavior that includes angiogenesis and inflammation. These multifaceted pathways present a potential target in developing novel inhibition strategies for cancer therapy. The present work aimed at detecting the prevalence of expression of angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, and their receptor Tie-2 in 56 Egyptian de novo acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients by conventional RT-PCR to verify the prognostic impact of their expression on the response to induction chemotherapy. Thirty age- and sex-matched healthy volunteers were subjected to the same analysis as a control group. High expression of Ang-1 was detected in the patient group but not the control group. AML patients expressing Ang-2 either solely or in combination with high Ang-1 and/or Tie-2 showed unfavorable response to induction chemotherapy, either failed induction or death during induction. These data provide evidence that the alternation of angiopoietin balance in favor of Ang-2 may play a critical role in the pathophysiology of AML. Furthermore, positive pre-therapeutic expression of Ang-2 indicates viable unfavorable prognostic marker in AML patients and may be used as a prognostic tool in the risk-adaptive management of AML.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacher U, Kern W, Schoch C et al (2006) Evaluation of complete disease remission in acute myeloid leukemia: a prospective study based on cytomorphology, interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization, and immunophenotyping during follow-up in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer 106(4):839–847
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT et al (1985) Proposed revised criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia. A report of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med 103(4):620–625
Cassileth PA, Lynch E, Hines JD et al (1992) Varying intensity of postremission therapy in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 79(8):1924–1930
de Bont ES, Rosati S, Jacobs S et al (2001) Increased bone marrow vascularization in patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: a possible role for vascular endothelial growth factor. Br J Haematol 113:296–304
De Greef G, Van W, Boogarts M (2005) criteria for defining a complete remission in acute myeloid leukemia. Br J Haematol 128(2):184
Dong D, Ni M, Li J et al (2008) Critical role of the stress chaperone GRP78/BiP in tumor proliferation, survival, and tumor angiogenesis in transgene-induced mammary tumor development. Cancer Res 68(2):498–505
Ferrara N, Alitalo K (1999) Clinical applications of angiogenic growth factors and their inhibitors. Nat Med 5(12):1359–1364
Fiedler U, Augustin HG (2006) Angiopoietins: a link between angiogenesis and inflammation. Trends Immunol 27(12):552–558
Giles FJ (2001) The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling pathway: a therapeutic target in patients with hematologic malignancies. Oncologist 6(Suppl 5):32–39
Goldstone AH, Burnett AK, Wheatley K et al (2001) Attempts to improve treatment outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in older patients: the results of the United Kingdom Medical Research Council AML11 trial. Blood 98(5):1302–1311
Grosicki S, Grosicka A, Hołowiecki J (2007) Clinical importance of angiogenesis and angiogenic factors in oncohematology. Wiad Lek 60(1–2):39–46
Hatfield KJ, Hovland R, Øyan AM et al (2008) Release of angiopoietin-1 by primary human acute myelogenous leukemia cells is associated with mutations of nucleophosmin, increased by bone marrow stromal cells and possibly antagonized by high systemic angiopoietin-2 levels. Leukemia 22(2):287–293
Hou HA, Choua WC, Lin LI et al (2008) Expression of angiopoietins and vascular endothelial growth factors and their clinical significance in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res 32:904–912
Kümpers P, Koenecke C, Hecker H et al (2008) Angiopoietin-2 predicts disease-free survival after allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with high-risk myeloid malignancies. Blood 112(5):2139–2148
Lee KW, Lip GY, Blann AD (2004) Plasma angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, angiopoietin receptor tie-2, and vascular endothelial growth factor levels in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 110(16):2355–2360
Lee CY, Tien HF, Hu CY et al (2007) Marrow angiogenesis-associated factors as prognostic biomarkers in patients with acute myelogenous leukaemia. Br J Cancer 97(7):877–882
Licht JD, Chomienne C, Goy A et al (1995) Clinical and molecular characterization of a rare syndrome of acute promyelocytic leukemia associated with translocation (11;17). Blood 85(4):1083–1094
Loges S, Heil G, Bruweleit M et al (2005) Analysis of concerted expression of angiogenic growth factors in acute myeloid leukemia: expression of angiopoietin-2 represents an independent prognostic factor for overall survival. J Clin Oncol 23(6):1109–1117
MacCallum PK, Rohatiner AZ, Davis CL et al (1995) Mitoxantrone and cytosine arabinoside as treatment for acute myeloblastic leukemia in older patients. Ann Hematol 71(1):35–39
Muller A, Lange K, Gaiser T et al (2002) Expression of angiopoietin-1 and its receptor TEK in hematopoietic cells from patients with myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res 26:163–168
Sampath D, Cortes J, Estrov Z et al (2006) Pharmacodynamics of cytarabine alone and in combination with 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01) in AML blasts in vitro and during a clinical trial. Blood 107(6):2517–2524
Schliemann C, Bieker R, Padro T et al (2006) Expression of angiopoietins and their receptor Tie2 in the bone marrow of patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica 91(9):1203–1211
Schliemann C, Bieker R, Thoennissen N et al (2007) Circulating angiopoietin-2 is a strong prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 21(9):1901–1906
Shim WS, Ho IA, Wong PE (2007) Angiopoietin: a TIE(d) balance in tumor angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res 5(7):655–665
Stone RM, Berg DT, George SL et al (2001) Postremission therapy in older patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: a randomized trial comparing mitoxantrone and intermediate-dose cytarabine with standard-dose cytarabine. Blood 98(3):548–553
Teng CL, Young JH, Hsu SL et al (2006) Lactate dehydrogenase, not vascular endothelial growth factor or basic fibroblast growth factor, positively correlates to bone marrow vascularity in acute myeloid leukemia. J Chin Med Assoc 69(11):534–537
Verstovsek S, Kantarjian H, Manshouri T et al (2002) Prognostic significance of cellular vascular endothelial growth factor expression in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 99:2265–2267
Wakabayashi M, Miwa H, Shikami M et al (2004) Autocrine pathway of angiopoietins-Tie2 system in AML cells; association with phosphatidyl-inositol 3 kinase. Hematol J 5:353–360
Watarai M, Miwa H, Shikami M et al (2002) Expression of endothelial cell-associated molecules in AML cells. Leukemia 16:112–119
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El Karaksy, S.M., El Guindy, N.M., Gouda, H.M. et al. Clinical relevance of angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, and their receptor Tie-2 expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Comp Clin Pathol 20, 341–347 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-010-1000-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00580-010-1000-y