Abstract
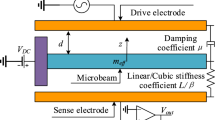
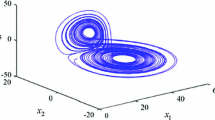
In this paper, a fuzzy stability control algorithm based on the type-2 sequential fuzzy neural network (T2SFNN) is proposed to suppress the chaotic motion of the MEMS resonator. The dynamical behaviors of the MEMS resonator are revealed by the bifurcation diagram, exponent diagram, phase diagram and corresponding time history. In the process of the controller design for backstepping control, the T2SFNN is used to tackle the unknown external disturbance and eliminate the effect of time delay, along with the cosine function to ensure that the output constraint is not violated. In addition, an absorber is employed to avoid the repeated derivative associated with the backstepping. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed scheme is verified by numerical simulation.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora R, Agarwal D, Bera TK (2019) Workspace analysis and trajectory tracking of a planar hybrid manipulator with ball screw feed drive. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41(9):378
Fossi DOT, Woafo P (2013) Generation of complex phenomena in a simple electromechanical system using the feedback control. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18(1):209–218
Hajjam A, Pourkamali S (2011) Fabrication and characterization of MEMS-based resonant organic gas sensors. IEEE Sens J 12(6):1958–1964
He S, Sun K, Mei X, Yan B, Xu S (2017) Numerical analysis of a fractional-order chaotic system based on conformable fractional-order derivative. Eur Phys J Plus 132(1):36
Liu YJ, Gao Y, Tong S et al (2016) Fuzzy approximation-based adaptive backstepping optimal control for a class of nonlinear discrete-time systems with dead-zone. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 24(1):16–28
Liu H, Pan Y, Li S et al (2017) Adaptive fuzzy backstepping control of fractional-order nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 47(8):2209–2217
Luo S, Song Y (2016) Chaos analysis-based adaptive backstepping control of the microelectromechanical resonators with constrained output and uncertain time delay. IEEE Trans Ind Electron 63(10):6217–6225
Luo S, Wang J, Wu S et al (2014) Chaos RBF dynamics surface control of brushless DC motor with time delay based on tangent barrier Lyapunov function. Nonlinear Dyn 78(2):1193–1204
Luo S, Lewis FL, Song Y, Vamvoudakis KG (2020a) Adaptive backstepping optimal control of a fractional-order chaotic magnetic-field electromechanical transducer. Nonlinear Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05518-5
Luo S, Lewis Frank L, Song Y, Hassen M (2020b) Accelerated adaptive fuzzy optimal control of three coupled fractional-order chaotic electromechanical transduces. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst. https://doi.org/10.1109/tfuzz.2020.2984998
Miandoab EM, Yousefi-Koma A, Pishkenari HN et al (2015) Study of nonlinear dynamics and chaos in MEMS/NEMS resonators. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 22(1–3):611–622
Mohammadzadeh A, Ghaemi S (2018) Robust synchronization of uncertain fraction-order chaotic systems with time-varying delay. Nonlinear Dyn 93:1809–1821
Niu B, Zhao J (2013) Barrier Lyapunov functions for the output tracking control of constrained nonlinear switched systems. Syst Control Lett 62(10):963–971
Park K, Chen Q, Lai YC (2008) Energy enhancement and chaos control in microelectromechanical systems. Phys Rev E 77(2):026210
Seleim A, Towfighian S, Delande E et al (2012) Dynamics of a close-loop controlled MEMS resonator. Nonlinear Dyn 69(1–2):615–633
Sharma M, Sarraf EH, Baskaran R et al (2012) Parametric resonance: amplification and damping in MEMS gyroscopes. Sens Actuators, A 177:79–86
Su Z, Li Y, Yang G, et al (2020) Dietary composition perception algorithm using social robot audition for Mandarin Chinese. In: IEEE Access, pp 8768–8782
Sun J, Liu C (2018) Distributed fuzzy adaptive backstepping optimal control for nonlinear multimissile guidance systems with input saturation. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 27(3):447–461
Tajaddodianfar F, Pishkenari HN, Yazdi MRH et al (2015) On the dynamics of bistable micro/nano resonators: analytical solution and nonlinear behavior. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 20(3):1078–1089
Tajaddodianfar F, Yazdi MRH, Pishkenari HN (2017) Nonlinear dynamics of MEMS/NEMS resonators: analytical solution by the homotopy analysis method. Microsyst Technol 23(6):1913–1926
Tee KP, Ge SS, Tay EH (2009) Barrier Lyapunov functions for the control of output-constrained nonlinear systems. Automatica 45(4):918–927
Timurdogan E, Alaca BE, Kavakli IH et al (2011) MEMS biosensorfor detection of Hepatitis A and C viruses in serum. Biosens Bioelectron 28(1):189–194
Yau HT, Wang CC, Hsieh CT et al (2011) Nonlinear analysis and control of the uncertain micro-electro-mechanical system by using a fuzzy sliding mode control design. Comput Math Appl 61(8):1912–1916
Yin SH, Epureanu BI (2007) Experimental enhanced nonlinear dynamics and identification of attractor morphing modes for damage detection. J Vib Acoust 129(6):763–770
Younis MI, Nayfeh AH (2003) A Study of the nonlinear response of a resonant microbeam to an electric actuation. Nonlinear Dyn 31(1):91–117
Younis MI, Ouakad HM, Alsaleem FM et al (2010) Nonlinear dynamics of MEMS arches under harmonic electrostatic actuation. J Microelectromech Syst 19(3):647–656
Zhankui S, Sun K (2013) Nonlinear and chaos control of a micro-electro-mechanical system by using second-order fast terminal sliding mode control. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 18(9):2540–2548
Acknowledgments
This work is funded by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guizhou Province (Nos. [2020]1Y274 and [2018]5781), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61863005) and Science and Technology Foundation of Guizhou Province (Nos. [2018]5702, [2020]6007, QKHZC [2019] 2814 and [2020]4Y056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Luo, S., Yang, G. et al. Chaos analysis and stability control of the MEMS resonator via the type-2 sequential FNN. Microsyst Technol 27, 173–182 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-04935-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00542-020-04935-1