Abstract
Background
This study compared proximal and distal approaches of intercostobrachial nerve block (ICBNB) combined with infraclavicular brachial plexus block (ICBPB) during superficialization of arteriovenous fistula.
Methods
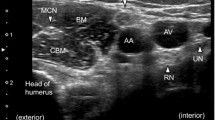
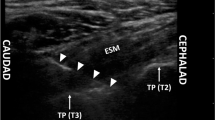
Seventy adult patients were randomized to receive ICBPB and 6 ml 0.25% bupivacaine at the level of the 3rd rib in the anterior axillary line between pectoralis minor and serratus anterior muscles (group P) or subcutaneously along the medial side of the upper arm (group D). The primary outcome was the achievement of complete sensory block. Secondary outcomes were onset of analgesia, volume of local anesthetic (LA) supplementation, fentanyl administration, success rate, and conversion to general anesthesia (GA).
Results
Complete sensory block in the medial side of the upper arm was achieved in 91% of patients in group P and 51% in group D. Failure rate of ICBNB was higher in group D (49%) than group P (14%). Conversion to GA was determined by the attending anesthesiologist in 26% of patients in group D and 0% in group P. LA supplementation was required in 5 patients in group P and 11 patients in group D, and the mean volume of LA was statistically higher in group D than group P (9.5 ± 1.5, 7.5 ± 2 ml, respectively). Onset of sensory block was faster in group P than group D (8.75 ± 1.67 and 10 ± 2.14 min, respectively). No differences were observed regarding fentanyl administration.
Conclusion
ICBNB proximal approach provides a high success rate with less amount of rescue analgesia compared to the distal approach.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loukas M, Hullett J, Louis RG Jr, Holdman S, Holdman D. The gross anatomy of the extrathoracic course of the intercostobrachial nerve. Clin Anat. 2006;19(2):106–11.
Roussel J, Thirkannad S. Comparison of 3 ultrasound-guided brachial plexus block approaches for cubital tunnel release surgery in 120 ambulatory patients. AANA J. 2014;82:121–6.
Sidawy AN, Gray R, Besarab A, Henry M, Ascher E, Silva M Jr, Miller A, Scher L, Trerotola S, Gregory RT, Rutherford RB, Kent KC. Recommended standards for reports dealing with arteriovenous hemodialysis accesses. J Vasc Surg. 2002;35:603–10.
Henry B, Graves MJ, Pękala JR, Sanna B, Hsieh WC, Tubbs RS, Walocha JA, Tomaszewski KA. Origin, branching, and communications of the intercostobrachial nerve: a meta-analysis with implications for mastectomy and axillary lymph node dissection in breast cancer. Cureus. 2017;9(3):e1101. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.1101.
Sandhu NS, Capan LM. Ultrasound guided infraclavicular brachial plexus block. Br J Anaesth. 2002;89(2):254–9.
Neal J. Cutaneous blocks for the upper extremity. In: Hadzic A, editor. Textbook of regional anesthesia and acute pain management. New York: McGraw-Hill; 2010. pp. 467–75.
Desgagnés MC, Lévesque S, Dion N, Nadeau MJ, Coté D, Brassard J, Nicole PC, Turgeon AF. A comparison of a single or triple injection technique for ultrasound-guided infraclavicular block: a prospective randomized controlled study. Anesth Analg. 2009;109(2):668–72.
O’Rourke MGE, Tang TS, Allison SI, Wood W. The anatomy of the extrathoracic intercostobrachial nerve. Aust N Z J Surg. 1999;69:860–4.
Loukas M, Hullett J, Louis RG, Holdman S, Holdman D. The gross anatomy of the extrathoracic course of the intercostobrachial nerve. Clin Anat. 2006;19:106–11.
Purcell N, Wu D. Novel use of the Pecs II block for upper limb fistula surgery. Anaesthesia. 2014;69:1294.
Seidel R, Gray AT, Wree A, Schulze M. Surgery of the axilla with combined brachial plexus and intercostobrachial nerve block in the subpectoral intercostal plane. Br J Anaesth. 2017;118:472–4.
Wijayasinghe N, Duriaud HM, Kehlet H, Andersen KG. Ultrasound guided intercostobrachial nerve blockade in patients with persistent pain after breast cancer surgery: a pilot study. Pain Physician. 2016;19(2):E309–18.
Hara K. Ultrasound guided intercostobrachial nerve block with ultrasound guided axillary brachial plexus block: a preliminary study. ESRA Acad. 2012;6:22047.
Magazzeni P, Jochum D, Iohom G, Mekler G, Albuisson E, Bouaziz H. Ultrasound-guided selective versus conventional block of the medial brachial cutaneous and the intercostobrachial nerves: a randomized clinical trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1097/AAP.0000000000000823 (Epub ahead of print).
MacIver MB, Tanelian DL. Activation of C fibers by metabolic perturbations associated with tourniquet ischemia. Anesthesiology. 1992;76:617–23.
Maria PS, Aitziber E, Pilar P, Zuriñe L, Ane A, Rafael M. Tourniquet pain after ultrasound-guided axillary blockade. J Anest Inten Care Med. 2017;3(5):555624. https://doi.org/10.19080/JAICM.2017.03.555624.
Wisotzky EM, Saini V, Kao C. Ultrasound guided intercostobrachial nerve block for intercostobrachial neuralgia in breast cancer patients: a case series. PM&R. 2016;8(3):273–7.
Roussel J, Thirkannad S. Comparison of 3 ultrasound-guided brachial plexus block approaches for cubital tunnel release surgery in 120 ambulatory patients. AANA J. 2014;82(2):121–6.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Moustafa A. Moustafa: this author helped conduct the study, collect data, and write the manuscript. Alaa A. Kandeel: this author helped conduct the study and collect data, and approved the final draft of the manuscript.
About this article
Cite this article
Moustafa, M.A., Kandeel, A.A. Randomized comparative study between two different techniques of intercostobrachial nerve block together with brachial plexus block during superficialization of arteriovenous fistula. J Anesth 32, 725–730 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-018-2547-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-018-2547-z