Abstract
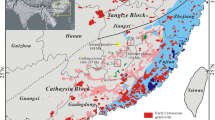
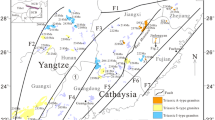
This paper presents precise zircon U–Pb, bulk-rock geochemical, and Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic data for metagabbro, quartz diorite, and granite units within the Tengchong Block of SW China, which forms the southeastern extension of the Himalayan orogeny and the southwestern section of the Sanjiang orogenic belt, a key region for furthering our understanding of the evolution of the eastern Paleo-Tethys. These data reveal four groups of zircon U–Pb ages that range from the late Paleozoic to the early Mesozoic, including a 263.6 ± 3.6 Ma quartz diorite, a 218.5 ± 5.4 Ma two-mica granite, a 205.7 ± 3.1 Ma metagabbroic unit, and a 195.5 ± 2.2 Ma biotite granite. The quartz diorite in this area contains low concentrations of SiO2 (60.71–64.32 wt%), is sodium-rich, and is metaluminous, indicating formation from magmas generated by a mixed source of metamafic rocks with a significant metapelitic sedimentary material within lower arc crust. The two-mica granites contain high concentrations of SiO2 (73.2–74.3 wt%), are strongly peraluminous, and have evolved Sr–Nd–Pb isotopic compositions, all of which are indicative of a crustal source, most probably from the partial melting of felsic pelite and metagreywacke/psammite material. The metagabbros contain low concentrations of SiO2 (50.17–50.96 wt%), are sodium-rich, contain high concentrations of Fe2O3T (9.79–10.06 wt%) and CaO (6.88–7.12 wt%), and are significantly enriched in the Sr (869–894 ppm) and LREE (198.14–464.60 ppm), indicative of derivation from magmas generated by a metasomatized mantle wedge modified by the sedimentary-derived component. The biotite granites are weakly peraluminous and formed from magmas generated by melting of metasedimentary sources dominated by metagreywacke/psammite material. Combining the petrology and geochemistry of these units with the regional geology of the Indosinian orogenic belt provides evidence for two stages of magmatism: an initial stage that generated magmas during partial melting of mantle-derived material associated with late Permian-to-Early Triassic subduction of the Paleo-Tethys, and a second stage that generated granitoid magmas by the partial melting of crustal-derived sources during the Late Triassic collision between the Lhasa and Tengchong blocks and the northern margin of the Australian continent. These rocks, therefore, provide evidence of a systematic late Permian-to-Late Triassic transition from a pre-collision/volcanic arc setting through a collisional setting to a final within-plate phase of magmatism. The previous research involving bulk-rock Sr–Nd analyses of units from the southern Sanjiang orogenic belt and zircon Hf isotopic analyses of units from the Tengchong Block suggests that these areas may record similar magmatic evolutionary trends from mantle- to crustal-derived sources during the evolution of the eastern Paleo-Tethys.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen T (2002) Correction of common lead in U–Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem Geol 192:59–79
Annel C, Blundy JD, Sparks RSJ (2006) The genesis of intermediate and silicic magmas in deep crustal hot zones[J]. J Petrol 47(3):505–539
Barbarin B (1999) A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments. Lithos 46:605–626
Barbarin B (2005) Mafic magmatic enclaves and mafic rocks associated with some granitoids of the central Sierra Nevada batholith, California: nature, origin, and relations with the hosts. Lithos 80:155–177
Batchelor RA, Bowden P (1985) Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chem Geol 48(85):43–55
Ben Othman D, White WM, Patchett J (1989) The geochemistry of marine sediments, island arc magma genesis, and crust-mantle recycling. Earth Planet Sci Lett 94:1–21
Bonin B (2007) A-type granites and related rocks: evolution of a concept, problems and prospects. Lithos 97:1–29
Brown M (1994) The generation, segregation, ascent and emplacement of granite magma: the migmatite-to-crustally-derived granite connection in thickened orogens. Earth Sci Rev 36:83–130
Castro A (2013) Tonalite–granodiorite suites as cotectic systems: a review of experimental studies with applications to granitoid petrogenesis [J]. Earth Sci Rev 124(9):68–95
Castro A, Gerya T, Garcíacasco A, Fernández C, Díazalvarado J, Morenoventas I, Löw I (2010) Melting relations of MORB-sediment Mélanges in underplated Mantle Wedge Plumes: implications for the origin of cordilleran-type Batholiths. J Petrol 51(6):1267–1295
Chappell BW, White AJR (1974) Two contrasting granite types. Pac Geol 8:173–174
Chappell BW, White AJR (1992) I- and S- type granites in Lachlan Fold Belt. Trans R Soc Edinburgh 83:1–26
Carter A, Roques D, Bristow C (2001) Understanding Mesozoic accretion in southeast Asia: significance of Triassic thermotectonism (Indosinian orogen) in Vietnam. Geology 29(3):211–214
Chen F, Li XH, Wang XL, Li QL, Siebel W (2007) Zircon age and Nd-Hf isotopic composition of the Yunnan Tethyan belt, southwestern China. Int J Earth Sci 96(6):1179–1194
Chen W, Yang T, Zhang S, Yang Z, Li H, Wu H et al (2012) Paleomagnetic results from the early cretaceous zenong group volcanic rocks, cuoqin, tibet, and their paleogeographic implications. Gondwana Res 22(2):461–469
Chen YL, Zhang KH, Yang ZM, Luo T (2006) Discovery of a complete ophiolite section in the Jueweng area, Nagqu County, in the central segment of the Bangong Co-Nujiang junction zone, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geol Bull China 25:694–699
Cheng H, Liu Y, Vervoort JD, Lu H (2015) Combined U–Pb, Lu–Hf, Sm–Nd and Ar–Ar multichronometric dating on the Bailang eclogite constrains the closure timing of the Paleo-tethys ocean in the Lhasa Terrane, Tibet. Gondwana Res 28(4):1482–1499
Chu ZY, Chen FK, Yang YH, Guo JH (2009) Precise determination of Sm, Nd concentrations and Nd isotopic compositions at the nanogram level in geological samples by thermal ionization mass spectrometry. J Anal At Spectrom 24:1534–1544
Clemens JD (2003) S-type granitic magmas-petrogenetic issues, models and evidence. Earth Sci Rev 61:1–18
Cong BL, Wu GY, Zhang Q, Zhang RY, Zhai MG, Zhao DS, Zhang WH (1993) Petrotectonic evolution of the Tethys zone in western Yunnan, China. Chin Bull (B) 23(11):1201–1207 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Cong F, Lin SL, Zou GF, Li ZH, Xie T, Peng ZM, Liang T (2010) Trace elements and Hf isotope compositions and U-Pb age of igneous zircons from the triassic granite in Lianghe, Western Yunnan. Acta Geol Sin 84:1155–1164
Defant MJ, Drummond MS (1990) Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature 347:662–665
De la Roche H, Leterrier J, Grandclaude P, Marchal M (1980) A classification ofvolcanic and plutonic rocks using R1R2-diagram and major-element analyses –its relationships with current nomenclature. Chem Geol 29:183–210
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Li CS, Wang CM (2014) Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Gondwana Research 26(2):419–437
Dewey JF, Shackleton RM, Chang CF (1988) The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan plateau. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser A Math Phys Sci [J] 327:379–413
Elliott T (2003) Tracers of the slab. In: Eiler J (ed) Inside the subduction factory, vol 138. American Geophysical Union, Geophysical Monograph, Washington DC, pp 23–45
Fan W, Wang Y, Zhang A, Zhang F, Zhang Y (2010) Permian arc-back-arc basin development along the Ailaoshan tectonic zone: geochemical, isotopic and geochronological evidence from the Mojiang volcanic rocks, southwest China. Lithos 119(3):553–568
Feeley TC, Hacker MD (1995) Intracrustal derivation of Na-rich andesitic and dacitic magmas: an example from volcán ollagüe, Andean central volcanic zone. J Geol 103(2):213–225
Feng QL, Chonglakmanib CP, Helmckec D, Ingavat-Helmckec R, Liua BP (2005) Correlation of Triassic stratigraphy between the Simao and Lampang–Phrae Basins: implications for the tectonopaleogeography of Southeast Asia. J Asian Earth Sci 24:777–785
Ferguson EM, Klein EM (1993) Fresh basalts from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge extend the Pacific geochemical province. Nature 366:330–333
Foley S, Tiepolo M, Vannucci R (2002) Growth of early continental crust controlled by melting of amphibolite in subduction zones. Nature 417:837–840
Frost TP, Mahood GA (1987) Field, chemical, and physical constraints on mafic-felsic magma interaction in the Lamarck Granodiorite, Sierra Nevada, California. Geol Soc Am Bull 99:272–291
Frost BR, Barnes CG, Collins WJ, Arculus RJ, Ellis DJ, Frost CD (2001) A geochemical classification for granitic rocks. J Petrol 42(11):2033–2048
Gaudemer Y, Jaupart C, Tapponnier P (1988) Thermal control on post-orogenic extension in collision belts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 89(1):48–62
Han BF (2007) Diverse post-collisional granitoids and their tectonic setting discrimination. Earth Sci Front 14(3):64–72 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hart SR (1984) A large-scale isotope anomaly in the Southern Hemisphere mantle. Nature 309:753–757
He ZH, Yang DM, Zheng CQ, Wang TW (2006) Isotopic dating of the Mamba granitoid in the Gangdese tectonic belt and its constraint on the subduction time of the Neotethys. Geol Rev 52(1):100–106 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hennig D, Lehmann B, Frei D, Belyatsky B, Zhao XF, Cabral AR, Zeng PS, Zhou MF, Schmidt K (2009) Early permian seafloor to continental arc magmatism in the eastern Paleo-tethys: U–Pb age and Nd–Sr isotope data from the southern Lancangjiang zone, Yunnan, China. Lithos 113(3):408–422
Hoskin PWO, Schaltegger U (2003) The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev Miner Geochem 53:27–62
Huang ZY, Qi XX, Tang GZ, Liu JK, Zhu LH, Hu ZC, Zhao YH, Zhang C (2013) The identification of early Indosinian tectonic movement in Tengchong block, western Yunnan: evidence of zircon U–Pb dating and Lu–Hf isotope for Nabang diorite. Geol China 40(3):730–741 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Hutchison CS (1989) Geological evolution of South-east Asia. Clarendon, Oxford and New York, pp 1–368
Janoušek V, Finger F, Roberts M, Frýda J, Pin C, Dolejš D (2004) Deciphering the petrogenesis of deeply buried granites: whole-rock geochemical constraints on the origin of largely undepleted felsic granulites from the Moldanubian Zone of the Bohemian Massif. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 389:141–159
Jian P, Liu DY, Sun XM (2004) SHRIMP dating of Jicha Alaskan-type gabbro in western Yunnan Province: evidence for the early Permian subduction. Acta Geol Sin 78:165–170
Jian P, Liu DY, Sun XM (2008) SHRIMP dating of the Permo-Carboniferous Jinshajiang ophiolite, southwestern China: geochronological constraints for the evolution of Paleo-Tethys. J Asian Earth Sci 32:371–384
Jian P, Liu DY, Kröner A, Zhang Q, Wang YZ, Sun XM, Zhang W (2009a) Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China (II): insights from zircon ages of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks and generation of the Emeishan CFB province. Lithos 113:767–784
Jian P, Liu DY, Kröner A, Zhang Q, Wang YZ, Sun XM, Zhang W (2009b) Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in southwest China (I): geochemistry of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks. Lithos 113:748–766
Jin XC (1996) Tectono-stratigraphic units in western Yunnan and their counterparts in southeast Asia. Cont Dyn 1:123–133
Jin X et al (2002) Permo-Carboniferous sequences of Gondwana affinity in southwest China and their paleogeographic implications. J Asian Earth Sci 6:633–646
Kapp P, Yin A, Harrison TM (2005) Cretaceous-Tertiary shortening, basin development, and volcanism in central Tibet [J]. Geol Soc Am Bull 117:865–878
Koteas GC, Williams ML, Seaman SJ, Dumond G (2010) Granite genesis and mafic-felsic magma interaction in the lower crust. Geology 38:1067–1070
Kou KH, Zhang ZC, Santosh M, Huang H, Hou T, Liao BL, Li HB (2012) Picritic porphyrites generated in a slab-window setting: implications for the transition from Paleo-Tethyan to Neo-Tethyan tectonics. Lithos 155:375–391
Li HQ (2009) The geological significance of Indosinian orogenesis occurred in the Lhasa Terrane, Tibet. Ph.D. Dissertation. Institute of Geology, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing (in Chinese with English summary)
Li C, Wang TW, Li HM, Zeng QG (2003) Discovery of Indosinian megaporphyritic granodiorite in the Gangdese area: evidence for the existence of Paleo-Gangdise. Geol Bull China 22(5):364–366 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Li XZ, Liu CJ, Ding J (2004) Correlation and connection of the main suture zones in the Greater Mekong subregion [J]. Sediment Geol Tethyan Geol 4:001
Li ZH, Lin SL, Cong F, Zou GF, Xie T (2010) Indosinian orogenesis of the Tengchong- Lianghe block, Western Yunnan: evidence from zircon U- Pb dating and petrogenesis of granitoids. Acta Petrological et Mineralogica 29(3):298–312
Li HQ, Xu ZQ, Cai ZH, Tang ZM, Yang M (2011) Indosinian epoch magmatic event and geological significance in the Tengchong block, western Yunnan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica 27(7):2165–2172
Liu QS, Jiang W, Jian P, Ye PS, Wu ZH, Hu DG (2006) Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age and petrochemical and geochemical features of Mesozoic muscovite monzonitic granite at Ningzhong, Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica 22(3):643–652 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Ludwig KR (2003) ISOPLOT 3.0: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Special Publication No. 4 Berkeley Geochronology Center
Mahawat C, Atherton MP, Brotherton MS (1990) The Tak batholith, Thailand: the evolution of contrasting granite types and implications for tectonic setting. J Southeast Asian Earth Sci 4:11–27
Mahoney JJ, Frel R, Tejada MLG, Mo XX, Leat PT, Nägler TF (1998) Tracing the Indian Ocean mantle domain through time: isotopic results from old west Indian, east Tethyan, and south Pacific seafloor. J Petrol 39:1285–1306
Martin H, Smithies RH, Rapp R, Moyen JF, Champion D (2005) An overview of adakite, tonalite–trondhjemite–granodiorite TTG, and sanukitoid: relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos 79:1–24
Meng Y, Xu Z, Santosh M, Ma X, Chen X, Guo G et al (2016) Late Triassic crustal growth in southern Tibet: evidence from the Gangdese magmatic belt. Gondwana Res 37:449–464
Metcalfe I (1996a) Pre-cretaceous evolution of SE Asian terranes. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 106(1):97–122
Metcalfe I (1996b) Gondwanaland dispersion, Asian accretion and evolution of eastern Tethys. Aust J Earth Sci 43(6):605–623
Metcalfe I (2002) Permian tectonic framework and palaeogeography of SE Asia. J Asian Earth Sci 20(6):551–566
Metcalfe I (2013) Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion: tectonic and paleogeography evolution of eastern Tethys. J Asian Earth Sci 66:1–33
Middlemost EAK (1994) Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth Sci Rev 37:215–224
Miyashiro A (1974) Volcanic rock series in island arcs and active continental margins. Am J Sci 274(4):321–355
Mo XX, Shen SY, Zhu QW (1998) Volcanics-ophiolite and mineralization of middle and southern part in Sanjiang, southern China. Geological Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–128 (in Chinese)
Nam TN, Sano Y, Terada K, Toriumi M, Quynh PV, Le TD (2001) First shrimp U–Pb zircon dating of granulites from the kontum massif (vietnam) and tectonothermal implications. J Asian Earth Sci 19(1–2):77–84
Patiño Douce AE (1999) What do experiments tell us about the relative contributions of crust and mantle to the origin of the granitic magmas. Geol Soc Lond 168:55–75
Pearce JA (1982) Trace element characteristics of lavas from destructive plate boundaries. In: Thorpe RS (ed) Andesites. Wiley, Chichester, pp 525–548
Pearce JA, Harris NBW, Tindle AG (1984) Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. J Petrol 25:956–983
Peng TP, Wang YP, Zhao GC, Fan WM, Peng BX (2008) Arc-like volcanic rocks from the southern Lancangjiang zone, SW China: geochronological and geochemical constraints on their petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Lithos 102:358–373
Peng TP, Wilde SA, Wang YJ, Fan WM, Peng BX (2013) Mid-Triassic felsic igneous rocks from the southern Lancangjiang zone, SW China: petrogenesis and implications for the evolution of Paleo-tethys. Lithos 168(2):15–32
Petrford N, Atherton M (1996) Na-rich partial melts from newly underplated basaltic crust: the Cordillera Blanca Batholith, Peru. J Petrol 37:1491–1521
Pitcher W (1983) Granite types and tectonic environment. In: Hsu K (ed) Mountain building processes. Academic, London, pp 19–40
Plank T (2005) Constraints from thorium/lanthanumon sediment recycling at subduction zones and the evolution of the continents. J Petrol 46:921–944
Plank T, Langmuir CH (1998) The chemical composition of subducting sediment and its consequences for the crust and mantle. Chem Geol 145(3–4):325–394
Price RC, Kennedy AK, Riggs-Sneeringer M, Frey FA (1986) Geochemistry of basalts from the Indian Ocean Triple Junction: implication for the generation and evolution of Indian Ocean Ridge basalts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 78:379–396
Qi L, Hu J, Gregoire DC (2000) Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 51:507–513
Rapp RP, Watson EB (1995) Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8–32 kbar: implications for continental growth and crust–mantle recycling. J Petrol 36:891–931
Ratajeski K, Sisson TW, Glazner AF (2005) Experimental and geochemical evidence for derivation of the el capitan granite, california, by partial melting of hydrous gabbroic lower crust. Contrib Miner Petrol 149(6):713–734
Rudnick RL, Barth MG, Horn I, McDonough WF (2000) Rutile-bearing refractory eclogites: missing link between continents and depleted mantle. Science 287:278–281
Rushmer T (1991) Partial melting of two amphibolites: contrasting experimental results under fluid-absent conditions. Contrib Miner Petrol 107:41–59
Saunders AD, Norry MJ, Tarney J (1988) Origin of MORB and chemically depleted mantle reservoirs: trace element constraints. J Petrol Spec (1):415–445
Sengör AMC (1984) The Cimmeride orogenic system and the tectonics of Eurasia. Geol Soc Am Spec Pap 195:1–82
Song SG, Niu YL, Wei CJ, Ji JQ, Su L (2010) Metamorphism, anatexis, zircon ages and tectonic evolution of the Gongshan block in the northern Indochina continent—an eastern extension of the Lhasa Block. Lithos 120:327–346
Springer W, Seck HA (1997) Partial fusion of basic granulites at 5 to 15 kbar: implications for the origin of TTG magmas. Contrib Miner Petrol 127:30–45
Stern RJ, Kohut E, Bloomer SH, Leybourne M, Fouch M, Vervoort J (2006) Subduction factory processes beneath the guguan cross-chain, mariana arc: no role for sediments, are serpentinites important? Contrib Miner Petrol 151(2):202–221
Stolz AJ, Vame R, Wheller GE, Foden JD, Abbott MJ (1988) The geochemistry and petrogenesis of K-rich alkaline volcanics from the Batu Tara volcano, eastern Sunda Arc. Contrib Miner Petrol 98:374–389
Stolz AJ, Vame R, Davies GR, Wheller GE, Foden JD (1990) Magma source components in an arc–continent collision zone: the Flores-Lembata sector, Sunda Arc, Indonesia. Contrib Miner Petrol 105:585–601
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications or mantle composition and processes. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 42(1):313–345
Sylvester PJ (1989) Post-collisional alkaline granites. J Geol 97:261–280
Sylvester PJ (1998) Postcollisional strongly peraluminous granites. Lithos 45:29–44
Van Der Voo R (1993) Paleomagnetism of the Atlantic, Tethys and Iapetus oceans. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wang X, Metcalfe I, Jian P, He L, Wang C (2000) The Jinshajiang–Ailaoshan Suture Zone, China: tectonostratigraphy, age and evolution. J Asian Earth Sci 18:675–690
Wang YJ, Fan WM, Zhang YH, Peng TP, Chen XY, Xu YG (2006) Kinematics and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Gaoligong and Chongshan shear systems, western Yunnan, China: implications for early Oligocene tectonic extrusion of SE Asia. Tectonophysics 418:235–254
Wang L, Pan G, Zhu D (2008) Carboniferous-Permian island arc Gangdise belt, Tibet, China: evidence from volcanic rocks and geochemistry[J]. Geol Bull China 27(9):1509–1534 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wang YJ, Zhang AM, Fan WM, Peng TP, Zhang FF, Zhang YH, Bi XW (2010) Petrogenesis of late Triassic post-collisional basaltic rocks of the Lancangjiang tectonic zone, southwest China, and tectonic implications for the evolution of the eastern Paleotethys: geochronological and geochemical constraints. Lithos 120(3–4):529–546
Wang YJ, Xing XW, Cawood PA, Lai SC, Xia XP, Fan WM, Liu HC, Zhang FF (2013) Petrogenesis of early Paleozoic peraluminous granite in the Sibumasu Block of SW Yunnan and diachronous accretionary orogenesis along the northern margin of Gondwana. Lithos 182:67–85
Wang CM, Deng J, Emmanuel JM, Carranza Santosh M (2014) Tin metallogenesis associated with granitoids in the southwestern Sanjiang Tethyan Domain: nature, deposit types, and tectonic setting. Gondwana Res 26(2):576–593
Wang Y, Li S, Ma L, Fan W, Cai Y, Zhang Y et al (2015) Geochronological and geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of early Eocene metagabbroic rocks in Nabang (SW Yunnan) and its implications on the NeoTethyan slab subduction. Gondwana Res 27(4):1474–1486
Wang Y, He H, Cawood PA, Fan W, Srithai B, Feng Q et al (2016) Geochronological, elemental and Sr–Nd–Hf–O isotopic constraints on the petrogenesis of the Triassic post-collisional granitic rocks in NW Thailand and its Paleotethyan implications. Lithos 266–267:264–286
Wolf MB, Wyllie PJ (1994) Dehydration-melting of amphibolite at 10 kbar: the effects of temperature and time. Contrib Miner Petrol 115(4):369–383
Xiao L, Xu YG, Chung SL, He B, Mei H (2003) Chemostratigraphic correlation of upper Permian lavas from Yunnan province, China: extent of the Emeishan large igneous province. Int Geol Rev 45(8):753–766
Xiao L, He Q, Pirajno F, Ni P, Du J, Wei Q (2004) Possible correlation between a mantle plume and the evolution of Paleo-Tethys Jinshajiang ocean: evidence from a volcanic rifted margin in the Xiaru-Tuoding area, Yunnan, SW China. Lithos 100(1):112–126
Xie JC, Zhu DC, Dong G, Zhao ZD, Wang Q, Mo X (2016) Linking the Tengchong terrane in SW Yunnan with the Lhasa terrane in southern Tibet through magmatic correlation. Gondwana Res 39:217–229
Xu X, Yang J, Li T (2007) SHRIMP U–Pb ages and inclusions of zircons from the Sumdo eclogite in the Lhasa block, Tibet, China[J]. Geol Bull China 26(10):1340–1355 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu YG, Lan JB, Yang QJ, Huang XL, Qiu HN (2008) Eocene break-off of the Neo-Tethyan slab as inferred from intraplate-type mafic dykes in the Gaoligong orogenic belt, eastern Tibet. Chem Geol 255:439–453
Xu YG, Yang QJ, Lan JB, Luo ZY, Huang XL, Shi YR, Xie LW (2012) Temporal-spatial distribution and tectonic implications of the batholiths in the Gaoligong-Tengliang-Yingjiang area, western Yunnan: constraints from zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes. J Asian Earth Sci 53:151–175
Yang JS, Xu ZQ, Li TF, Li HQ, Li ZL, Ren YF, Xu XZ, Chen SY (2007) Oceanic subduction-type eclogite in the Lhasa block, Tibet, China: remains of the Paleo-Tethys ocean basin? Geol Bull China 26(10):1277–1287
Yang J, Xu Z, Li Z, Xu X, Li T, Ren Y, Li H, Chen S, Robinson PT (2009) Discovery of an eclogite belt in the lhasa block, tibet: a new border for Paleo-Tethys? J Asian Earth Sci 34(1):76–89
Yang TN, Ding Y, Zhang HR, Fan JW, Liang MJ, Wang XH (2014) Two-phase subduction and subsequent collision defines the Paleotethyan tectonics of the southeastern Tibetan Plateau: evidence from zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry, and structural geology of the Sanjiang orogenic belt, southwest China. Geol Soc Am Bull 126(11/12):1654–1682
Y.B.G.M.R. (Yunnan Bureau Geological Mineral Resource) (1990) Regional geology of Yunnan Province. Geology Publication House, Beijing, pp 1–729 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Yin A, Harrison TM (2000) Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogeny. Earth Planet Sci Lett 28:211–280
Yuan HL, Gao S, Liu XM, Li HM, Gunther D, Wu FY (2004) Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Geo-standard Newsl 28:353–370
Zen E (1986) Aluminum enrichment in silicate melts by fractional crystallization: some mineralogical and petrographical constrains. J Petrol 27:1095–1117
Zhai QG, Jahn BM, Su L, Wang J, Mo XX, Lee HY, Wang KL, Tang S (2013) Triassic arc magmatism in the Qiangtang area, northern Tibet: zircon U–Pb ages, geochemical and Sr–Nd–Hf isotopic characteristics, and tectonic implications. J Asian Earth Sci 63:162–178
Zhang HF, Xu WC, Guo JQ, Zone KQ, Cai HM, Yuan HL (2007) Indosinian orogenesis of the gangdise terrane: evidences of zircon U-Pb dating and petrogenesis of granitoids. Earth Sci 32(2):155–166 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang ZM, Wang JL, Shen K, Shi C (2008) Paleozoic circus-Gondwana orogens: petrology and geochronology of the Namche Barwa Complex in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis, Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica 24:1627–1637 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang KJ, Tang XC, Wang Y, Zhang YX (2011) Geochronology, geochemistry, and Nd isotopes of early Mesozoic bimodal volcanismin northern Tibet, western China: constraints on the exhumation of the central Qiangtang metamorphic belt. Lithos 121:167–175
Zhang ZM, Dong X, Santosh M, Liu F, Wang W, Yiu F, He ZY, Shen K (2012) Petrology and geochronology of the Namche Barwa Complex in the eastern Himalayan syntaxis, Tibet: constrains on the origin and evolution of the north-eastern margin of the Indian craton. Gondwana Res 21:123–137
Zhao SW, Lai SC, Qin JF, Zhu RZ (2016) Tectono-magmatic evolution of the gaoligong belt, southeastern margin of the tibetan plateau: constraints from granitic gneisses and granitoid intrusions. Gondwana Res 1(1):56–66
Zhao CF et al (1999) Variscan and Indosinian granites in northern Tengchong, Yunnan. Reg Geol China 18(3):260–263
Zheng LL, Geng QR, Dong H, Ou CS, Wang XW (2003) The discovery and significance of the relicts of ophiolitic mélanges along the Parlung Zangbo in the Bomi region, eastern Xizang. Sediment Geol Tethyan Geol 23(1):27–30 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhong DL (1998) The paleotethys orogenic belt in west of Sichuan and Yunnan. Science Publishing House, Beijing, pp 1–230 (in Chinese)
Zhong DL (2000) Paleotethys sides in West Yunnan and Sichuan, China. Science, Beijing, pp 1–248 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhu D, Mo X, Niu Y (2009) Zircon U–Pb dating and in situ Hf isotopic analysis of Permian peraluminous granite in the Lhasa terrane, southern Tibet: implications for Permian collisional orogeny and paleogeography[J]. Tectonophysics 469:48–60
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Dilek Y, Hou ZQ, Mo XX (2013) The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Res 23:1429–1454
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Mo XX, Chung SL, Hou ZQ, Wang LQ, Wu FY (2011) The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth. Earth Planet Sci Lett 301:241–255
Zi JW, Cawood PA, Fan WM, Tohver E, Wang YJ, Mccuaig TC (2012a) Generation of early Indosinian enriched mantle-derived granitoid pluton in the Sanjiang orogen (SW China) in response to closure of the Paleo-Tethys. Lithos 140(5):166–182
Zi JW, Cawood PA, Fan WM, Wang YJ, Tohver E, Mccuaig TC, Peng TP (2012b) Triassic collision in the Paleo-Tethys ocean constrained by volcanic activity in SW China. Lithos 144(7):145–160
Zi JW, Cawood PA, Fan WM, Tohver E, Wang YJ, Mccuaig TC et al (2013) Late permian-triassic magmatic evolution in the Jinshajiang orogenic belt, sw china and implications for orogenic processes following closure of the paleo-tethys. Am J Sci 313(2):81–112
Zindle A, Hart SR (1986) Chemical geodynamics. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 14:493–571
Zou GF, Lin SL, Li ZH, Cong F, Xie T (2011) Geochronology and geochemistry of the Longtang granite in the Lianghe area, Western Yunnan and its tectonic implications. Geotectonica et Metallogenia 35:439–451
Acknowledgements
We thank the constructive and helpful comments from Prof. Wolf-Christan Dullo, Editor-in-Chief, Prof. Wenjiao Xiao and two anonymous reviewers, sincerely. We also thank the English improvement from Dr. Mike Fowler, University of Portsmouth. This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grants. 41421002, 41372067, and 41190072] and support was also provided by the MOST Special Fund from the State Key Laboratory of Continental Dynamics, Northwest University, and Province Key Laboratory Construction Item [08JZ62].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, RZ., Lai, SC., Qin, JF. et al. Petrogenesis of late Paleozoic-to-early Mesozoic granitoids and metagabbroic rocks of the Tengchong Block, SW China: implications for the evolution of the eastern Paleo-Tethys. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 107, 431–457 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-017-1501-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-017-1501-x