Abstract
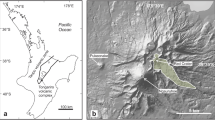
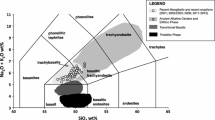
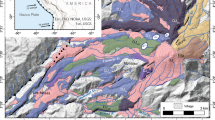
The bulk composition of magma erupted from Volcán Arenal has remained nearly constant (SiO2 = 53.6–54.9 wt%; MgO = 5.0–4.5 wt%) during almost 30 years of continuous activity (1969–1996). None the less, clinopyroxene (cpx) phenocrysts and their spinel inclusions record a much more complex open-system evolution in which steady-state production of the erupted basaltic andesitic magma is linked to episodic injections of basalt into Arenal's magma conduit/reservoir system. High-resolution major element zoning profiles (electron microprobe) on a large number of phenocrysts (>14,000 analyses), tied to back-scattered electron (BSE) images, have been used to assess the compositional characteristics of the magmatic end members as well as the timing and dynamics of magma replenishment events. No two cpx phenocrysts have exactly the same zoning profile. The vast majority of our analyses record the crystallization of cpx (Cr2O3 <0.12 wt%; Mg# = 65–79; Al/Ti = 2–7) from a liquid comparable to or more evolved than erupted magma compositions. However, half of all cpx grains are cored by high-Cr cpx (Cr2O3 = 0.2–0.72 wt%) or contain similar basaltic compositions as abrupt growth bands in phenocrysts with and without high-Cr cores; phenocrysts with high-Cr cpx occur throughout the ongoing activity. In a few cases, high-Cr cpx occurs very near the outer margin of the grain without an apparent growth hiatus, particularly in 1968/69 and 1992/93. The main conclusions are: (1) all basaltic andesitic lavas erupted at Arenal during the ongoing activity that began in July, 1968, are the products of magma mixing, (2) clinopyroxenes record multiple replenishment events of basaltic magma in contrast to the near constancy of erupted bulk compositions, (3) some phenocrysts preserve records of multiple interactions with basaltic magmas requiring magmatic processes to operate on timescales shorter than residence times of some phenocrysts, (4) multiple occurrences of clinopyroxene with high-Cr rims suggest that basalt replenishment events have occurred with sub-decadal frequency and may predate eruption by months or less. From this we infer that Arenal volcano is underlain by a continuously active, small-volume magmatic reservoir maintained in quasi-steady state by basalt recharge over several decades. The monotony of erupting Arenal magmas implies that fractionation, recharge, ascent, and eruption are well balanced in order for magmas to be essentially uniform while containing phenocrysts with vastly different growth histories at the time of eruption.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Streck, M.J., Dungan, M.A., Malavassi, E. et al. The role of basalt replenishment in the generation of basaltic andesites of the ongoing activity at Arenal volcano, Costa Rica: evidence from clinopyroxene and spinel. Bull Volcanol 64, 316–327 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-002-0209-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00445-002-0209-2