Abstract
Purpose
We evaluated the predictive role of EGFR mutation on the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor therapy in patients with advanced pulmonary adenocarcinoma while considering clinical factors such as PD-L1 expression, gender, and smoking status.
Methods
Patients were required to have available data for EGFR mutation, PD-L1 expression, and efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors.
Results
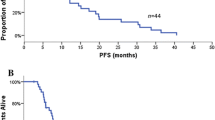
Among 178 patients with EGFR-mutant (n = 38) or wild-type (WT) (n = 140) tumors, the EGFR mutation group had a lower objective response rate (ORR) (15.8% vs. 32.9%, p = 0.04) than the EGFR WT group, similar to the pattern observed for other factors: weak/negative PD-L1 expression vs. strong PD-L1 expression (17.3% vs. 39.2%, p = 0.001); never smokers vs. smokers (19.4% vs. 35.1%, p = 0.03); and females vs. males (21.0% vs. 33.6%, p = 0.08). EGFR mutation and weak/negative PD-L1 expression were associated with a significantly shorter median PFS than EGFR WT (1.9 vs. 3.0 months, p = 0.04) and strong PD-L1 expression (1.6 vs. 3.9 months, p = 0.007), respectively. In multivariate analysis, EGFR mutation predicted worse ORR [hazard ratio (HR) 3.15; 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.15–8.63] and PFS (HR 1.75, 95% CI 1.11–2.75), as did weak/negative PD-L1 expression (ORR, HR 3.46, 95% CI 1.62–7.37; and PFS, HR 1.72, 95% CI 1.17–2.53).
Conclusions
Together with PD-L1 expression, EGFR mutation status is an important factor to predict the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in patients with pulmonary adenocarcinoma.



Similar content being viewed by others

References
Borghaei H et al (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:1627–1639. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1507643
Brahmer J et al (2015) Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 373:123–135. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1504627
Brahmer JR, R-AD RA, Hui R, Csoszi T, Fulop A et al (2017) Updated analysis of KEYNOTE-024: pembrolizumab vs platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced NSCLC with PD-L1 TPS ≥ 50%. J Thoracic Oncol 12:S1793–S1794
Carbone DP et al (2017) First-Line Nivolumab in Stage IV or recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 376:2415–2426. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1613493
Cho JH et al (2018) Retrospective molecular epidemiology study of PD-L1 expression in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res Treatm 50:95–102. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2016.591
ClinicalTrials.gov MEDI9447 Alone and in combination with MEDI4736 in adult subjects with select advanced solid tumors https://ClinicalTrialsgov/show/NCT02503774. Accessed 10 July, 2018
Conforti F et al (2018) Cancer immunotherapy efficacy and patients’ sex: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol 19:737–746. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30261-4
Eisenhauer EA et al (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45:228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Gainor JF et al (2016) EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements are associated with low response rates to PD-1 pathway blockade in non-small cell lung cancer: a retrospective analysis. Clin Cancer Res 22:4585–4593. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-3101
Garassino MCV, Kim JF, Lena J, Mazieres H, Powderly J, Dennis J, P (2016) Durvalumab in ≥ 3rd-line locally advanced or metastatic, EGFR/ALK wildtype NSCLC: results from the phase 2 ATLANTIC study. WCLC
Garassino MC et al (2018) Durvalumab as third-line or later treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ATLANTIC): an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 19:521–536. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30144-X
Herbst RS et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 387:1540–1550. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01281-7
Johnson DB, Sullivan RJ, Menzies AM (2017) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in challenging populations. Cancer 123:1904–1911. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.30642
Khan KA, Kerbel RS (2018) Improving immunotherapy outcomes with anti-angiogenic treatments and vice versa. Nat Rev Clin oncol 15:310–324. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2018.9
Kim H, Kwon HJ, Park SY, Park E, Chung JH (2017) PD-L1 immunohistochemical assays for assessment of therapeutic strategies involving immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: a. comparative study Oncotarget 8:98524–98532. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21567
Kowantz MSM, Zou W, McCleland M, Yang N, Chavez AL, Spira A, Mazieres J IMpower150: Efficacy of atezolizumab (atezo) plus bevacizumab (bev) and chemotherapy (chemo) in 1L metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC (mNSCLC) across key subgroups. Presented at: American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2018; April 16, 2018: Chicago, IL
Lisberg A, Garon EB (2018) The Italian Nivolumab expanded access program confirms the limitations of single-agent PD-1 inhibition in EGFR-mutant and never-smoking patients with NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol 13:1058–1059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.06.003
Lisberg A et al (2018) A phase II STUDY OF PEMBROLIZUMAB in EGFR-Mutant, PD-L1+, tyrosine kinase inhibitor naive patients with advanced NSCLC. J Thoracic Oncol 13:1138–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2018.03.035
Reck M et al (2016) Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375:1823–1833. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1606774
Rittmeyer A et al (2017) Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): a phase 3, open-label multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 389:255–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32517-X
Shi Y et al (2014) A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thoracic Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer 9:154–162. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0000000000000033
Socinski MAJR, Cappuzzo F, Orlandi FJ, Stroyakovskiy D, Nogami N, Rodriguez-Abreu D (2018) Overall survival (OS) analysis of IMpower150, a randomized Ph 3 study of atezolizumab (atezo) + chemotherapy (chemo) ± bevacizumab (bev) vs chemo + bev in 1L nonsquamous (NSQ) NSCLC. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 36
Streicher K et al (2017) Increased CD73 and reduced IFNG signature expression in relation to response rates to anti-PD-1(L1) therapies in EGFR-mutant NSCLC. J Clin Oncol 35:11505–11505. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.11505
Vijayan D, Young A, Teng MWL, Smyth MJ (2017) Targeting immunosuppressive adenosine in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 17:709–724. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.86
Wong A et al (2017) Clinical and palliative care outcomes for patients of poor performance status treated with antiprogrammed death-1 monoclonal antibodies for advanced melanoma Asia. Pac J Clin Oncol 13:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajco.12702
Yoneshima Y et al (2018) PD-L1 expression in lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR mutations or ALK rearrangements. Lung Cancer 118:36–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.01.024
Zhang YL et al (2016) The prevalence of EGFR mutation in patients with non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 7:78985–78993. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.12587
Acknowledgements
This paper was supported by the following grant(s): the National R & D Program for Cancer Control, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea (1720180).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Ethical approval
All the procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board at Samsung Medical Center in Seoul, Korea, and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig 1
. Correlation between PD-L1 expression as assessed by 22C3 PharmDx and SP263 antibodies (PDF 178 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, J.H., Jung, H.A., Lee, SH. et al. Impact of EGFR mutation on the clinical efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors in patients with pulmonary adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 145, 1341–1349 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02889-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-019-02889-0