Abstract
Purpose
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) affects quality of life for patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy. We aimed to assess the effect of lorazepam with granisetron on CINV in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Methods
We reviewed the records of 71 consecutive patients with newly diagnosed ALL who received chemotherapy including vincristine, anthracycline, and systemic steroids between January 2011 and December 2016 in our hospital. The number of chemotherapy cycles reviewed was 164. All patients received granisetron as CINV prophylaxis.
Results
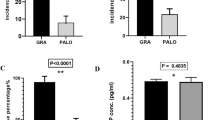
Nausea was observed in 51/71 patients (72%) and 93/164 cycles (57%). Vomiting was observed in 47/71 patients (66%) and 79/164 cycles (48%). Age and gender distribution were not significantly different between patients who received lorazepam at the initiation of the chemotherapy cycle (LZP group, n = 30) and those who did not receive lorazepam (non-LZP group, n = 134). There were no significant differences in the incidence of CIN and CIV between the LZP group and non-LZP group (CIN, 67% vs. 57%, P = 0.31; CIV, 53% vs. 47%, P = 0.98). In multivariate logistic regression, female gender and older age (> 5 years) were significant risk factors for CIV (female, odds ratio (OR) 2.5, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.3–5.0, P = 0.007; older age, OR 2.5, CI 1.3–4.8, P = 0.008).
Conclusions
We found no beneficial effect of providing lorazepam as adjuvant antiemetic for prevention of CINV in children with ALL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hesketh PJ (2008) Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. N Engl J Med 358(23):2482–2494
Cefalo MG, Ruggiero A, Maurizi P, Attinà G, Arlotta A, Riccardi R (2009) Pharmacological management of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in children with cancer. J Chemother 21(6):605–610
Flank J, Robinson PD, Holdsworth M, Phillips R, Portwine C, Gibson P, Maan C, Stefin N, Sung L, Dupuis LL (2016) Guideline for the treatment of breakthrough and the prevention of refractory chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in children with cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer 63:1144–1151
Rao KV, Faso A (2012) Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: optimizing prevention and management. Am Health Drug Benefits 5(4):232–240
Dupuis LL, Milne-Wren C, Cassidy M, Barrera M, Portwine C, Johnston DL, Silva MP, Sibbald C, Leaker M, Routh S, Sung L (2010) Symptom assessment in children receiving cancer therapy: the parents' perspective. Support Care Cancer 18(3):281–299
Dupuis LL, Nathan PC (2010) Optimizing emetic control in children receiving antineoplastic therapy beyond the guidelines. Pediatr Drugs 12(1):51–61
Roila F, Molassiotis A, Herrstedt J, Aapro M, Gralla RJ, Bruera E, Clark-Snow RA, Dupuis LL, Einhorn LH, Feyer P, Hesketh PJ, Jordan K, Olver I, Rapoport BL, Roscoe J, Ruhlmann CH, Walsh D, Warr D, van der Wetering M, On behalf of the participants of the MASCC/ESMO Consensus Conference Copenhagen2015 (2016) 2016 MASCC and ESMO guideline update for the prevention of chemotherapy-and radiotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting and of nausea and vomiting in advanced cancer patients. Ann Oncol 27(supplement 5):v119–v133
Hesketh PJ, Kris MG, Basch E, Bohlke K, Barbour SY, Clark-Snow RA, Danso MA, Dennis K, Dupuis LL, Dusetzina SB, Eng C, Feyer PC, Jordan K, Noonan K, Sparacio D, Somerfield MR, Lyman GH (2017) Antiemetics: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol 35(28):3240–3261
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. Antiemesis. Version 2.2017_March 28,2017. www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/antiemesis.pdf. Accessed Oct 4,2017
Takeuchi H, Saeki T, Aiba K, Tamura K, Aogi K, Eguchi K, Okita K, Kagami Y, Tanaka R, Nakagawa K, Fujii H, Boku N, Wada M, Akechi T, Udagawa Y, Okawa Y, Onozawa Y, Sasaki H, Shima Y, Shimoyama N, Takeda M, Nishidate T, Yamamoto A, Ikeda T, Hirata K (2016) Japanese Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guidelines 2010 for antiemesis in oncology: executive summary. Int J Clin Oncol 21(1):1–12
Malik IA, Khan WA, Qazilbash M, Ata E, Butt A, Khan MA (1995) Clinical efficacy of lorazepam in prophylaxis of anticipatory, acute, and delayed nausea and vomiting induced by high doses of cisplatin. A prospective randomized trial. Am J Clin Oncol 18(2):170–175
Molino A, Guglielmo L, Azzolini ME, Biondani P, Capelli MC, Grandinetti A, Griso C, Martinelli G, Martini N, Zanotti R et al (1991) The antiemetic activity of high-dose metoclopramide and high-dose alizapride in combination with lorazepam in patients receiving cancer chemotherapy. A prospective, randomized, double-blind study. Oncology 48(2):111–115
Relling MV, Mulhern RK, Fairclough D, Baker D, Pui CH (1993) Chlorpromazine with and without lorazepam as antiemetic therapy in children receiving uniform chemotherapy. J Pediatr 123(5):811–816
Dupuis LL, Nathan PC (2003) Options for the prevention and management of acute chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in children. Pediatr Drugs 5(9):597–613
Sepúlveda-Vildósola AC, Betanzos-Cabrera Y, Lastiri GG, Rivera-Márquez H, Villasis-Keever MA, Del Angel VW, Díaz FC, López-Aguilar E (2008) Palonosetron hydrochloride is an effective and safe option to prevent chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in children. Arch Med Res 39(6):601–606
Herrstedt J, Rapoport B, Warr D, Roila F, Bria E, Rittenberg C, Hesketh PJ (2011) Acute emesis: moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. Support Care Cancer 19(Supplement 1):S15–S23
Dupuis LL, Boodhan S, Holdsworth M, Robinson PD, Hain R, Portwine C, O’Shaughnessy E, Sung L (2013) Guideline for the prevention of acute nausea and vomiting due to antineoplastic medication in pediatric cancer patients. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60(7):1073–1082
Roila F, Warr D, Aapro M, Clark-Snow RA, Einhorn L, Gralla RJ, Herrstedt J, Saito M, Tonato M (2011) Delayed emesis: moderately emetogenic chemotherapy (single-day chemotherapy regimens only). Support Care Cancer 19(Supplement 1):S57–S62
Roila F, Warr D, Clark-Snow RA, Tonato M, Gralla RJ, Einhorn LH, Herrstedt J (2005) Delayed emesis: moderately emetogenic chemotherapy. Support Care Cancer 13(2):104–108
Dupuis LL, Boodhan S, Holdsworth M, Robinson PD, Hain R, Portwine C, O’Shaughnessy E, Sung L. Guideline for classification of the acute emetogenic potential of antineoplastic medication in pediatric cancer patients. Version date: February 28, 2013. http://www.pogo.ca/_media/File/guidelines/POGO%20Emetogenicity%20Classification%20Guideline%20Final-rev-%20250111.pdf. Accessed Oct 4,2017
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant 48(3):452–458
Shillingburg A, Biondo L (2014) Aprepitant and fosaprepitant use in children and adolescent at an academic medical center. J Pediatr Phamacol Ther 19(2):127–131
Holdsworth MT, Raisch DW, Frost J (2006) Acute and delayed nausea and emesis control in pediatric oncology patients. Cancer 106:931–940
Loeffen EAH, Kremer LCM, Mulder RL, Font-Gonzalez A, Dupuis LL, Sung L, Robinson PD, van de Wetering MD, Tissing WJE (2017) The importance of evidence-based supportive care practice guidelines in childhood cancer—a plea for their development and implementation. Support Care Cancer 25:1121–1125
Yokoi M, Tsuji D, Suzuki K, Kawasaki Y, Nakao M, Ayuhara H, Kogure Y, Shibata K, Hayashi T, Hirai K, Inoue K, Hama T, Takeda K, Nishio M, Itoh K (2018) Genetic risk factors for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in patients with cancer receiving cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Support Care Cancer 26(5):1505–1513
Sekine I, Segawa Y, Kubota K, Saeki T (2013) Risk factors of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting: index for personalized antiemetic prophylaxis. Cancer Sci 104(6):711–717
Kris MG, Hesketh PJ, Somerfield MR, Feyer P, Clark-Snow R, Koeller JM, Grunberg SM (2006) American Society of Clinical Oncology guideline for antiemetics in oncology: update 2006. J Clin Oncol 24(18):2932–2947
Laszlo J, Clark RA, Hanson DC, Tyson L, Crumpler L, Gralla R (1985) Lorazepam in cancer patients treated with cisplatin: a drug having antiemetic, amnesic, and anxiolytic effects. J Clin Oncol 3(6):864–869
Razavi D, Delvaux N, Farvacques C, De BF, Van HC, Kaufman L, Derde MP, Beauduin M, Piccart M (1993) Prevention of adjustment disorders and anticipatory nausea secondary to adjuvant chemotherapy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study assessing the usefulness of alprazolam. J Clin Oncol 11(7):1384–1390
Hayashi M, Takao Y, Hata C, Teramachi H, Tsuchiya T (2010) Clonazepam use for prevention of acute and delayed vomiting induced by cisplatin-based chemotherapy for lung cancer. Biol Pharm Bull 33(11):1907–1910
Mughal TI (1983) Improved tolerance of cytotoxic chemotherapy with lorazepam. A pilot study. Oncology 40(6):392–394
Bowcock SJ, Stockdale AD, Bolton JA, Kang AA, Retsas S (1984) Antiemetic prophylaxis with high dose metoclopramide or lorazepam in vomiting induced by chemotherapy. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 288(6434):1879
Harousseau JL, Zittoun R, Bonneterre J, Hedouin M, Ouvry J (2000) Improvement in the control of chemotherapy induced emesis with ondansetron, methylprednisolone and lorazepam combination in patients treated by a moderate emetic treatment and uncontrolled by a previous antiemetic combination. Bull Cancer 87(6):491–497
Ahn MJ, Lee JS, Lee KH, Suh C, Choi SS, Kim SH (1994) A randomized double-blind trial of ondansetron alone versus in combination with dexamethasone versus in combination with dexamethasone and lorazepam in the prevention of emesis due to cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol 17(2):150–156
Marx W, McCarthy AL, Ried K, McKavanagh D, Vitetta L, Sali A, Lohning A, Isenring E (2017) The effect of a standardized ginger extract on chemotherapy-induced nausea-related quality of life in patients undergoing moderately or highly emetogenic chemotherapy: a double blind, randomized, Placebo Controlled Trial. Nutrients 9(8):867
Lindley CM, Hirsch JD, O’Neill CV, Transau MC, Gilbert CS, Osterhaus JT (1992) Quality of life consequences of chemotherapy-induced emesis. Qual Life Res 1(5):331–340
Dupuis LL, Taddio A, Kerr EN, Kelly A, MacKeigan L (2006) Development and validation of the pediatric nausea assessment tool for use in children receiving antineoplastic agents. Pharmacotherapy 26(9):1221–1231
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the doctors and nurses of the Department of Hematology and Oncology in Hyogo Prefectural Kobe Children’s Hospital, Japan, for their support and cooperation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ono, A., Kishimoto, K., Hasegawa, D. et al. Impact of adjuvant lorazepam with granisetron on chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting in pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Support Care Cancer 27, 895–899 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4377-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-018-4377-9