Abstract
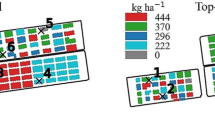
Clustering algorithms are critical data mining techniques used to analyze a wide range of data. This study compares the utility of ant colony optimization (ACO), genetic algorithm (GA), and K-means methods to cluster climatic variables affecting the yield of rainfed wheat in northeast Iran from 1984 to 2010 (27 years). These variables included sunshine hours, wind speed, relative humidity, precipitation, maximum temperature, minimum temperature, and the number of wet days. Seven climatic factors with higher correlations with detrended rainfed wheat yield were selected based on Pearson correlation coefficient significance (P value < 0.1). Three variables (i.e., sunshine hours, wind, and average relative humidity) were excluded for clustering. In the next step based on Pearson correlation (P value < 0.05) between the yield, and the seven climate attributes, fitness function, and silhouette index, only four attributes with higher correlation in its cluster were selected for reclustering. Four climate attributes had an extensive association with yield, so we used four-dimensional clustering to describe the common characteristics of low-, medium-, and high-yielding years, and this is the significance of this research that we have done four-dimensional clustering. The silhouette index showed that the best number of clusters for each station was equal to three clusters. At the last step, reclustering was done through the best-selected method. The results yielded that GA was the best method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah SS, Malek MA, Mustapha A, Aryanfar A (2014) Hybrid of artificial neural network-genetic algorithm for prediction of reference evapotranspiration (ET0) in arid and semiarid regions. J Agric Sci:Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education 6(3):191–200. https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v6n3p191
Ahmed M, Hassan F (2011) Cumulative effect of temperature and solar radiation on wheat yield. Not Bot Horti Agrobo 39(2):146–152. https://doi.org/10.15835/nbha3925406
Ahmed M, Akram MN, Asimc M, Aslam M, Hassan F, Higgins S, Stöckle C, Hoogenboom G (2016) Calibration and validation of APSIM-wheat and CERES-wheat for spring wheat under rainfed conditions: models evaluation and application. Comput Electron Agric 123:384–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2016.03.015
Alvarez R (2009) Predicting average regional yield and production of wheat in the argentine pampas by an artificial neural network approach. Eur J Agron 30:70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2008.07.005
Bannayan M, Sanjani S, Alizadeh A, Sadeghi Lotfabadi S, Mohamadian A (2010) Association between climate indices, aridity index, and rainfed crop yield in northeast of Iran. Field Crop Res 118:105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2010.04.011
Bannayan M, Lakzian A, Gorbanzadeh N, Roshani A (2011) Variability of growing season indices in northeast of Iran. Theor Appl Climatol 105:485–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-011-0404-1
Carvalho M, Serralheiro R, Corte-Real J, Valverde P (2015) Implications of climate variability and future trends on wheat production and crop technology adaptations in southern regions of Portugal. Water Utility Journal 9:13–18 http://hdl.handle.net/10174/14564
Celebi M, Kingravi H, Vela P (2013) A comparative study of efficient initialization methods for the k-means clustering algorithm. Expert Syst Appl 40:200–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2012.07.021
Chen G, Liu H, Zhang J, Liu P, Dong S (2012) Factors affecting summer maize yield under climate change in Shandong Province in the Huanghuaihai Region of China. Int J Biometeorol 56:621–629. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-011-0460-3
Chou C, Chen C-A, Tan P-H, Chen KT (2012) Mechanisms for global warming impacts on precipitation frequency and intensity. J Clim 25(9):3291–3306. https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-11-00239.1
De Amorim RC (2016) A survey on feature weighting based K-means algorithms. J Classif 33:210–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00357-016-9208-4
De Amorim RC, Mirkin B (2012) Minkowski metric, feature weighting and anomalous cluster initializing in K-means clustering. Pattern Recogn 45(2012):1061–1075. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2011.08.012
De Martonne E (1926) Une nouvelle function climatologique: L'indice d'aridité. La. Meteorologie 2:449–458
Deneubourg J-L, Gross S, Franks NR, Sendova-Franks A, Detrain C, Chretien L (1991) The dynamics of collective sorting: robot-like ants and ant-like robots. In: Meyer J-A, Wilson S (eds) Proc. The First International Conference on Simulation of Adaptive Behavior. From Animals to Animals J. MIT Press, Cambridge MA, pp 356–363
Dorigo M, Maniezzo V, Colorni A, 1991. The ant system: an autocatalytic optimizing process. Technical Report, Politecnico diMilano, Italy 91–106
Eyshi Rezaie E, Bannayan M (2012) Rainfed wheat yields under climate change in northeastern Iran. Meteorol Appl 19:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1002/met.268
FAO, Statistical Pocketbook (2015) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Rome, Italy
Halkidi M, Batistakis Y, Vazirgiannis M (2001) 2001. On clustering validation techniques. Intell Inf Syst J 17(2–3):107–145
Handl J, Meyer B (2002) Improved ant-based clustering and sorting in a document retrieval interface, proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Parallel Problem Solving from Nature. LNCS 2439:913–923. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-45712-7_88
Hertz A, Kobler D (2000) A framework for the description of evolutionary algorithms. Eur J Oper Res 126(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00435-X
Jing-Song S, Guang-Sheng Z, Xing-Huaa S (2012) Climatic suitability of the distribution of the winter wheat cultivation zone in China. Eur J Agron 43:77–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2012.05.009
Kao YT, Zahara E, Kao IW (2008) A hybridized approach to data clustering. Expert Syst Appl 34(3):1754–1762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2007.01.028
Kettlewell PS, Sothern RB, Koukkari WL (1999) U.K. wheat quality and economic value are dependent on the North Atlantic Oscillation. J Cereal Sci 29:205–209 Article No. jcrs.1999.0258, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Kim KJ, Ahn H (2008) A recommender system using GA K-means clustering in an online shopping market. Expert Syst Appl 34:1200–1209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2006.12.025
Krishna K, Narasimha Murty M (1999) Genetic K-means algorithm. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet B 29(3):433–439. https://doi.org/10.1109/3477.764879
Kuo RJ, Wang HS, Hu T-L, Chou SH (2005) Application of ant K-means on clustering analysis. Computers & Mathematics with Applications 50 (10-12):1709–1724
Laszlo M, Mukherjee S (2007) A genetic algorithm that exchanges neighboring centers for k-means clustering. Pattern Recogn Lett 28(16):2359–2366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2007.08.006
Li S, Wheeler T, Challinor A, Lind E, Ju H, Xu Y (2010) The observed relationships between wheat and climate in China. Agric Forest Meteor 150:1412–1419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2010.07.003
Liu Y, Li Z, Xiong H, Gao X, Wu J (2010) Understanding of internal clustering validation measures. IEEE Int Conf Data Min 2010:911–916. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICDM.2010.35
Lobell DB, Field CB (2007) Global scale climate-crop yield relationships and the impact of recent warming. Environ Res Lett 2(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/2/1/014002
Luo QY, Bellotti W, Williams M, Bryan B (2005) The potential impact of climate change on wheat yield in South Australia. Agric For Meteorol 132(3–4):273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2005.08.003
Machnik L (2006) ACO documents clustering—details of processing and results of experiments. Annales UMCS Informatica AI 5:279–289 http://www.annales.umcs.lublin.pl/
Ministry of Jihad-e-Agriculture (Iran). 2009. Crop statistics. [2009-04-03]. http://dpe.agri-jahad.ir/portal/File/ShowFile.aspx?ID=bd799699-4e89-437f-8a30-5e15a014d332. (In Persian)
Mirkin B, 2011. Choosing the number of clusters. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. WIREs Data Min Knowl Discov 1: 252–260. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1002/widm.15
Mualik U, Bandyopadhyay S (2000) Genetic algorithm based clustering technique. Pattern Recogn 33(9):1455–1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(99)00137-5
Niknam T, Amiri B (2010) An efficient hybrid approach based on pso, aco, and k-means for cluster analysis. Appl Soft Comput 10(1):183–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2009.07.001
Niknam T, Taherian Fard E, Pourjafarian N, Rousta A (2011) An efficient hybrid algorithm based on modified imperialist competitive algorithm and K-means for data clustering. Eng Appl Artif Intell 24:306–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engappai.2010.10.001
Olgun M, Okan Onarcan A, Özkan K, Isik S, Sezer O, Özgisi K, Gözde Ayter N, Budak Basçiftçi Z, Ardiç M, Koyuncu O (2016) Wheat grain classification by using dense SIFT features with SVM classifier. Comput Electron Agric 122:185–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2016.01.033
Rahimi J, Khalili A, Bazrafshan J (2014) Estimation of effective precipitation for winter wheat in different regions of Iran using an extended soil-water balance model. Desert. 19(2):91–98
Rendón E, Abundez I, Arizmendi A, Quiroz EM (2011) Internal versus external cluster validation indexes. IntJ Comp Commun 1(5):27–34
Romero JR, Roncallo PF, Akkiraju PC, Ponzoni I, Echenique VC, Carballido JA (2013) Using classification algorithms for predicting durum wheat yield in the province of Buenos Aires. Comput Electron Agric 96:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compag.2013.05.006
Rostami Khaleghi M, Mohseni Saravi M, Hesami D, Rashidpour M, Salmani H (2014) Evaluation of groundwater quality in Mashhad city, using geostatistical methods in drought and wet periods. J Appl Hydrol 1(1):49–57
Rousseeuw P (1987) Silhouettes: a graphical aid to the interpretation and validation of cluster analysis. J Comput Appl Math 20(1):53–65
Salehnia N, Alizadeh A, Sanaeinejad H, Bannayan M, Zarrin A, Hoogenboom G (2017) Estimation of meteorological drought indices based on AgMERRA precipitation data and station-observed precipitation data. Journal of Arid Land 9(6):797–809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40333-017-0070-y
Shelokar PS, Jayaraman VK, Kulkarni BD (2004) An ant colony approach for clustering. Anal Chim Acta 509:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2003.12.032
Sung CS, Jin HW (2000) A tabu-search-based heuristic for clustering. Pattern Recogn 33(5):849–858. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-3203(99)00090-4
Tabari H, Talaee PH (2011a) Analysis of trends in temperature data in arid and semi-arid regions of Iran. Glob Planet Chang 79:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gloplacha.2011.07.008
Tabari H, Talaee PH (2011b) Temporal variability of precipitation over Iran: 1966–2005. J Hydrol 396(3):313–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.11.034
Tabari H, Shifteh Somee B, Rezaeian Zadeh M (2011) Testing for long-term trends in climatic variables in Iran. Atmos Res 100(1):132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosres.2011.01.005
Tsai CF, Tsai CW, Wu HC, Yang T (2004) ACODF: a novel data clustering approach for data mining in large databases. J Syst Softw 73(1):133–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0164-1212(03)00216-4
USDA Foreign Agricultural Service. 2010. Iran: crop progress report. FAS—Office of Global Analysis (OGA), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). International Operational Agriculture Monitoring Program. https://www.pecad.fas.usda.gov/pdfs/Iran/Iran_December_28_2009.pdf
Vardhan B, Ramesh D, Chander Goud O (2014) Density based clustering technique on crop yield prediction. Int J Electron Electr Eng 2(1):56–59. https://doi.org/10.12720/ijeee.2.1.56-59
Wheeler TR, Craufurd PQ, Ellis RH, Porter JR, Vara Prasad PV (2000) Temperature variability and the annual yield of crops. Agric Ecosyst Environ 82:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-8809(00)00224-3
Xu S, Bing Z, Lina Y, Shanshan L, Lianru G, 2010. Hyperspectral image clustering using ant colony optimization (ACO) improved by K-means algorithm, 3rd International Conference on Advanced Computer Theory and Engineering (ICACTE)
Zhang X, Wang J, Wu F, Fan Z, Li X (2006) A novel spatial clustering with obstacles constraints based on genetic algorithms and K-medoids, Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Intelligent Systems Design and Applications. IEEE. 1:605–610. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISDA.2006.75
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank K. Grace CRUMMER (Institute for Sustainable Food Systems, University of Florida, USA) for editing and improving the language of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported by a grant from the Ferdowsi University of Mashhad, Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehnia, N., Salehnia, N., Ansari, H. et al. Climate data clustering effects on arid and semi-arid rainfed wheat yield: a comparison of artificial intelligence and K-means approaches. Int J Biometeorol 63, 861–872 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01699-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-019-01699-w