Abstract
Background
Rice extract has been shown to protect gastric mucosa from stress-induced damage. In this study, the antibiotic effect and the anti-inflammatory effect of orally administered aqueous rice extract on Helicobacter pylori infection and H. pylori-induced gastritis, respectively, in Mongolian gerbils were investigated.
Methods
Fifty specific-pathogen-free male Mongolian gerbils, seven weeks old, were divided into four groups: uninfected, untreated animals (group A); uninfected, rice extract-treated animals (group B); H. pylori-infected, untreated animals (group C); and H. pylori-infected, rice extract-treated animals (group D). Group C and D animals were killed 12 weeks after H. pylori infection (i.e., at 19 weeks of age) and group A and B animals were also killed at age 19 weeks. The stomachs were removed for histopathological examination with hematoxylin-and-eosin staining and anti-5′-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine (BrdU) immunostaining, and to determine the bacterial burden. Serum anti-H. pylori antibody titers were also tested.
Results
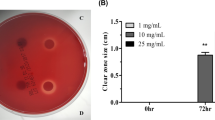
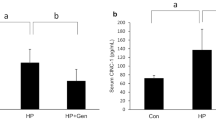
In groups A and B, the gastric mucosa showed no inflammatory cell infiltration and a few BrdU-reactive cells. Group C animals developed marked chronic active gastritis in the gastric mucosa, and BrdU-labeled cells in the gastric mucosa markedly increased in number. In group D animals, a significant reduction occurred in the degree of neutrophilic polymorphonuclear cell infiltration into the gastric mucosa, in the BrdU-labeling indices of gastric epithelial cells, and in anti-H. pylori antibody titers in the serum (P < 0.01), compared with although H. pylori was not completely eradicated.
Conclusions
The rice extract was effective in suppressing inflammation and epithelial cell proliferation in the gastric mucosa in H. pylori-infected Mongolian gerbils. The rice extract has potential to exhibit a protective effect on H. pylori-related gastric mucosal diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murakami, M., Ota, H., Sugiyama, A. et al. Suppressive effect of rice extract on Helicobacter pylori infection in a Mongolian gerbil model. J Gastroenterol 40, 459–466 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-005-1570-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-005-1570-7