Abstract
Optimal reactive power dispatch (RPD) for reducing the real power losses of the transmission system is one of the paramount concerns for the research community to investigate the efficiency of power systems. In this paper, strength of meta-heuristic computing paradigm based on fractional-order Darwinian particle swarm optimization (FO-DPSO) is exploited for optimization of RPD problems in energy sector. The fitness functions including line loss minimization and voltage deviation (voltage profile index) are constructed to find the optimal reactive power flow for IEEE 30- and 57-bus test systems. The rich heritage of fractional evolutionary computing through variants of FO-DPSO is applied to minimization problem of optimal power flow by determination of control variables in terms of VAR compensators, bus voltages and transformer tap settings. Comparison of the results shows that fractional swarming intelligence outperformed the state-of-the-art counterparts by means of both line loss minimization and voltage deviation. Superiority of the proposed scheme is also validated for different degrees of freedom in the optimal RPD problems.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gayatri MTL, Parimi AM, Kumar AP (2018) A review of reactive power compensation techniques in microgrids. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 81:1030–1036
Tushar MH, Assi C (2017) Volt-VAR control through joint optimization of capacitor bank switching, renewable energy, and home appliances. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 9:4077–4086
Acha E, Ambriz-Perez H, Fuerte-Esquivel CR (2000) Advanced transformer control modeling in an optimal power flow using Newton’s method. Power Syst IEEE Trans 15(1):290–298
Gotham DJ, Heydt GT (1998) Power flow control and power flow studies for systems with FACTS devices. IEEE Trans Power Syst 13(1):60–65
Mathur RM, Varma RK (2002) Thyristor-based FACTS controllers for electrical transmission systems. Wiley, New York
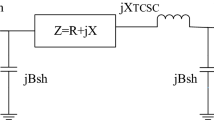
Kazemi A, Badrzadeh B (2004) Modeling and simulation of SVC and TCSC to study their limits on maximum loadability point. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 26(8):619–626
Orfanogianni T, Bacher R (2003) Steady-state optimization in power systems with series FACTS devices. IEEE Trans Power Syst 18(1):19–26
Zhao B, Guo CX, Cao YJ (2005) A multiagent-based particle swarm optimization approach for optimal reactive power dispatch. Power Syst IEEE Trans 20(2):1070–1078
Sulaiman MH, Mustaffa Z, Mohamed MR, Aliman O (2015) Using the gray wolf optimizer for solving optimal reactive power dispatch problem. Appl Soft Comput 32:286–292
Khazali AH, Kalantar M (2011) Optimal reactive power dispatch based on harmony search algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 33(3):684–692
Ghasemi M, Ghavidel S, Ghanbarian MM, Habibi A (2014) A new hybrid algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch problem with discrete and continuous control variables. Appl Soft Comput 22:126–140
Ghasemi A, Valipour K, Tohidi A (2014) Multi objective optimal reactive power dispatch using a new multi objective strategy. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 57:318–334
Kirschen DS, Van Meeteren HP (1988) MW/voltage control in a linear programming based optimal power flow. Power Syst IEEE Trans 3(2):481–489
Abril IP, Quintero JAG (2003) VAR compensation by sequential quadratic programming. IEEE Trans Power Syst 18(1):36–41
Soler EM, Asada EN, da Costa GRM (2013) Penalty-based nonlinear solver for optimal reactive power dispatch with discrete controls. Power Syst IEEE Trans 28(3):2174–2182
Varadarajan M, Swarup KS (2008) Differential evolution approach for optimal reactive power dispatch. Appl Soft Comput 8(4):1549–1561
Subbaraj P, Rajnarayanan PN (2009) Optimal reactive power dispatch using self-adaptive real coded genetic algorithm. Electr Power Syst Res 79(2):374–381
Lo KL, Zhu SP (1991) A decoupled quadratic programming approach for optimal power dispatch. Electr Power Syst Res 22(1):47–60
Deeb NI, Shahidehpour SM (1988) An efficient technique for reactive power dispatch using a revised linear programming approach. Electr Power Syst Res 15(2):121–134
Aoki K, Fan M, Nishikori A (1988) Optimal VAR planning by approximation method for recursive mixed-integer linear programming. IEEE Trans Power Syst 3(4):1741–1747
Granville S (1994) Optimal reactive dispatch through interior point methods. IEEE Trans Power Syst 9(1):136–146
AlRashidi MR, El-Hawary ME (2009) Applications of computational intelligence techniques for solving the revived optimal power flow problem. Electr Power Syst Res 79(4):694–702
Wu QH, Ma JT (1995) Power system optimal reactive power dispatch using evolutionary programming. IEEE Trans Power Syst 10(3):1243–1249
Durairaj S, Devaraj D, Kannan PS (2006) Genetic algorithm applications to optimal reactive power dispatch with voltage stability enhancement. J Inst Eng India Part El Electr Eng Div 87:42
Wu QH, Cao YJ, Wen JY (1998) Optimal reactive power dispatch using an adaptive genetic algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 20(8):563–569
Abido MA (2002) Optimal power flow using tabu search algorithm. Electr Power Compon Syst 30(5):469–483
Ayan K, Kılıc U (2012) Artificial bee colony algorithm solution for optimal reactive power flow. Appl Soft Comput 12(5):1477–1482
Vlachogiannis JG, Lee KY (2006) A comparative study on particle swarm optimization for optimal steady-state performance of power systems. Power Syst IEEE Trans 21(4):1718–1728
Sinsuphan N, Leeton U, Kulworawanichpong T (2013) Optimal power flow solution using improved harmony search method. Appl Soft Comput 13(5):2364–2374
Valipour K, Ghasemi A (2017) Using a new modified harmony search algorithm to solve multi-objective reactive power dispatch in deterministic and stochastic models. J. AI Data Min. 5(1):89–100
Heidari AA, Ali Abbaspour R, Rezaee Jordehi A (2017) Gaussian bare-bones water cycle algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch in electrical power systems. Appl Soft Comput 57:657–671
Mahadevan K, Kannan PS (2010) Comprehensive learning particle swarm optimization for reactive power dispatch. Appl Soft Comput 10(2):641–652
Mandal B, Roy PK (2013) Optimal reactive power dispatch using quasi-oppositional teaching learning-based optimization. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 53:123–134
Mukherjee A, Mukherjee V (2015) Solution of optimal reactive power dispatch by chaotic krill herd algorithm. IET Gener Transm Distrib 9(15):2351–2362
Rajan A, Malakar T (2015) Optimal reactive power dispatch using hybrid Nelder–Mead simplex-based firefly algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 66:9–24
Dai C, Chen W, Zhu Y, Zhang X (2009) Reactive power dispatch considering voltage stability with seeker optimization algorithm. Electr Power Syst Res 79(10):1462–1471
Tripathy M, Mishra S (2007) Bacteria foraging-based solution to optimize both real power loss and voltage stability limit. IEEE Trans Power Syst 22(1):240–248
Duman S, Güvenc U, Sönmez Y, Yörükeren N (2012) Optimal power flow using gravitational search algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 59:86–95
Shaw B, Mukherjee V, Ghoshal SP (2014) Solution of reactive power dispatch of power systems by an opposition-based gravitational search algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 55:29–40
Ng Shin Mei R, Sulaiman MH, Mustaffa Z, Daniyal H (2017) Optimal reactive power dispatch solution by loss minimization using moth-flame optimization technique. Appl Soft Comput 59:210–222
Bhattacharya A, Chattopadhyay PK (2010) Biogeography-based optimization for solution of optimal power flow problem. In: ECTI-CON2010: The 2010 ECTI International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, pp 435–439
Huang C-M, Huang Y-C (2012) Combined differential evolution algorithm and ant system for optimal reactive power dispatch. Energy Procedia 14:1238–1243
Mehdinejad M, Mohammadi-Ivatloo B, Dadashzadeh-Bonab R, Zare K (2016) Solution of optimal reactive power dispatch of power systems using hybrid particle swarm optimization and imperialist competitive algorithms. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 83:104–116
Solteiro Pires EJ, Tenreiro Machado JA, de Moura Oliveira PB (2014) Fractional particle swarm optimization mathematical methods in engineering. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 47–56
De Oliveira EC, Machado JAT (2014) A review of definitions for fractional derivatives and integral. Math Probl Eng 2014:238459
Davison M, Essex C (1998) Fractional differential equations and initial value problems. Math Sci 23(2):108–116
Couceiro MS, Rocha RP, Ferreira NF, Machado JT (2012) Introducing the fractional-order Darwinian PSO. SIViP 6(3):343–350
Couceiro M, Ghamisi P (2015) Fractional order Darwinian particle swarm optimization: applications and evaluation of an evolutionary algorithm. Springer, Berlin
Tenreiro Machado JA, Silva MF, Barbosa RS, Jesus IS, Reis CM, Marcos MG, Galhano AF (2010) Some applications of fractional calculus in engineering. Math Probl Eng 2010:639801. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/639801
Ghamisi P, Couceiro MS, Martins FM, Benediktsson JA (2014) Multilevel image segmentation based on fractional-order Darwinian particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Geosci Resens 52(5):2382–2394
Haji VH, Monje CA (2017) Fractional order fuzzy-PID control of a combined cycle power plant using Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm with an improved dynamic parameter selection. Appl Soft Comput 58:256–264
Ates A, Alagoz BB, Kavuran G, Yeroglu C (2017) Implementation of fractional order filters discretized by modified Fractional Order Darwinian Particle Swarm Optimization. Measurement 107:153–164
Yang Q, Chen D, Zhao T, Chen Y (2016) Fractional calculus in image processing: review. Fract Calc Appl Anal 19(5):1222–1249
Couceiro MS, Martins FM, Rocha RP, Ferreira NM (2012) Introducing the fractional order robotic Darwinian PSO. In: AIP conference proceedings, vol 1493, no 1. AIP, College Park, pp 242–251
Ghamisi P, Couceiro MS, Benediktsson JA (2015) A novel feature selection approach based on FODPSO and SVM. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 53(5):2935–2947
Paliwal KK, Singh S, Gaba P (2017) Feature selection approach of hyperspectral image using GSA–FODPSO–SVM. In: 2017 international conference on computing, communication and automation (ICCCA). IEEE, pp 1070–1075
Ghamisi P, Couceiro MS, Benediktsson JA (2013) Classification of hyperspectral images with binary fractional order Darwinian PSO and random forests. In: Bruzzone L (ed) Image and signal processing for remote sensing XIX, vol 8892. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham, p 88920S
Akbar S et al (2019) Novel application of FO-DPSO for 2-D parameter estimation of electromagnetic plane waves. Neural Comput Appl 31:1–10
Wang YY, Peng WX, Qiu CH, Jiang J, Xia SR (2018) Fractional-order Darwinian PSO-based feature selection for media-adventitia border detection in intravascular ultrasound images. Ultrasonics 92:1–7
Wang Y-Y, Zhang H, Qiu C-H, Xia S-R (2018) A novel feature selection method based on extreme learning machine and fractional-order Darwinian PSO. Comput Intell Neurosci 2018:5078268. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5078268
Zhu Q, Yuan M, Liu YL, Chen WD, Chen Y, Wang HR (2014) Research and application on fractional-order Darwinian PSO based adaptive extended Kalman filtering algorithm. IAES Int J Robot Autom 3(4):245
Yokoya N, Ghamisi P (2016) Land-cover monitoring using time-series hyperspectral data via fractional-order darwinian particle swarm optimization segmentation. In: 2016 8th workshop on hyperspectral image and signal processing: evolution in remote sensing (WHISPERS). IEEE, pp 1–5
Guo F, Peng H, Zou B, Zhao R, Liu X (2018) Localisation and segmentation of optic disc with the fractional-order Darwinian particle swarm optimization algorithm. IET Image Process 12:1303–1312
Łegowski A, Niezabitowski M (2016) Robot path control based on PSO with fractional-order velocity. In: International conference on robotics and automation engineering (ICRAE). IEEE, pp 21–25
Kosari M, Teshnehlab M (2018) Non-linear fractional-order chaotic systems identification with approximated fractional-order derivative based on a hybrid particle swarm optimization-genetic algorithm method. J AI Data Min 6(2):365–373
Li X, Wang Y, Li N, Han M, Tang Y, Liu F (2017) Optimal fractional order PID controller design for automatic voltage regulator system based on reference model using particle swarm optimization. Int J Mach Learn Cybern 8(5):1595–1605
Azar AT, Serrano FE (2018) Fractional order sliding mode PID controller/observer for continuous nonlinear switched systems with PSO parameter tuning. In: Hassanien A, Tolba M, Elhoseny M, Mostafa M (eds) International conference on advanced machine learning technologies and applications. Springer, Cham, pp 13–22
Katal N, Narayan S (2017) Design of robust fractional order PID controllers for coupled tank systems using multi-objective particle swarm optimization. Int J Syst Control Commun 8(3):250–267
Abdulkhader HK, Jacob J, Mathew AT (2018) Fractional-order lead-lag compensator-based multi-band power system stabiliser design using a hybrid dynamic GA-PSO algorithm. IET Gener Transm Distrib 12:3248–3260
Sodhro AH, Malokani AS, Sodhro GH, Muzammal M, Zongwei L (2019) An adaptive QoS computation for medical data processing in intelligent healthcare applications. Neural Comput Appl. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-018-3931-1
Sodhro AH, Shaikh FK, Pirbhulal S, Lodro MM, Shah MA (2017) Medical-QoS based telemedicine service selection using analytic hierarchy process. In: Khan S, Zomaya A, Abbas A (eds) Handbook of large-scale distributed computing in smart healthcare. Springer, Cham, pp 589–609
Magsi H, Sodhro AH, Chachar FA, Abro SAK, Sodhro GH, Pirbhulal S (2018) Evolution of 5G in Internet of medical things. In: 2018 International Conference on Computing, Mathematics and Engineering Technologies (iCoMET). IEEE, pp 1–7
Sodhro AH, Pirbhulal S, Sodhro GH, Gurtov A, Muzammal M, Luo Z (2019) A joint transmission power control and duty-cycle approach for smart healthcare system. IEEE Sens J 19(19):8479–8486
Sodhro AH, Pirbhulal S, de Albuquerque VHC (2019) Artificial intelligence driven mechanism for edge computing based industrial applications. IEEE Trans Ind Inform 15(7):4235–4243
Sodhro AH, Li Y, Shah MA (2016) Energy-efficient adaptive transmission power control for wireless body area networks. IET Commun 10(1):81–90
Korzun DG, Nikolaevskiy I, Gurtov A (2015) Service intelligence support for medical sensor networks in personalized mobile health systems. In: Balandin S, Andreev S, Koucheryavy Y (eds) Internet of things, smart spaces, and next generation networks and systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 116–127
Sodhro AH, Luo Z, Sodhro GH, Muzamal M, Rodrigues JJ, de Albuquerque VHC (2019) Artificial Intelligence based QoS optimization for multimedia communication in IoV systems. Future Gener Comput Syst 95:667–680
El Ela AAA, Abido MA, Spea SR (2011) Differential evolution algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch. Electr Power Syst Res 81(2):458–464
Pires EJS, Machado JAT, Oliveira PBM, Cunha JB, Mendes L (2010) Particle swarm optimization with fractional-order velocity. J. Nonlinear Dyn 61:295–301
Sabatier J, Agrawal OP, Tenreiro Machado JA (eds) (2007) Advances in fractional calculus—theoretical developments and applications in physics and engineering. Springer, Berlin. ISBN: 900 978-1-4020-6-0
Ortigueira MD, Tenreiro Machado JA (2003) Special issue on fractional signal processing. Signal Process 83:2285–2480
Zimmerman RD, Murillo-Sanchez CE, Thomas RJ (2011) MATPOWER: steady-state operations, planning, and analysis tools for power systems research and education. Power Syst IEEE Trans 26(1):12–19
Subburaj P, Sudha N, Rajeswari K, Ramar K, Ganesan L (2007) Optimum reactive power dispatch using genetic algorithm. Acad Open Internet J 21(PART 6):6
Abido MA (2006) Multiobjective optimal VAR dispatch using strength pareto evolutionary algorithm. In: IEEE congress on evolutionary computation, 2006. CEC 2006. IEEE
Durairaj MS, Kannan PS, Devaraj D (2005) Multi-objective VAR dispatch using particle swarm optimization. Int J Emerg Electr Power Syst 4(1):1–16
Abou AA, Ela EL, Abido MA, Spea SR (2009) Optimal power flow using differential evolution algorithm. Electr Eng 91(2):69–78
Bhattacharya A, Chattopadhyay PK (2010) Solution of optimal reactive power flow using biogeography-based optimization. Int J Energy Power Eng 3:269–277
Dai C, Chen W, Zhu Y, Zhang X (2009) Seeker optimization algorithm for optimal reactive power dispatch. IEEE Trans Power Syst 24:1218–1231
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declared that there are no potential conflicts of interest.
Human and animal rights
All authors declared that there is no research involving human and/or animal.
Informed consent
All authors declared that there is no material that required informed consent.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muhammad, Y., Khan, R., Ullah, F. et al. Design of fractional swarming strategy for solution of optimal reactive power dispatch. Neural Comput & Applic 32, 10501–10518 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04589-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-019-04589-9