Abstract
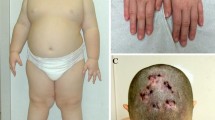
Submicroscopic duplications along the long arm of the X-chromosome with known phenotypic consequences are relatively rare events. The clinical features resulting from such duplications are various, though they often include intellectual disability, microcephaly, short stature, hypotonia, hypogonadism and feeding difficulties. Female carriers are often phenotypically normal or show a similar but milder phenotype, as in most cases the X-chromosome harbouring the duplication is subject to inactivation. Xq28, which includes MECP2 is the major locus for submicroscopic X-chromosome duplications, whereas duplications in Xq25 and Xq26 have been reported in only a few cases. Using genome-wide array platforms we identified overlapping interstitial Xq25q26 duplications ranging from 0.2 to 4.76 Mb in eight unrelated families with in total five affected males and seven affected females. All affected males shared a common phenotype with intrauterine- and postnatal growth retardation and feeding difficulties in childhood. Three had microcephaly and two out of five suffered from epilepsy. In addition, three males had a distinct facial appearance with congenital bilateral ptosis and large protruding ears and two of them showed a cleft palate. The affected females had various clinical symptoms similar to that of the males with congenital bilateral ptosis in three families as most remarkable feature. Comparison of the gene content of the individual duplications with the respective phenotypes suggested three critical regions with candidate genes (AIFM1, RAB33A, GPC3 and IGSF1) for the common phenotypes, including candidate loci for congenital bilateral ptosis, small head circumference, short stature, genital and digital defects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen RC, Zoghbi HY, Moseley AB, Rosenblatt HM, Belmont JW (1992) Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X-chromosome inactivation. Am J Hum Genet 51:1229–1239
Armstrong L, McGowan-Jordan J, Brierley K, Allanson JE (2003) De novo dup(X) (q22.3q26) in a girl with evidence that functional disomy of X-material is the cause of her abnormal phenotype. Am J Med Genet A 116A:71–76
Aughton DJ, AlSaadi AA, Johnson JA, Transue DJ, Trock GL (1993) Dir dup(X) (q13 ⟶ qter) in a girl with growth retardation, microcephaly, developmental delay, seizures, and minor anomalies. Am J Med Genet 46:159–164
Bauters M, Van EH, Marynen P, Froyen G (2005) X chromosome array-CGH for the identification of novel X-linked mental retardation genes. Eur J Med Genet 48:263–275
Bauters M, Van EH, Friez MJ, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Zenker M, Vianna-Morgante AM, Rosenberg C, Ignatius J, Raynaud M, Hollanders K, Govaerts K, Vandenreijt K, Niel F, Blanc P, Stevenson RE, Fryns JP, Marynen P, Schwartz CE, Froyen G (2008) Nonrecurrent MECP2 duplications mediated by genomic architecture-driven DNA breaks and break-induced replication repair. Genome Res 18:847–858
Brown D, Yu BD, Joza N, Benit P, Meneses J, Firpo M, Rustin P, Penninger JM, Martin GR (2006) Loss of Aif function causes cell death in the mouse embryo, but the temporal progression of patterning is normal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:9918–9923
Capurro MI, Xiang YY, Lobe C, Filmus J (2005) Glypican-3 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by stimulating canonical Wnt signaling. Cancer Res 65:6245–6254
Capurro MI, Xu P, Shi W, Li F, Jia A, Filmus J (2008) Glypican-3 inhibits Hedgehog signaling during development by competing with patched for Hedgehog binding. Dev Cell 14:700–711
Cheng SF, Rauen KA, Pinkel D, Albertson DG, Cotter PD (2005) Xq chromosome duplication in males: clinical, cytogenetic and array CGH characterization of a new case and review. Am J Med Genet A 135:308–313
Cheng E, Trombetta SE, Kovacs D, Beech RD, Ariyan S, Reyes-Mugica M, McNiff JM, Narayan D, Kluger HM, Picardo M, Halaban R (2006) Rab33A: characterization, expression, and suppression by epigenetic modification. J Invest Dermatol 126:2257–2271
Chiao E, Fisher P, Crisponi L, Deiana M, Dragatsis I, Schlessinger D, Pilia G, Efstratiadis A (2002) Overgrowth of a mouse model of the Simpson-Golabi–Behmel syndrome is independent of IGF signaling. Dev Biol 243:185–206
Cho N, Morre DJ (2009) Early developmental expression of a normally tumor-associated and drug-inhibited cell surface-located NADH oxidase (ENOX2) in non-cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58:547–552
D’Adamo P, Menegon A, Lo NC, Grasso M, Gulisano M, Tamanini F, Bienvenu T, Gedeon AK, Oostra B, Wu SK, Tandon A, Valtorta F, Balch WE, Chelly J, Toniolo D (1998) Mutations in GDI1 are responsible for X-linked non-specific mental retardation. Nat Genet 19:134–139
Garcia-Heras J, Martin JA, Day DW, Scacheri P, Witchel SF (1997) “De novo” duplication Xq23 ⟶ Xq26 of paternal origin in a girl with a mildly affected phenotype. Am J Med Genet 70:404–408
Ghezzi D, Sevrioukova I, Invernizzi F, Lamperti C, Mora M, D’Adamo P, Novara F, Zuffardi O, Uziel G, Zeviani M (2010) Severe X-linked mitochondrial encephalomyopathy associated with a mutation in apoptosis-inducing factor. Am J Hum Genet 86:639–649
Giannandrea M, Bianchi V, Mignogna ML, Sirri A, Carrabino S, D’Elia E, Vecellio M, Russo S, Cogliati F, Larizza L, Ropers HH, Tzschach A, Kalscheuer V, Oehl-Jaschkowitz B, Skinner C, Schwartz CE, Gecz J, Van EH, Raynaud M, Chelly J, de Brouwer AP, Toniolo D, D’Adamo P (2010) Mutations in the small GTPase gene RAB39B are responsible for X-linked mental retardation associated with autism, epilepsy, and macrocephaly. Am J Hum Genet 86:185–195
Klein JA, Longo-Guess CM, Rossmann MP, Seburn KL, Hurd RE, Frankel WN, Bronson RT, Ackerman SL (2002) The harlequin mouse mutation downregulates apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 419:367–374
Lee ST, McGlennen RC, Litz CE (1994) Clonal determination by the fragile X (FMR1) and phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) genes in hematological malignancies. Cancer Res 54:5212–5216
Lugtenberg D, de Brouwer AP, Kleefstra T, Oudakker AR, Frints SG, Schrander-Stumpel CT, Fryns JP, Jensen LR, Chelly J, Moraine C, Turner G, Veltman JA, Hamel BC, de Vries BB, van BH, Yntema HG (2006) Chromosomal copy number changes in patients with non-syndromic X-linked mental retardation detected by array CGH. J Med Genet 43:362–370
Madrigal I, Fernandez-Burriel M, Rodriguez-Revenga L, Cabrera JC, Marti M, Mur A, Mila M (2010) Xq26.2-q26.3 microduplication in two brothers with intellectual disabilities: clinical and molecular characterization. J Hum Genet 55:822–826
McMullan TF, Collins AR, Tyers AG, Robinson DO (2000) A novel X-linked dominant condition: X-linked congenital isolated ptosis. Am J Hum Genet 66:1455–1460
Morre DJ, Morre DM (2003) Cell surface NADH oxidases (ECTO-NOX proteins) with roles in cancer, cellular time-keeping, growth, aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Free Radic Res 37:795–808
Pilia G, Hughes-Benzie RM, MacKenzie A, Baybayan P, Chen EY, Huber R, Neri G, Cao A, Forabosco A, Schlessinger D (1996) Mutations in GPC3, a glypican gene, cause the Simpson–Golabi–Behmel overgrowth syndrome. Nat Genet 12:241–247
Ramocki MB, Tavyev YJ, Peters SU (2010) The MECP2 duplication syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 152A:1079–1088
Ricks CB, Masand R, Fang P, Roney EK, Cheung SW, Scott DA (2010) Delineation of a 1.65 Mb critical region for hemihyperplasia and digital anomalies on Xq25. Am J Med Genet A 152A:453–458
Rinaldi C, Grunseich C, Sevrioukova IF, Schindler A, Horkayne-Szakaly I, Lamperti C, Landoure G, Kennerson ML, Burnett BG, Bonnemann C, Biesecker LG, Ghezzi D, Zeviani M, Fischbeck KH (2012) Cowchock syndrome is associated with a mutation in apoptosis-inducing factor. Am J Hum Genet 91:1095–1102
Sanlaville D, Prieur M, de Blois MC, Genevieve D, Lapierre JM, Ozilou C, Picq M, Gosset P, Morichon-Delvallez N, Munnich A, Cormier-Daire V, Baujat G, Romana S, Vekemans M, Turleau C (2005) Functional disomy of the Xq28 chromosome region. Eur J Hum Genet 13:579–585
Sanlaville D, Schluth-Bolard C, Turleau C (2009) Distal Xq duplication and functional Xq disomy. Orphanet J Rare Dis 4:4
Schroer RJ, Beaudet AL, Shinawi M, Sahoo T, Patel A, Sun Q, Skinner C, Stevenson RE (2012) Duplication of OCRL and adjacent genes associated with autism but not Lowe syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 158A:2602–2605
Shaikh TH, Gai X, Perin JC, Glessner JT, Xie H, Murphy K, O’Hara R, Casalunovo T, Conlin LK, D’Arcy M, Frackelton EC, Geiger EA, Haldeman-Englert C, Imielinski M, Kim CE, Medne L, Annaiah K, Bradfield JP, Dabaghyan E, Eckert A, Onyiah CC, Ostapenko S, Otieno FG, Santa E, Shaner JL, Skraban R, Smith RM, Elia J, Goldmuntz E, Spinner NB, Zackai EH, Chiavacci RM, Grundmeier R, Rappaport EF, Grant SF, White PS, Hakonarson H (2009) High-resolution mapping and analysis of copy number variations in the human genome: a data resource for clinical and research applications. Genome Res 19:1682–1690
Stankiewicz P, Thiele H, Schlicker M, Cseke-Friedrich A, Bartel-Friedrich S, Yatsenko SA, Lupski JR, Hansmann I (2005) Duplication of Xq26.2-q27.1, including SOX3, in a mother and daughter with short stature and dyslalia. Am J Med Genet A 138:11–17
Sun Y, Bak B, Schoenmakers N, van Trotsenburg AS, Oostdijk W, Voshol P, Cambridge E, White JK, le TP, Gharavy SN, Martinez-Barbera JP, Stokvis-Brantsma WH, Vulsma T, Kempers MJ, Persani L, Campi I, Bonomi M, Beck-Peccoz P, Zhu H, Davis TM, Hokken-Koelega AC, Del Blanco DG, Rangasami JJ, Ruivenkamp CA, Laros JF, Kriek M, Kant SG, Bosch CA, Biermasz NR, Appelman-Dijkstra NM, Corssmit EP, Hovens GC, Pereira AM, den Dunnen JT, Wade MG, Breuning MH, Hennekam RC, Chatterjee K, Dattani MT, Wit JM, Bernard DJ (2012) Loss-of-function mutations in IGSF1 cause an X-linked syndrome of central hypothyroidism and testicular enlargement. Nat Genet 44:1375–1381
Tachdjian G, Aboura A, Benkhalifa M, Creveaux I, Foix-Helias L, Gadisseux JF, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Mohammed M, Labrune P (2004) De novo interstitial direct duplication of Xq21.1q25 associated with skewed X-inactivation pattern. Am J Med Genet A 131:273–280
Van EH, Bauters M, Ignatius J, Jansen M, Raynaud M, Hollanders K, Lugtenberg D, Bienvenu T, Jensen LR, Gecz J, Moraine C, Marynen P, Fryns JP, Froyen G (2005) Duplication of the MECP2 region is a frequent cause of severe mental retardation and progressive neurological symptoms in males. Am J Hum Genet 77:442–453
Vandewalle J, Van EH, Govaerts K, Verbeeck J, Zweier C, Madrigal I, Mila M, Pijkels E, Fernandez I, Kohlhase J, Spaich C, Rauch A, Fryns JP, Marynen P, Froyen G (2009) Dosage-dependent severity of the phenotype in patients with mental retardation due to a recurrent copy-number gain at Xq28 mediated by an unusual recombination. Am J Hum Genet 85:809–822
Veltman JA, Yntema HG, Lugtenberg D, Arts H, Briault S, Huys EH, Osoegawa K, de JP, Brunner HG, Geurts van KA, van BH, Schoenmakers EF (2004) High resolution profiling of X-chromosomal aberrations by array comparative genomic hybridisation. J Med Genet 41:425–432
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the patients for their invaluable contribution to this study. Wilhelm Johannsen Centre for Functional Genome Research is established by the Danish National Research Foundation. RU was supported by a grant from the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, NGFNplus, Grant No. PNR-01GS08161.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
R. S. Møller and L. R. Jensen contributed equally to this work.
Z. Tümer and T. Kleefstra contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Møller, R.S., Jensen, L.R., Maas, S.M. et al. X-linked congenital ptosis and associated intellectual disability, short stature, microcephaly, cleft palate, digital and genital abnormalities define novel Xq25q26 duplication syndrome. Hum Genet 133, 625–638 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1403-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-013-1403-3