Abstract
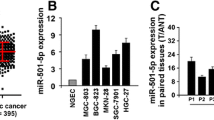
Esophageal cancer (EC) is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Recent studies highlight roles for microRNAs (miRNAs) in EC. Microarray analysis identified miR-194 as downregulated in EC. However, little is known about the role of miR-194 in regulating self-renewal or other biological properties of EC stem cells. RT-qPCR and Western blot confirmed the downregulation of miR-194 in EC stem cells and revealed the upregulation of protein regulator of cytokinesis 1 (PRC1) in EC. Dual-luciferase reporter assay confirmed miR-194 targeting of PRC1 resulting in its downregulation. MiR-194 overexpression or PRC1 silencing reduced PRC1 expression, preventing the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway prevented the proliferation, invasion, and self-renewal of EC stem cells while promoting apoptosis. Furthermore, overexpressing miR-194 or silencing PRC1 in nude mice decreased the tumor formation ability of EC stem cells in vivo. Taken together, miR-194 prevents the progression of EC by downregulating PRC1 and inactivating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.










Similar content being viewed by others

References
Alao JP (2007) The regulation of cyclin D1 degradation: roles in cancer development and the potential for therapeutic invention. Mol Cancer 6:24
Baarsma HA, Konigshoff M, Gosens R (2013) The WNT signaling pathway from ligand secretion to gene transcription: molecular mechanisms and pharmacological targets. Pharmacol Ther 138(1):66–83
Chen Q, Jin M, Yang F, Zhu J, Xiao Q, Zhang L (2013) Matrix metalloproteinases: inflammatory regulators of cell behaviors in vascular formation and remodeling. Mediators Inflamm 2013:928315
Chen X, Wang Y, Zang W, Du Y, Li M, Zhao G (2015) miR-194 targets RBX1 gene to modulate proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Tumour Biol 36(4):2393–2401
Chen Y, Jiang T, Mao A, Xu J (2014) Esophageal cancer stem cells express PLGF to increase cancer invasion through MMP9 activation. Tumour Biol 35(12):12749–12755
Chi H (2015) miR-194 regulated AGK and inhibited cell proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma by reducing PI3K-Akt-FoxO3a signaling. Biomed Pharmacother 71:53–57
Cui G, Liu D, Li W, Li Y, Liang Y, Shi W, Zhao S (2017) Original research: miR-194 inhibits proliferation and invasion and promotes apoptosis by targeting KDM5B in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 242(1):45–52
Domper Arnal MJ, Ferrandez Arenas A, Lanas Arbeloa A (2015) Esophageal cancer: risk factors, screening and endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries. World J Gastroenterol 21(26):7933–7943
Duex JE, Comeau L, Sorkin A, Purow B, Kefas B (2011) Usp18 regulates epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor expression and cancer cell survival via microRNA-7. J Biol Chem 286(28):25377–25386
Gao D, Xu Z, Zhang X, Wang H, Wang Y, Min W (2013) Molecular cloning, immunohistochemical localization, characterization and expression analysis of caspase-9 from the purse red common carp (Cyprinus carpio) exposed to cadmium. Aquat Toxicol 142–143:53–62
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) affy–analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20(3):307–315
Hemmatzadeh M, Mohammadi H, Karimi M, Musavishenas MH, Baradaran B (2016) Differential role of microRNAs in the pathogenesis and treatment of Esophageal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 82:509–519
Huang FL, Yu SJ (2018) Esophageal cancer: risk factors, genetic association, and treatment. Asian J Surg 41(3):210–215
Kimos MC, Wang S, Borkowski A, Yang GY, Yang CS, Perry K, Olaru A, Deacu E, Sterian A, Cottrell J, Papadimitriou J, Sisodia L, Selaru FM, Mori Y, Xu Y, Yin J, Abraham JM, Meltzer SJ (2004) Esophagin and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) are biomarkers of human esophageal neoplastic progression. Int J Cancer 111(3):415–417
Leveille N, Vermeulen L (2016) Polycomb complex PRC1 as gatekeeper of intestinal stem cell identity. Stem Cell Investig 3:22
Li Y, Ma J, Guo Q, Duan F, Tang F, Zheng P, Zhao Z, Lu G (2009) Overexpression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus 22(8):664–667
Liu X, Li Y, Meng L, Liu XY, Peng A, Chen Y, Liu C, Chen H, Sun S, Miao X, Zhang Y, Zheng L, Huang K (2018) Reducing protein regulator of cytokinesis 1 as a prospective therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis 9(5):534
Lovaas JD, Zhu L, Chiao CY, Byles V, Faller DV, Dai Y (2013) SIRT1 enhances matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression and tumor cell invasion in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 73(5):522–530
Maekawa T, Kulwattanaporn P, Hosur K, Domon H, Oda M, Terao Y, Maeda T, Hajishengallis G (2017) Differential expression and roles of secreted frizzled-related protein 5 and the Wingless homolog Wnt5a in periodontitis. J Dent Res 96(5):571–577
Meves V, Behrens A, Pohl J (2015) Diagnostics and early diagnosis of esophageal cancer. Viszeralmedizin 31(5):315–318
Miao J, Wang W, Wu S, Zang X, Li Y, Wang J, Zhan R, Gao M, Hu M, Li J, Chen S (2018) miR-194 suppresses proliferation and migration and promotes apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by targeting CDH2. Cell Physiol Biochem 45(5):1966–1974
Ran RZ, Chen J, Cui LJ, Lin XL, Fan MM, Cong ZZ, Zhang H, Tan WF, Zhang GQ, Zhang YJ (2019) miR-194 inhibits liver cancer stem cell expansion by regulating RAC1 pathway. Exp Cell Res 378(1):66–75
Rotschafer SE, Allen-Sharpley MR, Cramer KS (2016) Axonal cleaved caspase-3 regulates axon targeting and morphogenesis in the developing auditory brainstem. Front Neural Circuits 10:84
Shimo A, Nishidate T, Ohta T, Fukuda M, Nakamura Y, Katagiri T (2007) Elevated expression of protein regulator of cytokinesis 1, involved in the growth of breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci 98(2):174–181
Smyth GK (2004) Linear models and empirical Bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 3:Article3.
Song Y, Zhao F, Wang Z, Liu Z, Chiang Y, Xu Y, Gao P, Xu H (2012) Inverse association between miR-194 expression and tumor invasion in gastric cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 19(Suppl 3):S509-517
Strillacci A, Valerii MC, Sansone P, Caggiano C, Sgromo A, Vittori L, Fiorentino M, Poggioli G, Rizzello F, Campieri M, Spisni E (2013) Loss of miR-101 expression promotes Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway activation and malignancy in colon cancer cells. J Pathol 229(3):379–389
Su R, Cao S, Ma J, Liu Y, Liu X, Zheng J, Chen J, Liu L, Cai H, Li Z, Zhao L, He Q, Xue Y (2017) Knockdown of SOX2OT inhibits the malignant biological behaviors of glioblastoma stem cells via up-regulating the expression of miR-194-5p and miR-122. Mol Cancer 16(1):171
Sun B, Fang YT, Jin DJ, Chen ZY, Li ZY, Gu XD, Xiang JB (2019) miR-194 inhibits the proliferation of SW620 colon cancer stem cells through downregulation of SSH2 expression. Cancer Manag Res 11:10229–10238
Tan Z, Wortman M, Dillehay KL, Seibel WL, Evelyn CR, Smith SJ, Malkas LH, Zheng Y, Lu S, Dong Z (2012) Small-molecule targeting of proliferating cell nuclear antigen chromatin association inhibits tumor cell growth. Mol Pharmacol 81(6):811–819
Wang B, Shen ZL, Gao ZD, Zhao G, Wang CY, Yang Y, Zhang JZ, Yan YC, Shen C, Jiang KW, Ye YJ, Wang S (2015) MiR-194, commonly repressed in colorectal cancer, suppresses tumor growth by regulating the MAP4K4/c-Jun/MDM2 signaling pathway. Cell Cycle 14(7):1046–1058
Wang L, Wu X, Shi T, Lu L (2013) Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced corneal epithelial wound healing through nuclear factor kappaB subtype-regulated CCCTC binding factor (CTCF) activation. J Biol Chem 288(34):24363–24371
Wang Y, Shi F, Xing GH, Xie P, Zhao N, Yin YF, Sun SY, He J, Wang Y, Xuan SY (2017) Protein regulator of cytokinesis PRC1 confers chemoresistance and predicts an unfavorable postoperative survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. J Cancer 8(5):801–808
Zang B, Huang G, Wang X, Zheng S (2015) HPV-16 E6 promotes cell growth of esophageal cancer via downregulation of miR-125b and activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 8(10):13687–13694
Zeng H, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zuo T, Xia C, Zou X, Chen W (2016) Esophageal cancer statistics in China, 2011: estimates based on 177 cancer registries. Thorac Cancer 7(2):232–237
Zhan P, Zhang B, Xi GM, Wu Y, Liu HB, Liu YF, Xu WJ, Zhu QQ, Cai F, Zhou ZJ, Miu YY, Wang XX, Jin JJ, Li Q, Qian LP, Lv TF, Song Y (2017) PRC1 contributes to tumorigenesis of lung adenocarcinoma in association with the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Cancer 16(1):108
Zhang C, Shu L, Kim H, Khor TO, Wu R, Li W, Kong AN (2016) Phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) suppresses prostate cancer cell invasion epigenetically through regulating microRNA-194. Mol Nutr Food Res 60(6):1427–1436
Zhang M, Linghu E, Zhan Q, He T, Cao B, Brock MV, Herman JG, Xiang R, Guo M (2016) Methylation of DACT2 accelerates esophageal cancer development by activating Wnt signaling. Oncotarget 7(14):17957–17969
Zhang W, Shen C, Li C, Yang G, Liu H, Chen X, Zhu D, Zou H, Zhen Y, Zhang D, Zhao S (2016) miR-577 inhibits glioblastoma tumor growth via the Wnt signaling pathway. Mol Carcinog 55(5):575–585
Zheng H, Takahashi H, Murai Y, Cui Z, Nomoto K, Niwa H, Tsuneyama K, Takano Y (2006) Expressions of MMP-2, MMP-9 and VEGF are closely linked to growth, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res 26(5A):3579–3583
Zhu X, Li D, Yu F, Jia C, Xie J, Ma Y, Fan S, Cai H, Luo Q, Lv Z, Fan L (2016) miR-194 inhibits the proliferation, invasion, migration, and enhances the chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting forkhead box A1 protein. Oncotarget 7(11):13139–13152
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge and appreciate our colleagues for their valuable efforts and comments on this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Research involving human and animal participants
Animal experiments strictly abide by the relevant regulations of Guidance on Treating Experimental Animals released by the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, as well as the Guidelines for the Protection and Use of Laboratory Animals released by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) of the USA. Significant efforts were made to minimize both the number of animals used and their pain and suffering.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, S., Weng, Y. & Miao, F. MicroRNA-194 inhibits PRC1 activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to prevent tumorigenesis by elevating self-renewal of non-side population cells and side population cells in esophageal cancer stem cells. Cell Tissue Res 384, 353–366 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-021-03412-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-021-03412-z