Abstract
Purpose
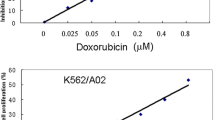
Resistance to chemotherapy drugs remains a difficult problem in bladder cancer treatment. Protein expression is an important factor underlying multidrug resistance (MDR) in bladder cancer. The aim of the study was to explore differentially expressed proteins responsible for MDR between an adriamycin-resistant human bladder cancer cell line (pumc-91/ADM) and its parental cell line (pumc-91).
Methods
Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) combining image analysis was used to screen the differentially expressed protein spots between the pumc-91/ADM and pumc-91 cell lines. Then, the protein spots were identified using MALDI-TOF/TOF mass spectrometry. Among the identified proteins, annexin A2 (ANXA2) and nucleophosmin (NPM1) were then further verified using RT-PCR and Western blot analysis.
Results
A total of 30 proteins, including 19 up-regulated and 11 down-regulated proteins, were successfully identified in pumc-91/ADM. According to their different functions, these 30 proteins were classified into 12 categories. Annexin A2 (ANXA2) and nucleophosmin (NPM1) were up-regulated in pumc-91/ADM compared with pumc-91.
Conclusion
The proteins identified may have an important clinical significance in MDR, and ANXA2 and NPM1 may take part in mechanism of MDR in bladder cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baguley BC (2010) Multi-drug resistance in cancer. Methods Mol Biol 596:1–9
Borer RA, Lehner CF, Eppenberger HM et al (1989) Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell 56:379–390
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cole SP, Pinkoski MJ, Bhardwaj G et al (1992) Elevated expression of annexin II (lipocortin II, p36) in a multidrug resistant small cell lung cancer cell line. Br J Cancer 65(4):498–502
Colombo E, Marine JC, Danovi D et al (2002) Nucleophosmin regulates the stability and transcriptional activity of p53. Nat Cell Biol 4:529–533
Dhar SK, Lynn BC, Daosukho C et al (2004) Identification of nucleophosmin as an NF-kappaB co-activator for the induction of the human SOD2 gene. J Biol Chem 279:28209–28219
Emoto K, Sawada H, Yamada Y et al (2001a) Annexin II overexpression is correlated with poor prognosis in human gastric carcinoma. Anticancer Res 21:1339–1345
Emoto K, Yamada Y, Sawada H et al (2001b) Annexin II overexpression correlates with stromal tenascin-C overexpression: a prognostic marker in colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 92:1419–1426
Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E et al (2005) Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med 352:254–266
Flood EC, Hajjar KA (2011) The annexin A2 system and vascular homeostasis. Vasc Pharmacol 54:59–67
Gerke V, Moss SE (2002) Annexins: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 82:331–371
Gingrich JR (2011) Chemohyperthermia for bladder cancer—clinically effective? Nat Rev Urol 8:414–416
Hasegawa S, Abe T, Naito S et al (1995) Expression of multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP), MDR1 and DNA topoisomerase II in human multidrug-resistant bladder cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer 71:907–913
Hayes MJ, Moss SE (2004) Annexins and disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322:1166–1170
Herrera JE, Savkur R, Olson MO (1995) The ribonuclease activity of nucleolar protein B23. Nucleic Acids Res 23:3974–3979
Hong L, Piao Y, Han Y et al (2005) Zinc ribbon domain containing 1 (ZNRD1) mediates multidrug resistance of leukemia cells through regulation of P-glycoprotein and Bcl-2. Mol Cancer Ther 4:1936–1942
Hsu CY, Yung BY (2000) Over-expression of nucleophosmin/B23 decreases the susceptibility of human leukemia HL-60 cells to retinoic acid-induced differentiation and apoptosis. Int J Cancer 88:392–400
Hu J, Lin M, Liu T et al (2011) DIGE-based proteomic analysis identifies nucleophosmin/B23 and nucleolin C23 as over-expressed proteins in relapsed/refractory acute leukemia. Leukemia Res 35:1087–1109
Ichimi T, Enokida H, Okuno Y et al (2009) Identification of novel microRNA targets based on microRNA signatures in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer 125:345–352
Kikuta K, Tochigi N, Shimoda T et al (2009) Nucleophosmin as a candidate prognostic biomarker of Ewing’s sarcoma revealed by proteomics. Clin Cancer Res 15:2885–2894
Korgaonkar C, Hagen J, Tompkins V et al (2005) Nucleophosmin (B23) targets ARF to nucleoli and inhibits its function. Mol Cell Biol 25:1258–1271
Liang Y, McDonnell S, Clynes M (2002) Examining the relationship between cancer invasion/metastasis and drug resistance. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2(3):257–277
Lim MJ, Wang XW (2006) Nucleophosmin and human cancer. Cancer Detect Prev 30:481–490
Lin CY, Liang YC, Yung Benjamin YM (2006) Nucleophosmin/B23 regulates transcriptional activation of E2F1 via modulating the promoter binding of NF-κB, E2F1 and pRB. Cell Signal 18:2041–2048
Liu JW, Shen JJ, Tanzillo-Swarts A et al (2003) Annexin II expression is reduced or lost in prostate cancer cells and its re-expression inhibits prostate cancer cell migration. Oncogene 22:1475–1485
Liu X, Liu ZX, Jang SW et al (2007) Sumoylation of nucleophosmin/B23 regulates its subcellular localization, mediating cell proliferation and survival. PNAS 104(23):9679–9684
Nakagawa M, Emoto A, Nasu N et al (1997) Clinical significance of multi-drug resistance associated protein and P-glycoprotein in patients with bladder cancer. J Urol 157:1260–1265
Nozawa Y, Van Belzen N, Vander Made AC et al (1996) Expression of nucleophosmin/B23 in normal and neoplastic colorectal mucosa. J Pathol 178:48–52
Pastorelli R, Carpi D, Campagna R et al (2007) Proteome characterization of a human urothelial cell line resistant to the bladder carcinogen 4-aminobiphenyl. Proteome Sci 5:6–14
Pianta A, Puppin C, Deganuto M et al (2010) Nucleophosmin is overexpressed in thyroid tumors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:499–504
Schulz DM, llner CB, Thomas G et al (2009) Identification of differentially expressed proteins in triple-negative breast carcinomas using DIGE and mass spectrometry. J Proteome Res 8:3430–3438
Sharma MR, Koltowski L, Ownbey RT et al (2006) Angiogenesis-associated protein annexin II in breast cancer: selective expression in invasive breast cancer and contribution to tumor invasion and progression. Exp Mol Pathol 81:146–156
Subong EN, Shue MJ, Epstein JI et al (1999) Monoclonal antibody to prostate cancer nuclear matrix protein (PRO:4–216) recognizes nucleophosmin/B23. Prostate 39:298–304
Szebeni A, Olson MO (1999) Nucleolar protein B23 has molecular chaperone activities. Protein Sci 8:905–912
Tada Y, Wada M, Kuroiwa K et al (2000) MDR1 overexpression and altered degree of methylation at the promoter region in bladder cancer during chemotherapeutic treatment. Clin Cancer Res 6:4618–4627
Tanaka M, Sasaki H, Kino I et al (1992) Genes preferentially expressed in embryo stomach are predominantly expressed in gastric cancer. Cancer Res 52:3372–3377
Tokuyama Y, Horn HF, Kawamura K et al (2001) Specific phosphorylation of nucleophosmin on Thr(199) by cyclin dependent kinase 2-cyclin E and its role in centrosome duplication. J Biol Chem 276:21529–21537
Tsui KH, Cheng AJ, Chang PL et al (2004) Association of nucleophosmin/b23 mRNA expression with clinical outcome in patients with bladder carcinoma. Urology 64:839–844
Tusi KH, Juang HH, Lee TH et al (2008) Association of nucleophosmin/B23 with bladder cancer recurrence based on immunohistochemical assessment in clinical samples. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29(3):364–370
Verhaak RG, Goudswaard CS, van Putten W et al (2005) Mutations in nucleophosmin (NPM1) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML): association with other gene abnormalities and previously established gene expression signatures and their favorable prognostic significance. Blood 106:3747–3754
Vishwanatha JK, Chiang Y, Kumble KD et al (1993) Enhanced expression of annexin II in human pancreatic carcinoma cells and primary pancreatic cancers. Carcinogenesis 14:2575–2579
Wu MH, Chang JH, Yung BY (2002a) Resistance to UV-induced cell-killing in nucleophosmin/B23 over-expressed NIH 3T3 fibroblasts: enhancement of DNA repair and up-regulation of PCNA in association with nucleophosmin/B23 over-expression. Carcinogenesis 23:93–100
Wu MH, Chang JH, Chou CC, Yung BY (2002b) Involvement of nucleophosmin/B23 in the response of HeLa cells to UV irradiation. Int J Cancer 97:297–305
Xu RH, Pelicano H, Zhou Y et al (2005) Inhibition of glycolysis in cancer cells: a novel strategy to overcome drug resistance associated with mitochondrial respiratory defect and hypoxia. Cancer Res 65:613–621
Yang YX, Hu HD, Zhang DZ et al (2007) Identification of proteins responsible for the development of adriamycin resistance in human gastric cancer cells using comparative proteomics analysis. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:853–860
Yao HX, Zhang ZQ, Xiao ZQ et al (2009) Identification of metastasis associated proteins in human lung squamous. carcinoma using two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis and laser capture microdissection. Lung Cancer 65:41–48
Ye KQ (2005) Nucleophosmin/B23, a multifunctional protein that can regulate apoptosis. Cancer Biol Ther 4:918–923
Yung BY, Busch H, Chan PK (1985) Translocation of nucleolar phosphoprotein B23 (37 kDa/pI 5.1) induced by selective inhibitors of ribosome synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 826:167–173
Zhang M, Jin S, Zhang M (2009a) Establishing human multi-drug resistant bladder cancer cell lines Pumc-91/ADM and evaluating its biological characteristics. J Med Res 38(1):70–72
Zhang Fei, Zhang Lin, Zhang Bin et al (2009b) Anxa2 plays a critical role in enhanced invasiveness of the multidrug resistant human breast cancer cells. J Proteome Res 8:3430–3438
Acknowledgments
Research supported by Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, Q., Lei, T., Zhang, M. et al. Identification of proteins differentially expressed in adriamycin-resistant (pumc-91/ADM) and parental (pumc-91) human bladder cancer cell lines by proteome analysis. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 139, 509–519 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1350-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-012-1350-8