Abstract
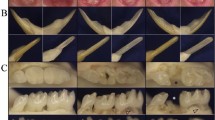
The dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP) gene (4q21.3) encodes two major noncollagenous dentin matrix proteins: dentin sialoprotein (DSP) and dentin phosphoprotein (DPP). Defects in the human gene encoding DSPP cause inherited dentin defects, and these defects can be associated with bilateral progressive high-frequency sensorineural hearing loss. Clinically, five different patterns of inherited dentin defects are distinguished and are classified as dentinogenesis imperfecta (DGI) types I, II, and III, and dentin dysplasia types I and II. The genetic basis for this clinical heterogeneity is unknown. Among the 11 members recruited from the studied kindred, five were affected with autosomal dominant DGI type II. The mutation (g.1188C→G, IVS2-3C→G) lay in the third from the last nucleotide of intron 2 and changed its sequence from CAG to GAG. The mutation was correlated with the affection status and was absent in 104 unaffected individuals (208 alleles) with the same ethnic and geological background. The proband was in the primary dentition stage and presented with multiple pulp exposures. The occlusal surface of his dental enamel was generally abraded, and the dentin was heavily worn and uniformly shaded brown. The dental pulp chambers appeared originally to be within normal limits without any sign of obliteration, but over time (by age 4), the pulp chambers became partially or completely obliterated. The oldest affected member (age 59) showed mild hearing loss at high-frequency (8 kHz). Permanent dentition was severely affected in the adults, who had advanced dental attrition, premature loss of teeth, and extensive dental reconstruction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bayes M, Hartung AJ, Ezer S, Pispa J, Thesleff I, Srivastava AK, Kere J (1998) The anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia gene (EDA) undergoes alternative splicing and encodes ectodysplasin-A with deletion mutations in collagenous repeats. Hum Mol Genet 7:1661–1669
Bischoff AM, Luijendijk MW, Huygen PL, Duijnhoven G van, De Leenheer EM, Oudesluijs GG, Van Laer L, Cremers FP, Cremers CW, Kremer H (2004) A novel mutation identified in the DFNA5 gene in a Dutch family: a clinical and genetic evaluation. Audiol Neurotol 9:34–46
Bixler D (1976) Heritable disorders affecting dentin. In: Stewart RE, Prescott GH (eds) Oral facial genetics. Mosby, St. Louis, pp 227–261
Black DL (2003) Mechanisms of alternative pre-messenger RNA splicing. Annu Rev Biochem 72:291–336
Butler WT (1987) Dentin-specific proteins. Methods Enzymol 145:290–303
Butler WT (1992) Dentin extracellular matrix and dentinogenesis. Oper Dent 5:18–23
Butler WT, Brunn JC, Qin C (2003) Dentin extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins: comparison to bone ECM and contribution to dynamics of dentinogenesis. Connect Tissue Res 44:171–178
Clark F, Thanaraj TA (2002) Categorization and characterization of transcript-confirmed constitutively and alternatively spliced introns and exons from human. Hum Mol Genet 11:451–464
Dean JA, Hartsfield JK Jr, Wright JT, Hart TC (1997) Dentin dysplasia, type II linkage to chromosome 4q. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol 17:172–177
Dimuzio MT, Veis A (1978) Phosphophoryns—major noncollagenous proteins of rat incisor dentin. Calcif Tissue Res 25:169–178
Gajko-Galicka A (2002) Mutations in type I collagen genes resulting in osteogenesis imperfecta in humans. Acta Biochim Pol 49:433–441
Kere J, Srivastava AK, Montonen O, Zonana J, Thomas N, Ferguson B, Munoz F, Morgan D, Clarke A, Baybayan P, Chen EY, Ezer S, Saarialho-Kere U del, Chapelle A, Schlessinger D (1996) X-linked anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia is caused by mutation in a novel transmembrane protein. Nat Genet 13:409–416
Krawczak M, Reiss J, Cooper DN (1992) The mutational spectrum of single base-pair substitutions in mRNA splice junctions of human genes: causes and consequences. Hum Genet 90:41–54
Lammi L, Halonen K, Pirinen S, Thesleff I, Arte S, Nieminen P (2003) A missense mutation in PAX9 in a family with distinct phenotype of oligodontia. Eur J Hum Genet 11:866–871
Lawrence HP, Garcia RI, Essick GK, Hawkins R, Krall EA, Spiro A III, Vokonas PS, Kong L, King T, Koch GG (2001) A longitudinal study of the association between tooth loss and age-related hearing loss. Spec Care Dent 21:129–140
Leaver AG, Triffitt JT, Holbrook IB (1975) Newer knowledge of non-collagenous protein in dentin and cortical bone matrix. Clin Orthop 110:269–292
Linde A (1989) The extracellular matrix of dental pulp and dentin. J Dent Res 64:523–529
Linde A, Bhown M, Butler WT (1980) Noncollagenous proteins of dentin. A re-examination of proteins from rat incisor dentin utilizing techniques to avoid artifacts. J Biol Chem 255:5931–5942
MacDougall M, Simmons D, Luan X, Nydegger J, Feng J, Gu TT (1997) Dentin phosphoprotein and dentin sialoprotein are cleavage products expressed from a single transcript coded by a gene on human chromosome 4. Dentin phosphoprotein DNA sequence determination. J Biol Chem 272:835–842
Malmgren B, Lindskog S (2003) Assessment of dysplastic dentin in osteogenesis imperfecta and dentinogenesis imperfecta. Acta Odontol Scand 61:72–80
Malmgren B, Lindskog S, Elgadi A, Norgren S (2004) Clinical, histopathologic, and genetic investigation in two large families with dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. Hum Genet 114:491–498
Mann S, Webb J, Williams RJP (1989) Biomineralization, chemical and biochemical perspectives. Weinheim, New York
Maquat LE (2002) Molecular biology. Skiing toward nonstop mRNA decay. Science 295:2221–2222
Miletich I, Sharpe PT (2003) Normal and abnormal dental development. Hum Mol Genet 12:R69–R73
Moore MJ (2002) RNA events. No end to nonsense. Science 298:370–371
Nagasaka H, Matsukubo T, Takaesu Y, Kobayashi Y, Sato T, Ishikawa T (2002) Changes and equalization in hearing level induced by dental treatment and instruction in bilaterally equalized chewing: a clinical report. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll 43:243–250
Oliveira RJ, Hammer B, Stillman A, Holm J, Jons C, Margolis RH (1992) A look at ear canal changes with jaw motion. Ear Hear 13:464–466
Padgett RA, Grabowski PJ, Konarska MM, Seiler S, Sharp PA (1986) Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem 55:1119–1150
Pallos D, Hart PS, Cortelli JR, Vian S, Wright JT, Korkko J, Brunoni D, Hart TC (2001) Novel COL1A1 mutation (G599C) associated with mild osteogenesis imperfecta and dentinogenesis imperfecta. Arch Oral Biol 46:459–470
Qin C, Brunn JC, Jones J, George A, Ramachandran A, Gorski JP, Butler WT (2001) A comparative study of sialic acid-rich proteins in rat bone and dentin. Eur J Oral Sci 109:133–141
Qin C, Brunn JC, Cadena E, Ridall A, Tsujigiwa H, Nagatsuka H, Nagai N, Butler WT (2002) The expression of dentin sialophosphoprotein gene in bone. J Dent Res 81:392–394
Qin C, Brunn JC, Cadena E, Ridall A, Butler WT (2003) Dentin sialoprotein in bone and dentin sialophosphoprotein gene expressed by osteoblasts. Connect Tissue Res 44:179–183
Rajpar MH, Koch MJ, Davies RM, Mellody KT, Kielty CM, Dixon MJ (2002) Mutation of the signal peptide region of the bicistronic gene DSPP affects translocation to the endoplasmic reticulum and results in defective dentine biomineralization. Hum Mol Genet 11:2559–2565
Ritchie HH, Shigeyama Y, Somerman MJ, Butler WT (1996) Partial cDNA sequencing of mouse dentine sialoprotein and detection of its specific expression by odontoblasts. Arch Oral Biol 41:571–575
Semina EV, Reiter R, Leysens NJ, Alward WL, Small KW, Datson NA, Siegel-Bartelt J, Bierke-Nelson D, Bitoun P, Zabel BU, Carey JC, Murray JC (1996) Cloning and characterization of a novel bicoid-related homeobox transcription factor gene, RIEG, involved in Rieger syndrome. Nat Genet 14:392–399
Shields ED, Bixler D, el-Kafrawy AM (1973) A proposed classification for heritable human dentine defects with a description of a new entity. Arch Oral Biol 18:543–553
Sreenath T, Thyagarajan T, Hall B, Longenecker G, D’Souza R, Hong S, Wright JT, MacDougall M, Sauk J, Kulkarni AB (2003) Dentin sialophosphoprotein knockout mouse teeth display widened predentin zone and develop defective dentin mineralization similar to human dentinogenesis imperfecta type III. J Biol Chem 278:24874–24880
Stenson PD, Ball EV, Mort M, Phillips AD, Shiel JA, Thomas NS, Abeysinghe S, Krawczak M, Cooper DN (2003) Human gene mutation database (HGMD): 2003 update. Hum Mutat 21:577–581
Stockton DW, Das P, Goldenberg M, D’Souza RN, Patel PI (2000) Mutation of PAX9 is associated with oligodontia. Nat Genet 24:18–19
Thesleff I (2003) Epithelial-mesenchymal signalling regulating tooth morphogenesis. J Cell Sci 116:1647–1648
Thesleff I, Jernvall J (1997) The enamel knot: a putative signaling center regulating tooth development. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 62:257–267
Thesleff I, Sharpe P (1997) Signalling networks regulating dental development. Mech Dev 67:111–123
Tucker AS, Sharpe PT (1999) Molecular genetics of tooth morphogenesis and patterning: the right shape in the right place. J Dent Res 78:826–834
Vastardis H (2000) The genetics of human tooth agenesis: new discoveries for understanding dental anomalies. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 117:650–656
Vastardis H, Karimbux N, Suthua SW, Seidman JG, Seidman CE (1996) A human MSX1 homeodomain missense mutation causes selective tooth agenesis. Nat Genet 13:417–421
Veis A, Perry A (1967) The phosphoprotein of the dentin matrix. Biochemistry 6:2409–2416
Wagner E, Lykke-Andersen J (2002) mRNA surveillance: the perfect persist. J Cell Sci 115:3033–3038
Xiao S, Yu C, Chou X, Yuan W, Wang Y, Bu L, Fu G, Qian M, Yang J, Shi Y, Hu L, Han B, Wang Z, Huang W, Liu J, Chen Z, Zhao G, Kong X (2001) Dentinogenesis imperfecta 1 with or without progressive hearing loss is associated with distinct mutations in DSPP. Nat Genet 27:201–204
Zhang X, Zhao J, Li C, Gao S, Qiu C, Liu P, Wu G, Qiang B, Lo WH, Shen Y (2001) DSPP mutation in dentinogenesis imperfecta Shields type II. Nat Genet 27:151–152
Acknowledgements
We thank all the family members for their cooperation, and the students of Seoul National University, School of Dentistry for donating their blood for this study. This investigation was supported in part by the Foundation of the American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry, and USPHS Research Grants DE12769 and DE11301 from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JW., Nam, SH., Jang, KT. et al. A novel splice acceptor mutation in the DSPP gene causing dentinogenesis imperfecta type II. Hum Genet 115, 248–254 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1143-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1143-5