Abstract
There existed systematic review on studies investigating the association between hip fractures and external risk factors including meteorological factors. Albeit the fact that most serious common fall injury is a hip fracture, it cannot account for all injuries forms of fall. There was a lack of systematic review covering all fall-related injury or deaths to thoroughly summarise meteorological aspects of fall. This study aimed to systematically review epidemiological studies of fall and fall-related circumstances without restriction to hip fracture. A systematic search in three databases, namely PubMed, CINAHL Plus and EMBASE, was performed. Searches in two Chinese databases named the Wanfang Med Online and the China Journal Net were done in addition. A total of 29 studies were identified. The study site, fall cases identification, meteorological factors and findings of all the selected studies were being extracted. The quality of the studies was critically appraised. We identified some of the environmental risk factors to fall among those studies. Ranging from the lower ambient temperature, the presence of snow cover, seasonal factors, and time of the day to location of fall, these factors have different levels of impact related to higher incidence or mortality of fall. To conclude, a better understanding of injury mechanisms is a prerequisite for preventive interventions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharonoff GB, Dennis MG, Elshinawy A, Zuckerman JD, Koval KJ (1998) Circumstances of falls causing hip fractures in the elderly. Clin Orthop Relat Res 348:10–14
American Geriatrics Society, British Geriatrics Society, & American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Panel on Falls Prevention (2001) Guideline for the prevention of falls in older persons. J Am Geriatr Soc 49(5):664–672
Arbes S, Berzlanovich A (2015) Injury pattern in correlation with the height of fatal falls. Wien Klin Wochenschr 127(1–2):57–61
Atherton WG, Harper WM, Abrams KR (2005) A year’s trauma admissions and the effect of the weather. Injury 36(1):40–46
Bastow MD, Rawlings J, Allison SP (1983) Undernutrition, hypothermia, and injury in elderly women with fractured femur: an injury response to altered metabolism? Lancet 1(8317):143–146
Berg WP, Alessio HM, Mills EM, Tong C (1997) Circumstances and consequences of falls in independent community-dwelling older adults. Age Ageing 26(4):261–268
Bergstralh EJ, Sinaki M, Offord KP, Wahner HW, Melton LJ (1990) Effect of season on physical activity score, back extensor muscle strength, and lumbar bone mineral density. J Bone Miner Res 5(4):371–377
Bergstrom U, Bjornstig U, Stenlund H, Jonsson H, Svensson O (2008) Fracture mechanisms and fracture pattern in men and women aged 50 years and older: a study of a 12-year population-based injury register, Umea, Sweden. Osteoporos Int 19(9):1267–1273
Bulajic-Kopjar M (2000) Seasonal variations in incidence of fractures among elderly people. Inj Prev 6(1):16–19
Campbell AJ, Spears GF, Borrie MJ, Fitzgerald JL (1988) Falls, elderly women and the cold. Gerontology 34(4):205–208
Carpenter CR (2009) Will my patient fall? Ann Emerg Med 53(3):398–400
Centers for Disease Control & Prevention (2004) Fall-related injuries during the holiday season—United States, 2000-2003. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 53(48):1127–1129
Chu LW, Chi I, Chiu AY (2005) Incidence and predictors of falls in the Chinese elderly. Ann Acad Med Singap 34(1):60–72
Chu LW, Chi I, Chiu AY (2007) Falls and fall-related injuries in community-dwelling elderly persons in Hong Kong: a study on risk factors, functional decline, and health services utilization after falls. Hong Kong Med J 13(Suppl 1):S8–S12
Collins KJ, Easton JC, Belfield-Smith H, Exton-Smith AN, Pluck RA (1985) Effects of age on body temperature and blood pressure in cold environments. Clin Sci (Lond) 69(4):465–470
Douglas S, Bunyan A, Chiu KH, Twaddle B, Maffulli N (2000) Seasonal variation of hip fracture at three latitudes. Injury 31(1):11–19
Driedger MR, Gupta A, Wells B, Dixon E, Ball CG (2016) “Oh the weather outside is frightful”: severe injury secondary to falls while installing residential Christmas lights. Injury 47(1):277–279
Gallerani M, Manfredini R (2013) Seasonal variation in the occurrence of delirium in patients admitted to medical units of a general hospital in Italy. Acta Neuropsychiatr 25(3):179–183
Gevitz K, Madera R, Newbern C, Lojo J, Johnson CC (2017) Risk of fall-related injury due to adverse weather events, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 2006-2011. Public Health Rep 132(1_suppl):53s–58s
Gyllencreutz L, Bjornstig J, Rolfsman E, Saveman BI (2015) Outdoor pedestrian fall-related injuries among Swedish senior citizens—injuries and preventive strategies. Scand J Caring Sci 29(2):225–233
Hemenway D, Colditz GA (1990) The effect of climate on fractures and deaths due to falls among white women. Accid Anal Prev 22(1):59–65
Ip D, Ip FK (2006) Elderly patients with two episodes of fragility hip fractures form a special subgroup. Journal of Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 14(3):245–248
Jacobsen SJ, Sargent DJ, Atkinson EJ, O'Fallon WM, Melton LJ (1995) Population-based study of the contribution of weather to hip fracture seasonality. Am J Epidemiol 141(1):79–83
Kannus P, Parkkari J, Koskinen S, Niemi S, Palvanen M, Jarvinen M, Vuori I (1999) Fall-induced injuries and deaths among older adults. J Am Med Assoc 281(20):1895–1899
Keatinge WR, Coleshaw SR, Cotter F, Mattock M, Murphy M, Chelliah R (1984) Increases in platelet and red cell counts, blood viscosity, and arterial pressure during mild surface cooling: factors in mortality from coronary and cerebral thrombosis in winter. Br Med J 289(6456):1405–1408
Kojima S, Furuna T, Ikeda N, Nakamura M, Sawada Y (2008) Falls among community-dwelling elderly people of Hokkaido, Japan. Geriatr Gerontol Int 8(4):272–277
Lewis LM, Lasater LC (1994) Frequency, distribution, and management of injuries due to an ice storm in a large metropolitan area. South Med J 87(2):174–178
Lilley JM, Arie T, Chilvers CE (1995) Accidents involving older people: a review of the literature. Age Ageing 24(4):346–365
Lin LW, Lin HY, Hsu CY, Rau HH, Chen PL (2015) Effect of weather and time on trauma events determined using emergency medical service registry data. Injury 46(9):1814–1820
Liu Y, Liu WW, Wang LL (2015) Lao Nian Ren Die Dao De Wei Xian Yin Su Ji Hu Li Gan Yu [Risk factors of fall among elderly]. J Mod Med Health 31(5):688–690
Lopez-Soto PJ, Smolensky MH, Sackett-Lundeen LL, De Giorgi A, Rodriguez-Borrego MA, Manfredini R, . . . Fabbian F (2016) Temporal patterns of in-hospital falls of elderly patients. Nurs Res 65(6)435–445
Lord SR, Sherrington C, Menz HB (2001) Falls in older people : risk factors and strategies for prevention. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lord S, Sherrington C, Menz H, Close J (2007) Falls in older people. Risk factors and strategies for prevention, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lund C, Sheafor ML (1985) Is your patient about to fall? J Gerontol Nurs 11(4):37–41
Luukinen H, Koski K, Kivela SL (1996) The relationship between outdoor temperature and the frequency of falls among the elderly in Finland. J Epidemiol Community Health 50(1):107
Magota C, Sawatari H, Ando S-i, Nishizaka MK, Tanaka K, Horikoshi K, . . . Chishaki A (2017) Seasonal ambient changes influence inpatient falls. Age Ageing, 46(3)513–517
Mamdani MM, Upshur RE (2001) Fall-related hospitalizations: what's in season? Can J Public Health 92(2):113–116
Mertz KJ, Lee DC, Sui X, Powell KE, Blair SN (2010) Falls among adults: the association of cardiorespiratory fitness and physical activity with walking-related falls. Am J Prev Med 39(1):15–24
Modarres R, Ouarda TB, Vanasse A, Orzanco MG, Gosselin P (2012) Modeling seasonal variation of hip fracture in Montreal, Canada. Bone 50(4):909–916
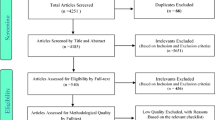
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman D, Group, P (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151(4):264–269
Mondor L, Charland K, Verma A, Buckeridge DL (2015) Weather warnings predict fall-related injuries among older adults. Age Ageing 44(3):403–408
Morency P, Voyer C, Burrows S, Goudreau S (2012) Outdoor falls in an urban context: winter weather impacts and geographical variations. Can J Public Health 103(3):218–222
Nagurney JT, Borczuk P, Thomas SH (1998) Elderly patients with closed head trauma after a fall: mechanisms and outcomes. J Emerg Med 16(5):709–713
National Center for Injury Prevention and Control (2004). Web-based injury statistics query and reporting system. Retrieved from http://www.cdc.gov/ncipc/wisqars
Parker MJ, Martin S (1994) Falls, hip fractures and the weather. Eur J Epidemiol 10(4):441–442
Parker MJ, Twemlow TR, Pryor GA (1996) Environmental hazards and hip fractures. Age Ageing 25(4):322–325
Pipas L, Schaefer N, Brown LH (2002) Falls from rooftops after heavy snowfalls: the risks of snow clearing activities. Am J Emerg Med 20(7):635–637
Riley MW, Cochran DJ (1984) Dexterity performance and reduced ambient temperature. Hum Factors 26(2):207–214
Roman Ortiz C, Tenias JM, Estarlich M, Ballester F (2015) Systematic review of the association between climate and hip fractures. Int J Biometeorol 59(10):1511–1522
Rubenstein LZ, Josephson KR (2002) The epidemiology of falls and syncope. Clinics in Geriatrics Medicine. W.B Saunders Co., Philadelphia
Ryynanen OP, Kivela SL, Honkanen R (1991) Times, places, and mechanisms of falls among the elderly. Z Gerontol 24(3):154–161
Saari P, Heikkinen E, Sakari-Rantala R, Rantanen T (2007) Fall-related injuries among initially 75- and 80-year old people during a 10-year follow-up. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 45(2):207–215
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (2015). Critical appraisal: notes and checklists. Retrieved from http://www.sign.ac.uk/methodology/checklists.html
Smith RW, Nelson DR (1998) Fractures and other injuries from falls after an ice storm. Am J Emerg Med 16(1):52–55
Stalenhoef PA, Crebolder HF, Knottnerus JA, Van Der Horst FG (1997) Incidence, risk factors, and consequences of falls among elderly subjects living in the community: a criteria-based analysis. Eur J Pubic Health 7(3):328–334
Sterling DA, O'Connor JA, Bonadies J (2001) Geriatric falls: injury severity is high and disproportionate to mechanism. J Trauma 50(1):116–119
Stevens JA, Thomas KE, Sogolow ED (2007) Seasonal patterns of fatal and nonfatal falls among older adults in the U.S. Accid Anal Prev 39(6):1239–1244
Todd C, Skelton D (2004) What are the main risk factors for falls among older people and what are the most effective interventions to prevent these falls? WHO Regional Office for Europe, Health Evidence Network report, Copenhagen
Turner RM, Hayen A, Dunsmuir WT, Finch CF (2011) Air temperature and the incidence of fall-related hip fracture hospitalisations in older people. Osteoporos Int 22(4):1183–1189
Vikman I, Nordlund A, Naslund A, Nyberg L (2011) Incidence and seasonality of falls amongst old people receiving home help services in a municipality in northern Sweden. Int J Circumpolar Health 70(2):195–204
Yeung PY, Chau PH, Woo J, Yim WT, Rainer TH (2011) Higher incidence of falls in winter among older people in Hong Kong. J Clin Gerontol Geriatr 2(1):13–16
Zautcke JL, Coker SB Jr, Morris RW, Stein-Spencer L (2002) Geriatric trauma in the state of Illinois: substance use and injury patterns. Am J Emerg Med 20(1):14–17
Acknowledgements
This study is not funded by any projects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chow, K.P., Fong, D.Y.T., Wang, M.P. et al. Meteorological factors to fall: a systematic review. Int J Biometeorol 62, 2073–2088 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-018-1627-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-018-1627-y