Abstract
Background
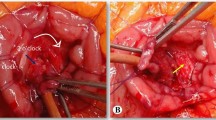
Trans-duodenal ampullectomy (TDA) is a surgical option for the treatment of selected ampullary neoplasms. The aim of this study was to evaluate our experience with TDA for the treatment of ampullary neoplasms, focusing on indications, technical aspects, and short- and long-term outcomes.
Methods
All TDAs for ampullary neoplasms performed between January 2010 and December 2018 at our institution were retrospectively evaluated. Patients had ampullary neoplasms with low-grade dysplasia or in situ carcinoma (Tis) not suitable for an endoscopic approach, ampullary carcinoma unfit for pancreaticoduodenectomy (PD), or ampullary neuroendocrine G1-tumours.
Results
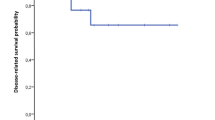
Thirty-six patients were included in the study: 9 (25.0%) with neoplasms with low-grade dysplasia, 4 (11.1%) with G1 neuroendocrine tumours and 23 (63.9%) with Tis or invasive carcinoma. Mean operative time was 252.5 min. Overall and severe (Clavien–Dindo > IIIa) morbidity rate was 44.4% and 13.9%, respectively. No 90-day mortality was observed. At follow-up, no deaths were observed and local recurrence rate was 11.1% for patients with ampullary adenomas with low-grade dysplasia. Among four patients with neuroendocrine neoplasms, only one developed recurrence (pulmonary). Tis, T1 and T2 lesions were found in 16 (69.6%), 2 (8.7%) and 5 (21.7%) patients, respectively: recurrence occurred in 3 patients with Tis lesions (one malignant), no patients with T1 neoplasms and 2 patients with T2 lesions (3 patients had a survival of > 3 years).
Conclusions
TDA is a feasible and effective surgical procedure for the treatment of ampullary adenomas with low-grade dysplasia when endoscopic approach is contraindicated or has failed. For lesions with evidence of malignancy, TDA seems to be an oncological safe procedure for Tis ampullary cancer and a good palliative procedure for patients unfit for PD. Moreover, TDA may be appropriate for the treatment of G1 ampullary neuroendocrine neoplasms. A large multicentre study of TDA for early ampullary cancers is needed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results (SEER). SEER stat database: incidence-SEER regs limited use. http://www.seer.cancer.gov. Accessed 2019
Treitschke F, Beger HG (1999) Local resection of benign periampullary tumors. Ann Oncol 10(Suppl 4):212–214
Stolte M, Psherer C (1996) Adenoma-carcinoma sequence in the papilla of Vater. Scand J Gastroenterol 60:497–500
Hernandez LV, Catalano MF (2008) Endoscopic papillectomy. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24:617–622
De Palma GD (2014) Endoscopic papillectomy: indications, techniques, and results. World J Gastroenterol 20:1537–1543
Kobayashi A, Konishi M, Nakagohri T, Takahashi S, Kinoshita T (2006) Therapeutic approach to tumours of the ampulla of Vater. Am J Surg 192:161–164
Winter JM, Cameron JL, Olino K, Herman JM, de Jong MC, Hruban RH, Wolfgang CL, Eckhauser F, Edil BH, Choti MA, Schulick RD, Pawlik TM (2010) Clinicopathological analysis of ampullary neoplasms in 450 patients: implications for surgical strategy and long-term prognosis. J Gastrointest Surg 14:379–387
Halsted WS (1989) Contributions to the surgery of the bile passages, especially of the common bile duct. Boston Med Surg J 141:645–654
Kim AL, Choi YI (2017) Safety of duodenal ampullectomy for benign periampullary tumours. Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg 21:146–150
Dubuois M, Labgaa I, Dorta G, Halkic N (2016) Endoscopic and surgical ampullectomy for non-invasive ampullary tumours: short-term outcomes. BioScience Trends 10:507–511
Lindell G, Borch K, Tingstedt B, Enell EL, Ihse I (2003) Management of cancer of the ampulla of Vater: does local resection play a role? Dig Surg 20:511–515
Schneider L, Contin P, Fritz S, Strobel O, Buchler MW, Hackert T (2016) Surgical ampullectomy: an underestimated operation in the era of endoscopy. HPB 18:65–71
Song J, Liu H, Li Z, Yang C, Sun Y, Wang C (2015) Long-term prognosis of surgical treatment for early ampullary cancers and implications for local ampullectomy. BMC Surg 15:32
Sauvanet A, Dokmak S, Cros J, Cazals-Hatem D, Ponsot P, Palazzo M (2017) Surgical ampullectomy with complete resection of the common bile duct: a new-procedure for radical resection of non-invasive ampulloma with biliary extension. J Gastrointest Surg 21:1533–1539
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213
Bassi C, Marchegiani G, Dervenis C, Sarr M, Abu-Hilal M, Adham M, Allen P, Andersson R, Asbun HJ, Besselink MG, Conlon K, Del Chiaro M, Falconi M, Fernandez-Cruz L, Fernandez-Del-Castillo C, Fingerhut A, Friess H, Gouma DJ, Hackert T, Izbicki J, Lillemoe KD, Neoptolemos JP, Olah A, Schulick R, Shrikhande SV, Takada T, Takaori K, Traverso W, Vollmer CR, Wolfgang CL, Yeo CJ, Salvia R, Buchler M, International Study Group on Pancreatic Surgery (ISGPS) (2017) The 2016 update of the International Study Group (ISGPS) definition and grading of postoperative pancreatic fistula: 11 years after. Surgery 161:584–591
AJCC (2017) Cancer staging manual, 8th edn. Springer, New York. Corr. 3rd printing 2018 Edition
Petrone G, Ricci R, Familiari P, Inzani F, Matsuoka M, Mutignani M, Delle Fave G, Costamagna G, Rindi G (2013) Endoscopic snare papillectomy: a possible radical treatment for a subgroup of T1 ampullary adenocarcinomas. Endoscopy 45:401–404
Will U, Muller AK, Fueldner F, Wanzar I, Meyer F (2013) Endoscopi papillectomy: data of a prospective observational study. World J Gastroenterol 19:4316–4324
Bellizzi AM, Kahaleh M, Stelow EB (2009) The assessment of specimens procedure by endoscopic ampullectomy. Am J Clin Pathol 132:506–513
Lee SY, Jang KT, Lee KT, Lee JK, Choi SH, Heo JS, Paik SW, Rhen JC (2006) Can endoscopic resection be applied for early stage ampulla of Vater cancer? Gastrointest Endosc 63:783–788
Seewald S, Omar S, Soehendra N (2006) Endoscopic resection of tumours of the ampulla of Vater: how far up and how deep down can we go? Gastrointest Endosc 63:789–791
Tsuji S, Itoi T, Sofuni A, Mukais S, Tonozuka R, Morivasu F (2015) Tips and tricks in endoscopic papillectomy of ampullary tumours: single-center experience with large case series (with videos). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 22:E22–E27
Panzeri F, Crippa S, Castelli P, Aleotti F, Pucci A, Partelli S, Zamboni G, Falconi M (2015) Management of ampullary neoplasms: a tailored approach between endoscopy and surgery. World J Gastroenterol 21:7970–7987
Ceppa EP, BurbridgeRA Rialon KL, Omotosho PA, Emick D, Jowell PS, Branch MS, Pappas TN (2013) Endoscopic versus surgical ampullectomy: an algorithm to treat disease of the ampulla of Vater. Ann Surg 257:315–322
Hong S, Song KB, Lee YJ, Park KM, Kim SC, Hwang DW, Lee KH, Shin SH, Kwon J, Ma CH, Hwang S, Park G, Park Y, Lee SJ, Kim YW (2018) Transduodenal ampullectomy for ampullary tumours—single center experience of consecutive 26 patients. Ann Surg Treat Res 95:22–28
Lee H, Park JY, Kwon W, Heo JS, Choi DW, Choi SH (2016) Transduodenal ampullectomy for the treatment of early-stage ampulla of Vater cancer. World J Surg 40:967–973
Trikudanathan G, Niei B, Attam R, Arain M, Shaukat A (2014) Staging accuracy of ampullary tumours by endoscopic ultrasound: meta-analysis and systematic review. Dig Endosc 26:617–626
Milanetto AC, Pasquali C, Da Broi M, Brambilla T, Capretti G, Zerbi A (2018) Ampullary neuroendocrine neoplasms: surgical experience of a rare and challenging entity. Langenbecks Arch Surg 403:581–589
Roggins KK, Yeh JJ, Ferrone CR, Riedel E, Gardas H, Klimstra DS, Jacques DP, Brennan MF (2005) Limitations of ampullectomy in the treatment of nonfamilial ampullary neoplasms. Ann Surg Oncol 12:971–980
Klein P, Reingruber B, Kastil S, Dworak O, Hohenberger W (1996) Is local excision of pT1-ampullary carcinomas justified? Eur J Surg Oncol 22:366–378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
Gennaro Nappo, Damiano Gentile, Jacopo Galvanin, Giovanni Capretti, Cristina Ridolfi, Tommasangelo Petitti, Paola Spaggiari, Silvia Carrara, Francesca Gavazzi, Alessandro Repici and Alessandro Zerbi have nothing to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nappo, G., Gentile, D., Galvanin, J. et al. Trans-duodenal ampullectomy for ampullary neoplasms: early and long-term outcomes in 36 consecutive patients. Surg Endosc 34, 4358–4368 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-07206-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-019-07206-x