Abstract
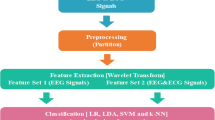
Electroencephalography (EEG) has been used as a promising tool for investigation of brain activity during cognitive processes. The aim of this study is to reveal whether EEG signals can be used for classifying cognitive processes: arithmetic tasks and text reading. A recently introduced EEG database, which is constructed from 18 healthy subjects during a slide show including 60 slides of simple arithmetic tasks and easily readable texts, is used for this purpose. Multi-order difference plot-based time-domain attributes, number of values in specified regions after scattering the sequential difference values with several degrees, are extracted. For classification, improved extreme learning machine (ELM) scheme, namely luELM, by the use of lower–upper triangularization method instead of singular value decomposition which has disadvantages when used with huge data is proposed. As a result, higher accuracy results are achieved with reduced training time for proposed luELM classifier than traditional ELM classifier for both subject-dependent and subject-independent analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baretta L, Tomitch LMB, MacNair N, Lim VK, Waldie KE (2009) Inference making while reading narrative and expository texts: An ERP study. Psychol Neurosci 2(2):137
Bunch JR, Hopcroft JE (1974) Triangular factorization and inversion by fast matrix multiplication. Math Comput 28(125):231–236
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2001) Pattern classification. 2nd edition. A Wiley-Interscience publication
Eberhard-Moscicka AK, Jost LB, Raith M, Maurer U (2015) Neurocognitive mechanisms of learning to read: print tuning in beginning readers related to word-reading fluency and semantics but not phonology. Dev Sci 18(1):106–118
Eraldemir SG (2014) Analysis of EEG signals during text reading and mathematical processing
Eraldemir SG, Yildirim E (2014) Classification of simple text reading and mathematical tasks from EEG. In: Signal processing and communications applications conference (SIU). IEEE, pp 180–183
Eraldemir SG, Yıldırım E, Kutlu Y (2014) Classification of mathematical tasks from EEG signals using k-NN algorithm. In: Elektrik Elektronik Bilgisayar ve Biyomedikal Mhendislii Sempozyumu (Eleco 2014), Bursa, Turkey. pp 551–554
Eraldemir SG Yıldırım E, Yıldırım S, Kutlu Y (2014) Kognitif EEG isaretleri icin oznitelik secimi tabanli kanal secimi ve siniflandirma. In: Akilli Sistemlerde Yenilikler ve Uygulamalari Sempozyumu (ASYU). Izmir, Turkey
Galán FC, Beal CR (2012) EEG estimates of engagement and cognitive workload predict math problem solving outcomes. In: User modeling, adaptation, and personalization. Springer, pp 51–62
Golub GH, Reinsch C (1970) Singular value decomposition and least squares solutions. Numer Math 14(5):403–420
Golub GH, Van Loan CF (2012) Matrix computations. 4th edition. JHU Press, Baltimore
Gundel A, Wilson GF (1992) Topographical changes in the ongoing EEG related to the difficulty of mental tasks. Brain Topogr 5(1):17–25
Hall MA (1999) Correlation-based feature selection for machine learning. Ph.D. thesis, The University of Waikato
Horata P, Chiewchanwattana S, Sunat K (2013) Robust extreme learning machine. Neurocomputing 102:31–44
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501. doi:10.1016/j.neucom.2005.12.126
Krogh A, Vedelsby J et al (1995) Neural network ensembles, cross validation, and active learning. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 7:231–238
Kutlu Y, Yayik A, Yildirim E, Yildirim S (2015) Orthogonal extreme learning machine based P300 visual event-related BCI. In: Neural information processing. Springer, pp 284–291
Liang NY, Huang GB, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N (2006) A fast and accurate online sequential learning algorithm for feedforward networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17(6):1411–1423
Lin CL, Jung M, Wu YC, Lin CT, She HC (2012) Brain dynamics of mathematical problem solving. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2012 annual international conference of the IEEE. IEEE, pp 4768–4771
Meyer CD (2000) Matrix analysis and applied linear algebra. Siam publication
Osaka M (1984) Peak alpha frequency of EEG during a mental task: task difficulty and hemispheric differences. Psychophysiology 21(1):101–105
Pachori RB, Hewson D, Snoussi H, Duchêne J (2009) Postural time-series analysis using empirical mode decomposition and second-order difference plots. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, 2009. ICASSP 2009. IEEE, pp 537–540
Pachori RB, Patidar S (2014) Epileptic seizure classification in EEG signals using second-order difference plot of intrinsic mode functions. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 113(2):494–502. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.11.014
Ramsden S, Richardson FM, Josse G, Shakeshaft C, Seghier ML, Price CJ (2013) The influence of reading ability on subsequent changes in verbal IQ in the teenage years. Dev Cogn Neurosci 6:30–39
Regression AA (1972) The Moore–Penrose pseudoinverse. Academic, New-York
Rosazza C, Cai Q, Minati L, Paulignan Y, Nazir TA (2009) Early involvement of dorsal and ventral pathways in visual word recognition: an ERP study. Brain Res 1272:32–44
Thuraisingham R (2010) A classification system to detect congestive heart failure using second-order difference plot of RR intervals. Cardiol Res Pract. doi:10.4061/2009/807379
Thuraisingham RA (2009) A classification system to detect congestive heart failure using second-order difference plot of RR intervals. Cardiol Res Pract 2009:1–8
Tzeng J (2013) Split-and-combine singular value decomposition for large-scale matrix. J Appl Math. doi:10.1155/2013/683053
Yayık A, Kutlu Y (2011) Diagnosis of congestive heart failure using poincare map plot. In: Signal process and communication conference
Yayık A, Kutlu Y, Yıldırım E (2014) Epileptic state detection: pre-ictal, inter-ictal, post-ictal. In: International conference on advanced technology and sciences
Zhu QY, Qin AK, Suganthan PN, Huang GB (2005) Evolutionary extreme learning machine. Pattern Recogn 38(10):1759–1763
Acknowledgements
The authors are very grateful to Mr. Server Göksel Eraldemir for his efforts to construct the EEG-MaTeP database.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kutlu, Y., Yayık, A., Yildirim, E. et al. LU triangularization extreme learning machine in EEG cognitive task classification. Neural Comput & Applic 31, 1117–1126 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3142-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-017-3142-1