Abstract
Main conclusion
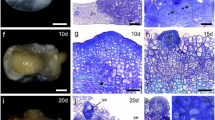
Promoters of lettuce cis-prenyltransferase 3 (LsCPT3) and CPT-binding protein 2 (LsCBP2) specify gene expression in laticifers, as supported by in situ β-glucuronidase stains and microsection analysis.
Abstract
Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) has articulated laticifers alongside vascular bundles. In the cytoplasm of laticifers, natural rubber (cis-1,4-polyisoprene) is synthesized by cis-prenyltransferase (LsCPT3) and CPT-binding protein (LsCBP2), both of which form an enzyme complex. Here we determined the gene structures of LsCPT3 and LsCBP2 and characterized their promoter activities using β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter assays in stable transgenic lines of lettuce. LsCPT3 has a single 7.4-kb intron while LsCBP2 has seven introns including a 940-bp intron in the 5′-untranslated region (UTR). Serially truncated LsCPT3 promoters (2.3 kb, 1.6 kb, and 1.1 kb) and the LsCBP2 promoter with (1.7 kb) or without (0.8 kb) the 940-bp introns were fused to GUS to examine their promoter activities. In situ GUS stains of the transgenic plants revealed that the 1.1-kb LsCPT3 and 0.8-kb LsCBP2 promoter without the 5′-UTR intron are sufficient to express GUS exclusively in laticifers. Fluorometric assays showed that the LsCBP2 promoter was several-fold stronger than the CaMV35S promoter and was ~ 400 times stronger than the LsCPT3 promoter in latex. Histochemical analyses confirmed that both promoters express GUS exclusively in laticifers, recognized by characteristic fused multicellular structures. We concluded that both the LsCPT3 and LsCBP2 promoters specify gene expression in laticifers, and the LsCBP2 promoter displays stronger expression than the CaMV35S promoter in laticifers. For the LsCPT3 promoter, it appears that unknown cis-elements outside of the currently examined LsCPT3 promoter are required to enhance LsCPT3 expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar-El ML, Vaňková P, Yeheskel A, Simhaev L, Engel H, Man P, Haitin Y, Giladi M (2020) Structural basis of heterotetrameric assembly and disease mutations in the human cis-prenyltransferase complex. Nat Commun 11(1):1–3. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18970-z
Barreda VD, Palazzesi L, Tellería MC et al (2010) Eocene patagonia fossils of the daisy family. Science 329:1621. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1193108
Barreda VD, Palazzesi L, Katinas L et al (2012) An extinct Eocene taxon of the daisy family (Asteraceae): evolutionary, ecological and biogeographical implications. Ann Bot 109:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcs001
Bassuner BM, Lam R, Lukowitz W, Yeung EC (2007) Auxin and root initiation in somatic embryos of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 26:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-006-0207-5
Bird DA, Franceschi VR, Facchini PJ (2003) A tale of three cell types: alkaloid biosynthesis is localized to sieve elements in opium poppy. Plant Cell 15:2626–2635
Brasher MI, Surmacz L, Leong B et al (2015) A two‐component enzyme complex is required for dolichol biosynthesis in tomato. Plant J 82:903–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.03.012
Bushman BS, Scholte AA, Cornish K et al (2006) Identification and comparison of natural rubber from two Lactuca species. Phytochemistry 67:2590–2596. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.09.012
Callis J, Fromm M, Walbot V (1987) Introns increase gene expression in cultured maize cells. Genes Dev 1:1183–1200. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1.10.1183
Casas-Mollano JA (2006) Intron-regulated expression of SUVH3, an Arabidopsis Su(var)3–9 homologue. J Exp Bot 57:3301–3311. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erl093
Chakrabarty R, Qu Y, Ro D-K (2015) Silencing the lettuce homologs of small rubber particle protein does not influence natural rubber biosynthesis in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Phytochemistry 113:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.12.003
Cornish K (2017) Alternative Natural rubber crops: why should we care? Technol Innov 18:244–255. https://doi.org/10.21300/18.4.2017.245
De Vries IM (1997) Origin and domestication of Lactuca sativa L. Genet Resour Crop Evol 44:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008611200727
Dempewolf H, Rieseberg LH, Cronk QC (2008) Crop domestication in the Compositae: a family-wide trait assessment. Genet Resour Crop Evol 55:1141–1157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-008-9315-0
Edani BH, Grabińska KA, Zhang R, Park EJ, Siciliano B, Surmacz L, Ha Y, Sessa WC (2020) Structural elucidation of the cis-prenyltransferase NgBR/DHDDS complex reveals insights in regulation of protein glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117:20794–20802. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2008381117
Epping J, van Deenen N, Niephaus E et al (2015) A rubber transferase activator is necessary for natural rubber biosynthesis in dandelion. Nat Plants 1:15048. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.48
Evert R (2006) Internal secretory structures. In: Evert R (ed) Esau’s Plant Anatomy, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York
Grabińska KA, Park EJ, Sessa WC (2016) cis-Prenyltransferase: new insights into protein glycosylation, rubber synthesis, and human diseases. J Biol Chem 291:18582–18590. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R116.739490
Hagel JM, Yeung EC, Facchini PJ (2008) Got milk? The secret life of laticifers. Trends Plant Sci 13:631–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2008.09.005
Harrison KD, Park EJ, Gao N, Kuo A, Rush JS, Waechter CJ, Lehrman MA, Sessa WC (2011) Nogo-B receptor is necessary for cellular dolichol biosynthesis and protein N-glycosylation. EMBO J 30:2490–2500. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.147
Ikezawa N, Göpfert JC, Nguyen DT et al (2011) Lettuce costunolide synthase (CYP71BL2) and its homolog (CYP71BL1) from sunflower catalyze distinct regio- and stereoselective hydroxylations in sesquiterpene lactone metabolism. J Biol Chem 286:21601–21611. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.216804
Karimi M, Inzé D, Depicker A (2002) GATEWAY vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Trends Plant Sci. 7:193–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1360-1385(02)02251-3.
Koyama T, Yoshida I, Ogura K (1988) Undecaprenyl diphosphate synthase from Micrococcus luteus BP 26: essential factors for the enzymatic activity. J Biochem 103:867–871. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122363
Kwon M, Kwon E-JG, Ro DK (2016) cis-Prenyltransferase polymer analysis from a natural rubber perspective. Methods Enzymol 576:121–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.mie.2016.02.026
Lakusta AM, Kwon M, Kwon E-JG, et al (2019) Molecular studies of the protein complexes involving cis-prenyltransferase in guayule (Parthenium argentatum), an alternative rubber-producing plant. Front Plant Sci 10:165. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2019.00165
Lange BM, Turner GW (2013) Terpenoid biosynthesis in trichomes-current status and future opportunities. Plant Biotechnol J 11:2–22. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-7652.2012.00737.x
Le Hir H, Nott A, Moore MJ (2003) How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci 28:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0968-0004(03)00052-5
Lindqvist K (1960) On the origin of cultivated lettuce. Hereditas 46:319–350. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.1960.tb03091.x
Nguyen DT, Göpfert JC, Ikezawa N et al (2010) Biochemical conservation and evolution of germacrene A oxidase in Asteraceae. J Biol Chem 285:16588–16598. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.111757
Nguyen T-D, Kwon M, Kim S-U et al (2019) Catalytic plasticity of germacrene A oxidase underlies sesquiterpene lactone diversification. Plant Physiol 181:945–960. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.19.00629
Odell JT, Nagy F, Chua NH. Identification of DNA (1985) sequences required for activity of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Nature. 313:810–812. https://doi.org/10.1038/313810a0.
Oldridge DA, Wood AC, Weichert-Leahey N, et al (2015) Genetic predisposition to neuroblastoma mediated by a LMO1 super-enhancer polymorphism. Nature 528:418–421. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15540
Olson KC, Tibbitts TW, Sruckmeyer BE (1967) Morphology and significance of laticifer rupture in lettuce tipburn. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 91:377–385
Olson KC, Tibbitts TW, Struckmeyer BE (1969) Leaf histogenesis in Lactuca sativa with emphasis upon laticifer ontology. Am J Bot 56:1212–1216. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1969.tb09778.x
Panero JL, Funk VA (2008) The value of sampling anomalous taxa in phylogenetic studies: Major clades of the Asteraceae revealed. Mol Phylogenet Evol 47:757–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ympev.2008.02.011
Pattanaik S, Patra B, Singh SK, Yuan L (2014) An overview of the gene regulatory network controlling trichome development in the model plant. Arabidopsis Front Plant Sci 5:259. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2014.00259
Pickard WF (2008) Laticifers and secretory ducts: Two other tube systems in plants. New Phytol 177:877–888. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2007.02323.x
Qu Y, Chakrabarty R, Tran HT et al (2015) A lettuce (Lactuca sativa) homolog of human Nogo-B receptor interacts with cis-prenyltransferase and is necessary for natural rubber biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 290:1898–1914. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.616920
Ramos MV, Demarco D, da Costa Souza IC, de Freitas CDT (2019) Laticifers, latex, and their role in plant defense. Trends Plant Sci 24:553–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2019.03.006
Rech P, Grima-Pettenati J, Jauneau A (2003) Fluorescence microscopy: a powerful technique to detect low GUS activity in vascular tissues. Plant J 33:205–209. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.016017.x
Reyes-Chin-Wo S, Wang Z, Yang X et al (2017) Genome assembly with in vitro proximity ligation data and whole-genome triplication in lettuce. Nat Commun 8:14953. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14953
Rose AB, Last RL (1997) Introns act post-transcriptionally to increase expression of the Arabidopsis thaliana tryptophan pathway gene PAT1. Plant J 11:455–464. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.11030455.x
Sessa RA (2000) Metabolite profiling of sesquiterpene lactones from Lactuca species: Major latexcomponents are novel oxalate and sulfate conjugates of lactucin and its derivatives. J Biol Chem 275:26877–26884. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M000244200
Stahl EA, Raychaudhuri S, Remmers EF, et al (2010) Genome-wide association study meta-analysis identifies seven new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci. Nat Genet 42:508. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.582
St-Pierre B, Vazquez-Flota FA, De Luca V (1999) Multicellular compartmentation of Catharanthus roseus alkaloid biosynthesis predicts intercellular translocation of a pathway intermediate. Plant Cell 11:887–900. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.11.5.887
Tata SK, Choi JY, Jung J-Y et al (2012) Laticifer tissue-specific activation of the Hevea SRPP promoter in Taraxacum brevicorniculatum and its regulation by light, tapping and cold stress. Ind Crops Prod 40:219–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2012.03.012
Tomlinson PB (2003) Development of gelatinous (reaction) fibers in stems of Gnetum gnemon (Gnetales). Am J Bot 90:965–972. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.90.7.965
United Nations (2018) Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC. Accessed 20 Jun 2020
Wahler D, Gronover CS, Richter C, et al (2009) Polyphenoloxidase silencing affects latex coagulation in Taraxacum Species. Plant Physiol 151:334 LP – 346. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.138743
Wang G (2014) Recent progress in secondary metabolism of plant glandular trichomes. Plant Biotechnol 31:353–361. https://doi.org/10.5511/plantbiotechnology.14.0701a
Weid M, Ziegler J, Kutchan TM (2004) The roles of latex and the vascular bundle in morphine biosynthesis in the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:13957–13962. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0405704101
Yeung EC (1984) Histological and histochemical staining procedures. In: Vasil I (ed) Cell culture and somatic cell genetics of plants. Academic Press, Orlando, FL, pp 689–697
Yeung EC, Chan CKW (2015) Glycol methacrylate: the art of embedding and serial sectioning. Botany 93:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjb-2014-0177
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Richard Michelmore (University of California, Davis) for providing us the lettuce cultivar Ninja for this work and Susan Roth for technical support for GUS staining.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) (04874-2017) to D.K.R. and E.C.Y. This work was also supported by a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (SSAC, grant number: PJ01326501), RDA, Republic of Korea, and Basic Science Research Program by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (2017R1A6A3A03003409) to M.K. and S.W.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Anastasios Melis.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barnes, E.K., Kwon, M., Hodgins, C.L. et al. The promoter sequences of lettuce cis-prenyltransferase and its binding protein specify gene expression in laticifers. Planta 253, 51 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03566-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-021-03566-8