Abstract
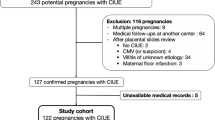
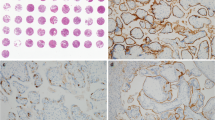
Chronic intervillositis of unknown etiology (CIUE) is a rare placental lesion associated with infiltration of mononuclear inflammatory cells into the intervillous space, poor perinatal outcomes (intrauterine fetal demise or fetal growth restriction), and high rates of recurrence. CD39 is the ectonucleotidase that protects tissues from inflammatory stress and cell injury, which is localized on the surface of villi in normal placentas; however, its expression and role in CIUE are unknown. The aims of this retrospective study were to determine the expression of CD39 in CIUE and its significance in pregnancy outcomes. We compared the number of CD68- and CD3-positive cells, CD39 expression, and complement 4d (C4d) and fibrin deposition in placental tissues from patients with CIUE (n = 22) and gestational age-matched controls (n = 20), and between CIUE pregnancies with poor and good outcomes. The numbers of CD68- or CD3-positive cells were significantly higher (P < 0.0001), whereas CD39 expression on the surface of villi and endothelial cells of the stem villi was significantly lower in the CIUE group than that in controls (45% vs. 95%, P < 0.0001 and 77% vs. 96%, P < 0.001, respectively). C4d and fibrin deposition were also significantly increased in CIUE compared with those of controls. Furthermore, CD39 downregulation and the number of CD68 cells were strongly associated with poor pregnancy outcomes (P < 0.01 and P < 0.05, respectively), but other histological parameters (CD3, C4d, and fibrin) did not show this association. Our study suggests that CD39 downregulation is a useful marker of CIUE and is associated with poor pregnancy outcomes in patients with CIUE.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Labarrere C, Mullen E (1987) Fibrinoid and trophoblastic necrosis with massive chronic intervillositis: an extreme variant of villitis of unknown etiology. Am J Reprod Immunol Microbiol 15(3):85–91
Doss BJ, Greene MF, Hill J, Heffner LJ, Bieber FR, Genest DR (1995) Massive chronic intervillositis associated with recurrent abortions. Hum Pathol 26:1245–1251
Boyd TK, Redline RW (2000) Chronic histiocytic intervillositis: a placental lesion associated with recurrent reproductive loss. Hum Pathol 31(11):1389–1396
Contro E, deSouza R, Bhide A (2010) Chronic intervillositis of the placenta: a systematic review. Placenta 31(12):1106–1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2010.10.005
Nowak C, Joubert M, Jossic F, Masseau A, Hamidou M, Philippe HJ, Le Vaillant C (2016) Perinatal prognosis of pregnancies complicated by placental chronic villitis or intervillositis of unknown etiology and combined lesions: about a series of 178 cases. Placenta 44:104–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.04.017
Koby L, Keating S, Malinowski AK, D'Souza R (2018) Chronic histiocytic intervillositis - clinical, biochemical and radiological findings: an observational study. Placenta 64:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.02.002
Parant O, Capdet J, Kessler S, Aziza J, Berrebi A (2009) Chronic intervillositis of unknown etiology (CIUE): relation between placental lesions and perinatal outcome. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 143(1):9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2008.06.012
Reus AD, van Besouw NM, Molenaar NM, Steegers EA, Visser W, de Kuiper RP, de Krijger RR, Roelen DL, Exalto N (2013) An immunological basis for chronic histiocytic intervillositis in recurrent fetal loss. Am J Reprod Immunol 70(3):230–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/aji.12125
Heller DS (2012) CD68 immunostaining in the evaluation of chronic histiocytic intervillositis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 136(6):657–659. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2011-0328-OA
Marchaudon V, Devisme L, Petit S, Ansart-Franquet H, Vaast P, Subtil D (2011) Chronic histiocytic intervillositis of unknown etiology: clinical features in a consecutive series of 69 cases. Placenta 32(2):140–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.placenta.2010.11.021
Bendon RW, Coventry S, Thompson M, Rudzinski ER, Williams EM, Oron AP (2015) Significance of C4d immunostaining in placental chronic intervillositis. Pediatr Dev Pathol 18(5):362–368. https://doi.org/10.2350/14-12-1582-OA.1
Kaczmarek E, Koziak K, Sévigny J, Siegel JB, Anrather J, Beaudoin AR, Bach FH, Robson SC (1996) Identification and characterization of CD39/vascular ATP diphosphohydrolase. J Biol Chem 271(51):33116–33122
Zhao H, Bo C, Kang Y, Li H (2017) What else can CD39 tell us? Front Immunol 8:727. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00727
Makita K, Shimoyama T, Sakurai Y, Yagi H, Matsumoto M, Narita N, Sakamoto Y, Saito S, Ikeda Y, Suzuki M, Titani K, Fujimura Y (1998) Placental ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase: its structural feature distinct from CD39, localization and inhibition on shear-induced platelet aggregation. Int J Hematol 68(3):297–310
McRae JL, Russell PA, Chia JS, Dwyer KM (2013) Overexpression of CD39 protects in a mouse model of preeclampsia. Nephrology 18(5):351–355. https://doi.org/10.1111/nep.12058
Furukoji E, Matsumoto M, Yamashita A, Yagi H, Sakurai Y, Marutsuka K, Hatakeyama K, Morishita K, Fujimura Y, Tamura S, Asada Y (2005) Adenovirus-mediated transfer of human placental ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase to vascular smooth muscle cells suppresses platelet aggregation in vitro and arterial thrombus formation in vivo. Circulation 111(6):808–815. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000155239.46511.79
Samudra AN, Dwyer KM, Selan C, Freddi S, Murray-Segal L, Nikpour M, Hickey MJ, Peter K, Robson SC, Sashindranath M, Cowan PJ, Nandurkar HH (2018) CD39 and CD73 activity are protective in a mouse model of antiphospholipid antibody-induced miscarriages. J Autoimmun 88:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2017.10.009
Khong TY, Mooney EE, Ariel I, Balmus NC, Boyd TK, Brundler MA, Derricott H, Evans MJ, Faye-Petersen OM, Gillan JE, Heazell AE, Heller DS, Jacques SM, Keating S, Kelehan P, Maes A, McKay EM, Morgan TK, Nikkels PG, Parks WT, Redline RW, Scheimberg I, Schoots MH, Sebire NJ, Timmer A, Turowski G, van der Voorn JP, van Lijnschoten I, Gordijn SJ (2016) Sampling and definitions of placental lesions: Amsterdam placental workshop group consensus statement. Arch Pathol Lab Med 140(7):698–713. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2015-0225-CC
Bos M, Nikkels PGJ, Cohen D, Schoones JW, Bloemenkamp KWM, Bruijn JA, Baelde HJ, van der Hoorn MLP, Turner RJ (2018) Towards standardized criteria for diagnosing chronic intervillositis of unknown etiology: a systematic review. Placenta 61:80–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2017.10.009.Khong
Rudzinski E, Gilroy M, Newbill C, Morgan T (2013) Positive C4d immunostaining of placental villous syncytiotrophoblasts supports host-versus-graft rejection in villitis of unknown etiology. Pediatr Dev Pathol 16(1):7–13. https://doi.org/10.2350/12-05-1195-OA.1
Moriguchi-Goto S, Yamashita A, Tamura N, Soejima K, Takahashi M, Nakagaki T, Goto S, Asada Y (2009) ADAMTS-13 attenuates thrombus formation on type I collagen surface and disrupted plaques under flow conditions. Atherosclerosis 203(2):409–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.07.043
Kittel A, Csapó ZS, Csizmadia E, Jackson SW, Robson SC (2004) Co-localization of P2Y1 receptor and NTPDase1/CD39 within caveolae in human placenta. Eur J Histochem 48(3):253–259
Smith SB, Xu Z, Novitskaya T, Zhang B, Chepurko E, Pu XA, Wheeler DG, Ziolo M, Gumina RJ (2017) Impact of cardiac-specific expression of CD39 on myocardial infarct size in mice. Life Sci 179:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.10.016
Sutton NR, Hayasaki T, Hyman MC, Anyanwu AC, Liao H, Petrovic-Djergovic D, Badri L, Baek AE, Walker N, Fukase K, Kanthi Y, Visovatti SH, Horste EL, Ray JJ, Goonewardena SN, Pinsky DJ (2017) Ectonucleotidase CD39-driven control of postinfarction myocardial repair and rupture. JCI Insight 2(1):e89504. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.89504
Acknowledgments
We thank Ritsuko Sotomura and Takako Tokumitsu for their assistance with immunohistochemical staining. We would also like to thank Editage (www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Funding
This study was partly supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research in Japan (No. 19K07417) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, and a Grant-in-Aid for clinical research from Miyazaki University Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS, KM, and MA conceived and designed the study and wrote the manuscript. AY, YS, YK, and YM collected and analyzed the data. HS and YA wrote, edited, and reviewed the manuscript. All authors participated in the interpretation of the results and writing of the report and approved the final version submitted. YS takes full responsibility for the work, as a whole, including the study design, access to data, and the decision to submit and publish the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Miyazaki on September 4, 2018 (project number 0-0401).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, Y., Maekawa, K., Aman, M. et al. CD39 downregulation in chronic intervillositis of unknown etiology. Virchows Arch 475, 357–364 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-019-02598-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-019-02598-6