Abstract
Purpose
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. Lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR-activating mutations will inevitably acquire resistance to first-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). EGFR T790M mutation and cMET amplification are common mechanisms. Further study is needed to explore unknown genomic alterations contributing to drug resistance.
Methods
Tumor and blood samples from 69 stage IIIB–IV NSCLC patients defined as acquired resistance to first-generation EGFR TKIs (gefitinib, erlotinib or ecotinib) were collected. The cobas® and Droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) were used to detect T790M mutations in tumor samples and plasma ctDNA. cMET amplification was evaluated by fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Exome sequencing was performed in four T790M wildtype/cMET-unamplified samples.
Results
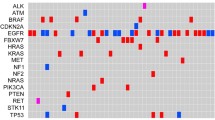
The overall T790M-positive rate was 52.2% considering all testing methods. Out of 21 samples in which tumor re-biopsy was performed, 14 were T790M positive (66.7%). cMET amplification was identified in three out of seven T790M-negative samples. Exome sequencing in four T790M wildtype/cMET-unamplified samples and paired white blood cells identified a cohort of candidate key mutated genes including BRAF, FGFR1, PAK1, PCNT, PEBP4 and SOX3.
Conclusions
EGFR T790M mutation and cMET amplification are main mechanisms leading to EGFR TKI resistance in lung adenocarcinoma. These key mutated genes identified in the present study would need further validation in large number of patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
DePristo MA, Banks E, Poplin R, Garimella KV, Maguire JR, Hartl C, Philippakis AA, del Angel G, Rivas MA, Hanna M, McKenna A, Fennell TJ, Kernytsky AM, Sivachenko AY, Cibulskis K, Gabriel SB, Altshuler D, Daly MJ (2011) A framework for variation discovery and genotyping using next-generation DNA sequencing data. Nat Genet 43:491–498. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.806
Dummler B, Ohshiro K, Kumar R, Field J (2009) Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-008-9168-1
Eswaran J, Li DQ, Shah A, Kumar R (2012) Molecular pathways: targeting p21-activated kinase 1 signaling in cancer–opportunities, challenges, and limitations. Clin Cancer Res 18:3743–3749. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-1952
Jardim DL, Tang C, Gagliato Dde M, Falchook GS, Hess K, Janku F, Fu S, Wheler JJ, Zinner RG, Naing A, Tsimberidou AM, Holla V, Li MM, Roy-Chowdhuri S, Luthra R, Salgia R, Kurzrock R, Meric-Bernstam F, Hong DS (2014) Analysis of 1,115 patients tested for MET amplification and therapy response in the MD Anderson Phase I Clinic. Clin Cancer Res 20:6336–6345. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1293
Kim E, Youn H, Kwon T, Son B, Kang J, Yang HJ, Seong KM, Kim W, Youn B (2014) PAK1 tyrosine phosphorylation is required to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance in lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 74:5520–5531. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0735
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324
Li H, Durbin R (2010) Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 26:589–595. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp698
Li C, Sun Y, Fang R, Han X, Luo X, Wang R, Pan Y, Hu H, Zhang Y, Pao W, Shen L, Ji H, Chen H (2012) Lung adenocarcinomas with HER2-activating mutations are associated with distinct clinical features and HER2/EGFR copy number gains. J Thorac Oncol 7:85–89. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318234f0a2
Lin CC, Chen JT, Lin MW, Chan CH, Wen YF, Wu SB, Chung TW, Lyu KW, Chou HC, Chan HL (2015) Identification of protein expression alterations in gefitinib-resistant human lung adenocarcinoma: PCNT and mPR play key roles in the development of gefitinib-associated resistance. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 288:359–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2015.08.008
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The genome analysis toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20:1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.107524.110
Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim HR, Ramalingam SS, Shepherd FA, He Y, Akamatsu H, Theelen WS, Lee CK, Sebastian M, Templeton A, Mann H, Marotti M, Ghiorghiu S, Papadimitrakopoulou VA, Investigators A (2017) Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med 376:629–640. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1612674
Ohashi K, Sequist LV, Arcila ME, Moran T, Chmielecki J, Lin YL, Pan Y, Wang L, de Stanchina E, Shien K, Aoe K, Toyooka S, Kiura K, Fernandez-Cuesta L, Fidias P, Yang JC, Miller VA, Riely GJ, Kris MG, Engelman JA, Vnencak-Jones CL, Dias-Santagata D, Ladanyi M, Pao W (2012) Lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors occasionally harbor BRAF gene mutations but lack mutations in KRAS, NRAS, or MEK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E2127-2133. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1203530109
Oxnard GR, Arcila ME, Chmielecki J, Ladanyi M, Miller VA, Pao W (2011) New strategies in overcoming acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 17:5530–5537. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2571
Pilotto S, Bria E, Peretti U, Massari F, Garassino M, Pelosi G, Tortora G (2013) Lung adenocarcinoma patient refractory to gefitinib and responsive to crizotinib, with concurrent rare mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (L861Q) and increased ALK/MET/ROS1 gene copy number. J Thorac Oncol 8:e105-106. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e3182a00e37
Schildhaus HU, Schultheis AM, Ruschoff J, Binot E, Merkelbach-Bruse S, Fassunke J, Schulte W, Ko YD, Schlesinger A, Bos M, Gardizi M, Engel-Riedel W, Brockmann M, Serke M, Gerigk U, Hekmat K, Frank KF, Reiser M, Schulz H, Kruger S, Stoelben E, Zander T, Wolf J, Buettner R (2015) MET amplification status in therapy-naive adeno- and squamous cell carcinomas of the lung. Clin Cancer Res 21:907–915. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0450
Schultheis AM, Bos M, Schmitz K, Wilsberg L, Binot E, Wolf J, Buttner R, Schildhaus HU (2014) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) amplification is a potential therapeutic target in small-cell lung cancer. Mod Pathol 27:214–221. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2013.141
Sells MA, Knaus UG, Bagrodia S, Ambrose DM, Bokoch GM, Chernoff J (1997) Human p21-activated kinase (Pak1) regulates actin organization in mammalian cells. Curr Biol 7:202–210
Semenova G, Chernoff J (2017) Targeting PAK1. Biochem Soc Trans 45:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20160134
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D, Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Gettinger S, Cosper AK, Akhavanfard S, Heist RS, Temel J, Christensen JG, Wain JC, Lynch TJ, Vernovsky K, Mark EJ, Lanuti M, Iafrate AJ, Mino-Kenudson M, Engelman JA (2011) Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med 3:75ra26. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3002003
Sos ML, Koker M, Weir BA, Heynck S, Rabinovsky R, Zander T, Seeger JM, Weiss J, Fischer F, Frommolt P, Michel K, Peifer M, Mermel C, Girard L, Peyton M, Gazdar AF, Minna JD, Garraway LA, Kashkar H, Pao W, Meyerson M, Thomas RK (2009) PTEN loss contributes to erlotinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer by activation of Akt and EGFR. Cancer Res 69:3256–3261. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-4055
Suda K, Tomizawa K, Fujii M, Murakami H, Osada H, Maehara Y, Yatabe Y, Sekido Y, Mitsudomi T (2011) Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in an epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung cancer cell line with acquired resistance to erlotinib. J Thorac Oncol 6:1152–1161. https://doi.org/10.1097/JTO.0b013e318216ee52
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A (2015) Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin 65:87–108. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21262
Wu DW, Wu TC, Chen CY, Lee H (2016) PAK1 is a novel therapeutic target in tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistant lung adenocarcinoma activated by the PI3K/AKT signaling regardless of EGFR mutation. Clin Cancer Res 22:5370–5382. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2724
Yoshimura K, Inui N, Karayama M, Inoue Y, Enomoto N, Fujisawa T, Nakamura Y, Takeuchi K, Sugimura H, Suda T (2017) Successful crizotinib monotherapy in EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma with acquired MET amplification after erlotinib therapy. Respir Med Case Rep 20:160–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmcr.2017.02.009
Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS, Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M, Riely GJ (2013) Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res 19:2240–2247. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2246
Acknowledgements
We thank Yongsheng Sha, Hao He, Lu Ye, Mei Liu, Aiping Xu and Yan Yan for managing clinical samples.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0905501, 2016YFC0905500), National Natural Science Foundation of China (81302001, 81772484) and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M550147, 2015T80225).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, C., Liu, H., Zhang, B. et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies key mutated genes in T790M wildtype/cMET-unamplified lung adenocarcinoma with acquired resistance to first-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144, 1079–1086 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2634-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2634-4