Abstract
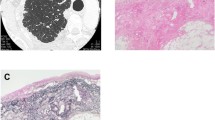
Patients with autoimmune disease–related interstitial lung disease (AID-ILD) occasionally develop radiologic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (PPFE)–like lesions. However, the significance of AID as an etiology of PPFE has not been fully elucidated. The aim of this study is to verify the increase of elastic fibers in AID-ILD patients and evaluate the prevalence of histological PPFE in patients with AID-ILD. We selected cases of clinically diagnosed AID-ILD and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), in which an autopsy had been performed or in which the patient had undergone pneumonectomy for lung transplantation. We quantified the collagen fibers and elastic fibers in each lobe as the percentage of the non-aerated lung area (collagen fiber score and elastic fiber score, respectively) in histological specimens from a total of 73 patients (AID-ILD, n = 24; IPF, n = 49). There were no significant differences in the collagen fiber scores of the AID-ILD and IPF groups. Meanwhile, the elastic fiber scores of the AID-ILD group were significantly greater than those of the IPF group in the whole lung (17.3 ± 7.70 vs 11.6 ± 4.55), and the upper (16.6 ± 8.11 vs 11.2 ± 5.18), and lower (18.0 ± 9.68 vs 12.0 ± 5.55) lobes (all p < 0.01). Histological PPFE pattern was found in 12 of 24 AID-ILD patients (50%), and histological PPFE pattern as a dominant pattern of fibrosis was found in 2 of the 24 patients (8%). Thus, PPFE can be a manifestation of AID-ILD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, King TE Jr, Lynch DA, Nicholson AG, Ryerson CJ, Ryu JH, Selman M, Wells AU, Behr J, Bouros D, Brown KK, Colby TV, Collard HR, Cordeiro CR, Cottin V, Crestani B, Drent M, Dudden RF, Egan J, Flaherty K, Hogaboam C, Inoue Y, Johkoh T, Kim DS, Kitaichi M, Loyd J, Martinez FJ, Myers J, Protzko S, Raghu G, Richeldi L, Sverzellati N, Swigris J, Valeyre D, ATS/ERS Committee on Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias (2013) An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 188:733–748. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST
Frankel SK, Cool CD, Lynch DA, Brown KK (2004) Idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: description of a novel clinicopathologic entity. Chest 126:2007–2013. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.126.6.2007
Amitani R, Niimi A, Kuse F (1992) Idiopathic pulmonary upper lobe fibrosis. Kokyu 11:693–699
Reddy TL, Tominaga M, Hansell DM, von der Thusen J, Rassl D, Parfrey H, Guy S, Twentyman O, Rice A, Maher TM, Renzoni EA, Wells AU, Nicholson AG (2012) Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: a spectrum of histopathological and imaging phenotypes. Eur Respir J 40:377–385. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00165111
Oda T, Ogura T, Kitamura H, Hagiwara E, Baba T, Enomoto Y, Iwasawa T, Okudela K, Takemura T, Sakai F, Hasegawa Y (2014) Distinct characteristics of pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis with usual interstitial pneumonia compared with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 146:1248–1255. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.13-2866
Watanabe K (2013) Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: its clinical characteristics. Curr Respir Med Rev 9:229–237. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573398X0904140129125307
Enomoto N, Kusagaya H, Oyama Y, Kono M, Kaida Y, Kuroishi S, Hashimoto D, Fujisawa T, Yokomura K, Inui N, Nakamura Y, Suda T (2014) Quantitative analysis of lung elastic fibers in idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis (IPPFE): comparison of clinical, radiological, and pathological findings with those of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). BMC Pulm Med 14:91. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2466-14-91
Kinoshita Y, Watanabe K, Ishii H, Kushima H, Fujita M, Nabeshima K (2017) Proliferation of elastic fibres in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a whole-slide image analysis and comparison with pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis. Histopathology 71:934–942. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.13312
von der Thüsen JH, Hansell DM, Tominaga M, Veys PA, Ashworth MT, Owens CM, Nicholson AG (2011) Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis in patients with pulmonary disease secondary to bone marrow transplantation. Mod Pathol 24:1633–1639. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2011.114
Beynat-Mouterde C, Beltramo G, Lezmi G, Pernet D, Camus C, Fanton A, Foucher P, Cottin V, Bonniaud P (2014) Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis as a late complication of chemotherapy agents. Eur Respir J 44:523–527. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00214713
Camus P, von der Thüsen J, Hansell DM, Colby TV (2014) Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: one more walk on the wild side of drugs? Eur Respir J 44:289–296. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00088414
Jacob J, Odink A, Brun AL, Macaluso C, de Lauretis A, Kokosi M, Devaraj A, Desai S, Renzoni E, Wells AU (2018) Functional associations of pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis and emphysema with hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respir Med 138:95–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2018.03.031
Petrie GR, Bloomfield P, Grant IW, Crompton GK (1980) Upper lobe fibrosis and cavitation in rheumatoid disease. Br J Dis Chest 74:263–267
Enomoto Y, Nakamura Y, Colby TV, Johkoh T, Sumikawa H, Nishimoto K, Yoshimura K, Matsushima S, Oyama Y, Hozumi H, Kono M, Fujisawa T, Enomoto N, Inui N, Iwashita T, Suda T (2017) Radiologic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis-like lesion in connective tissue disease-related interstitial lung disease. PLoS One 12:e0180283. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180283
Enomoto Y, Nakamura Y, Satake Y, Sumikawa H (2017) Clinical diagnosis of idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: a retrospective multicenter study. Respir Med 133:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2017.11.003
Khiroya R, MacAluso C, Montero MA et al (2017) Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis: a review of histopathologic features and the relationship between histologic parameters and survival. Am J Surg Pathol 41:1683–1689. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000928
Shiboski SC, Shiboski CH, Criswell LA, Baer AN, Challacombe S, Lanfranchi H, Schiødt M, Umehara H, Vivino F, Zhao Y, Dong Y, Greenspan D, Heidenreich AM, Helin P, Kirkham B, Kitagawa K, Larkin G, Li M, Lietman T, Lindegaard J, McNamara N, Sack K, Shirlaw P, Sugai S, Vollenweider C, Whitcher J, Wu A, Zhang S, Zhang W, Greenspan JS, Daniels TE, Sjögren’s International Collaborative Clinical Alliance (SICCA) Research Groups (2012) American College of Rheumatology classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a data-driven, expert consensus approach in the Sjögren’s International Collaborative Clinical Alliance cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64:475–487
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 292:403–407
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med 292:344–347
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO III, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JMW, Hobbs K, Huizinga TWJ, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Ménard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovský J, Wolfe F, Hawker G (2010) 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27584
Masi AT (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum 23:581–590. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780230510
Petri M, Orbai A-M, Alarcón GS, Gordon C, Merrill JT, Fortin PR, Bruce IN, Isenberg D, Wallace DJ, Nived O, Sturfelt G, Ramsey-Goldman R, Bae SC, Hanly JG, Sánchez-Guerrero J, Clarke A, Aranow C, Manzi S, Urowitz M, Gladman D, Kalunian K, Costner M, Werth VP, Zoma A, Bernatsky S, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Khamashta MA, Jacobsen S, Buyon JP, Maddison P, Dooley MA, van Vollenhoven RF, Ginzler E, Stoll T, Peschken C, Jorizzo JL, Callen JP, Lim SS, Fessler BJ, Inanc M, Kamen DL, Rahman A, Steinsson K, Franks AG Jr, Sigler L, Hameed S, Fang H, Pham N, Brey R, Weisman MH, McGwin G Jr, Magder LS (2012) Derivation and validation of the systemic lupus international collaborating clinics classification criteria for systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 64:2677–2686. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.34473.Derivation
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, Flores-Suarez LF, Gross WL, Guillevin L, Hagen EC, Hoffman GS, Jayne DR, Kallenberg CGM, Lamprecht P, Langford CA, Luqmani RA, Mahr AD, Matteson EL, Merkel PA, Ozen S, Pusey CD, Rasmussen N, Rees AJ, Scott DGI, Specks U, Stone JH, Takahashi K, Watts RA (2013) 2012 revised international Chapel Hill consensus conference nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum 65:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37715
American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society (2002) American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:277–304. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.ats01
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, Lynch DA, Ryu JH, Swigris JJ, Wells AU, Ancochea J, Bouros D, Carvalho C, Costabel U, Ebina M, Hansell DM, Johkoh T, Kim DS, King te Jr, Kondoh Y, Myers J, Müller NL, Nicholson AG, Richeldi L, Selman M, Dudden RF, Griss BS, Protzko SL, Schünemann HJ, ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Committee on Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (2011) An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183:788–824. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.2009-040GL
Travis WD, Hunninghake G, King TE et al (2008) Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: report of an American Thoracic Society Project. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:1338–1347. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200611-1685OC
Kinoshita Y, Watanabe K, Ishii H, Kushima H, Fujita M, Nabeshima K (2018) Significant increases in the density and number of lymphatic vessels in pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis. Histopathology 73:417–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.13634
Denton CP, Black CM, Abraham DJ (2006) Mechanisms and consequences of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2:134–144. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncprheum0115
Krieg T, Abraham D, Lafyatis R (2007) Fibrosis in connective tissue disease: the role of the myofibroblast and fibroblast-epithelial cell interactions. Arthritis Res Ther 9:S4. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar2188
Felício CHC, Parra ER, Capelozzi VL (2007) Idiopathic and collagen vascular disease nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: clinical significance of remodeling process. Lung 185:39–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-006-0104-2
Fischer A, West SG, Swigris JJ, Brown KK, du Bois RM (2010) Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: a call for clarification. Chest 138:251–256. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.10-0194
Hirota T, Yoshida Y, Kitasato Y, Yoshimi M, Koga T, Tsuruta N, Minami M, Harada T, Ishii H, Fujita M, Nabeshima K, Nagata N, Watanabe K (2015) Histological evolution of pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis. Histopathology 66:545–554. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12554
Arulkumaran N, Periselneris N, Gaskin G, Strickland N, Ind PW, Pusey CD, Salama AD (2011) Interstitial lung disease and ANCA-associated vasculitis: a retrospective observational cohort study. Rheumatology 50:2035–2043. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/ker236
Yamakawa H, Oda T, Baba T, Ogura T (2018) Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis with positive MPO-ANCA diagnosed with a CT-guided percutaneous needle biopsy. BMJ Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2017-223287
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Ms. H. Fukagawa, Department of Pathology, Fukuoka University School of Medicine and Hospital, for her skillful assistance with the preparation and staining of the tissue samples.
Funding
This study was partially supported by a grant from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan awarded to the Study Group on Diffuse Pulmonary Disorders, Scientific Research/Research on Intractable Diseases.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YK contributed to the design and concept of the study, data analysis, and writing of the manuscript. KW contributed to the design and concept of the study, data analysis, and development of the manuscript. KN contributed to the data analysis and gave advice on the design and concept of the study. HI, HK, MH, and MF contributed to the collection of the data and final approval of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by The Fukuoka University Hospital Institutional Review Board, and it approved the study protocol and waived the requirement for informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kinoshita, Y., Watanabe, K., Ishii, H. et al. Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis as a histological background of autoimmune diseases. Virchows Arch 474, 97–104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-018-2473-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-018-2473-3