Abstract
Purposes
Uncontrolled proliferation is a key characteristic of gastric carcinogenesis and the precise mechanisms underlying the altered proliferation behaviors of GC cells have not been clearly elucidated. miRNAs has been suggested to play a crucial role in the pathogenesis and development of various cancers. In the present study, we employed an impedance-based real-time cell electronic sensing (RT-CES) system to detect the effects of ectopically expressed miRNAs on GC cell proliferation.
Methods
miRNA mimics were transfected into gastric cancer cell line SGC7901 and the effect of individual miRNA on the proliferation rate of the cells was measured by the RT-CES system. The screening results were validated with qRT-PCR and miR-137 was selected for further research. The effects of ectopically expressed miR-137 on GC cell growth and cell cycle progress were measured using MTT assay and flow cytometry. The target gene of miR-137 was predicted using different bioinformatics tools and the direct interaction between miR-137 and the 3’-UTR was confirmed with a luciferase reporter assay. The in vivo effect of miR-137 on GC cell proliferation was examined with a tumor-bearing nude mouse model. The correlation between miR-137 expression and patients’ prognosis was explored in a cohort of 38 patients. Prognosis was explored in a cohort of 38 patients.
Results
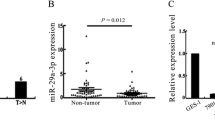
Ectopic expression of miR-137 was sufficient to inhibit GC cell proliferation both in vitro and in vivo. Bioinformatics prediction and luciferase reporter assay revealed CDK6 as a target gene through which miR-137 exerted an inhibitory function. Moreover, miR-137 expression positively correlated with better prognosis.
Conclusion
Our data indicated an important regulatory role of miR-137 in GC cell proliferation and that it may be explored as a prognostic marker for GC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balaguer F, Link A, Lozano JJ et al (2010) Epigenetic silencing of miR-137 is an early event in colorectal carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 70(16):6609–6618
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116(2):281–297
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233
Brito-Babapulle V, Gruszka-Westwood AM, Platt G et al (2002) Translocation t(2;7)(p12;q21-22) with dysregulation of the CDK6 gene mapping to 7q21-22 in a non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma with leukemia. Haematologica 87(4):357–362
Cai CK, Zhao GY, Tian LY et al (2012) miR-15a and miR-16-1 downregulate CCND1 and induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in osteosarcoma. Oncol Rep 28(5):1764–1770
Chen DL, Wang DS, Wu WJ et al (2013) Overexpression of paxillin induced by miR-137 suppression promotes tumor progression and metastasis in colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 34(4):803–811
Dai L, Wang W, Zhang S et al (2012) Vector-based miR-15a/16-1 plasmid inhibits colon cancer growth in vivo. Cell Biol Int 36(8):765–770
Du Y, Liu Z, Gu L et al (2012) Characterization of human gastric carcinoma-related methylation of 9 miR CpG islands and repression of their expressions in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 12:249
Feng L, Xie Y, Zhang H, Wu Y (2012) miR-107 targets cyclin-dependent kinase 6 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in gastric cancer cells. Med Oncol 29(2):856–863
Gao SM, Xing CY, Chen CQ, Lin SS, Dong PH, Yu FJ (2011) miR-15a and miR-16-1 inhibit the proliferation of leukemic cells by down-regulating WT1 protein level. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 30:110
Grossel MJ, Hinds PW (2006) From cell cycle to differentiation: an expanding role for cdk6. Cell Cycle 5(3):266–270
Han Z, Yang Q, Liu B et al (2012) MicroRNA-622 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting K-Ras and enhancing the anticarcinogenic effect of resveratrol. Carcinogenesis 33(1):131–139
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60(5):277–300
Lang Q, Ling C (2012) MiR-124 suppresses cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PIK3CA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 426(2):247–252
Liu M, Lang N, Qiu M et al (2011) miR-137 targets Cdc42 expression, induces cell cycle G1 arrest and inhibits invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Cancer 128(6):1269–1279
Luo C, Tetteh PW, Merz PR et al (2013) miR-137 inhibits the invasion of melanoma cells through downregulation of multiple oncogenic target genes. J Invest Dermatol 133(3):768–775
Nishida N, Mimori K, Fabbri M et al (2011) MicroRNA-125a-5p is an independent prognostic factor in gastric cancer and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells in combination with trastuzumab. Clin Cancer Res 17(9):2725–2733
Petrocca F, Visone R, Onelli MR et al (2008) E2F1-regulated microRNAs impair TGFbeta-dependent cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 13(3):272–286
Sawai CM, Freund J, Oh P et al (2012) Therapeutic targeting of the cyclin D3:CDK4/6 complex in T cell leukemia. Cancer Cell 22(4):452–465
Schipper DL, Wagenmans MJ, Peters WH, Wagener DJ (1998) Significance of cell proliferation measurement in gastric cancer. Eur J Cancer 34(6):781–790
Solly K, Wang X, Xu X, Strulovici B, Zheng W (2004) Application of real-time cell electronic sensing (RT-CES) technology to cell-based assays. Assay Drug Dev Technol 2(4):363–372
Ushijima T, Sasako M (2004) Focus on gastric cancer. Cancer Cell 5(2):121–125
Vrba L, Munoz-Rodriguez JL, Stampfer MR, Futscher BW (2013) miRNA gene promoters are frequent targets of aberrant DNA methylation in human breast cancer. PLoS ONE 8(1):e54398
Wang Y, Baskerville S, Shenoy A, Babiarz JE, Baehner L, Blelloch R (2008) Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs regulate the G1-S transition and promote rapid proliferation. Nat Genet 40(12):1478–1483
Wang F, Ma YL, Zhang P et al (2013) SP1 mediates the link between methylation of the tumour suppressor miR-149 and outcome in colorectal cancer. J Pathol 229(1):12–24
Wu WK, Lee CW, Cho CH et al (2010) MicroRNA dysregulation in gastric cancer: a new player enters the game. Oncogene 29(43):5761–5771
Xia J, Wu Z, Yu C et al (2012) miR-124 inhibits cell proliferation in gastric cancer through down-regulation of SPHK1. J Pathol 227(4):470–480
Zhang L, Liu X, Jin H et al (2013) miR-206 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation in part by repressing cyclin D2. Cancer Lett 332(1):94–101
Zhao Y, Li Y, Lou G et al (2012) MiR-137 targets estrogen-related receptor alpha and impairs the proliferative and migratory capacity of breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 7(6):e39102
Zhu X, Li Y, Shen H et al (2013a) miR-137 restoration sensitizes multidrug-resistant MCF-7/ADM cells to anticancer agents by targeting YB-1. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 45(2):80–86
Zhu X, Li Y, Shen H et al (2013b) miR-137 inhibits the proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting Cdc42 and Cdk6. FEBS Lett 587(1):73–81
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiushan Zheng, Jiaqiang Dong, Taiqian Gong and Zhiyong Zhang have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Dong, J., Gong, T. et al. MicroRNA library-based functional screening identified miR-137 as a suppresser of gastric cancer cell proliferation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 141, 785–795 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1847-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-014-1847-4