Abstract
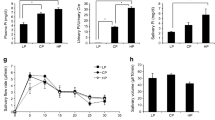
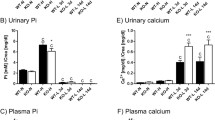
Ruminants have a unique utilization of phosphate (Pi) based on the so-called endogenous Pi recycling to guarantee adequate Pi supply for ruminal microbial growth and for buffering short-chain fatty acids. Large amounts of Pi enter the gastrointestinal tract by salivary secretion. The high saliva Pi concentrations are generated by active secretion of Pi from blood into primary saliva via basolateral sodium (Na+)-dependent Pi transporter type II. The following subsequent intestinal absorption of Pi is mainly carried out in the jejunum by the apical located secondary active Na+-dependent Pi transporters NaPi IIb (SLC34A2) and PiT1 (SLC20A1). A reduction in dietary Pi intake stimulates the intestinal Pi absorption by increasing the expression of NaPi IIb despite unchanged plasma 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 concentrations, which modulate Pi homeostasis in monogastric species. Reabsorption of glomerular filtrated plasma Pi is mainly mediated by the Pi transporters NaPi IIa (SLC34A1) and NaPi IIc (SLC34A3) in proximal tubule apical cells. The expression of NaPi IIa and the corresponding renal Na+-dependent Pi capacity were modulated by high dietary phosphorus (P) intake in a parathyroid-dependent manner. In response to reduced dietary Pi intake, the expression of NaPi IIa was not adapted indicating that renal Pi reabsorption in ruminants runs at a high level allowing no further increase when P intake is diminished. In bones and in the mammary glands, Na+-dependent Pi transporters are able to contribute to maintaining Pi homeostasis. Overall, the regulation of Pi transporter activity and expression by hormonal modulators confirms substantial differences between ruminant and non-ruminant species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berner W, Kinne R, Murer H (1976) Phosphate transport into brush-border membrane vesicles isolated from rat small intestine. Biochem J 160:467–474
Biber J, Murer H (1994) A molecular view of renal Na-dependent phosphate transport. Ren Physiol Biochem 17:212–215
Biber J, Murer H, Forster I (1998) The renal type II Na+/phosphate cotransporter. J Bioenerg Biomembr 30:187–194
Biber J, Hernando N, Forster I, Murer H (2009) Regulation of phosphate transport in proximal tubules. Pflugers Arch 458:39–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-008-0580-8
Blaustein MP (1993) Physiological effects of endogenous ouabain: control of intracellular Ca2+ stores and cell responsiveness. Am J Phys 264:C1367–C1387. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.1993.264.6.C1367
Breves G, Schroder B (1991) Comparative aspects of gastrointestinal phosphorus metabolism. Nutr Res Rev 4:125–140. https://doi.org/10.1079/NRR19910011
Breves G, Beyerbach M, Holler H, Lessmann HW (1985) Fluid exchange in the rumen of sheep in low and adequate phosphorus administration. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr 92:47–49
Capuano P, Radanovic T, Wagner CA, Bacic D, Kato S, Uchiyama Y, St-Arnoud R, Murer H, Biber J (2005) Intestinal and renal adaptation to a low-Pi diet of type II NaPi cotransporters in vitamin D receptor- and 1alphaOHase-deficient mice. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 288:C429–C434. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00331.2004
Caverzasio J, Danisi G, Straub RW, Murer H, Bonjour JP (1987) Adaptation of phosphate transport to low phosphate diet in renal and intestinal brush border membrane vesicles: influence of sodium and pH. Pflugers Arch 409:333–336
Danisi G, van Os CH, Straub RW (1984) Phosphate transport across brush border and basolateral membrane vesicles of small intestine. Prog Clin Biol Res 168:229–234
Danisi G, Caverzasio J, Trechsel U, Bonjour JP, Straub RW (1990) Phosphate transport adaptation in rat jejunum and plasma level of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Scand J Gastroenterol 25:210–215
Elfers K, Wilkens MR, Breves G, Muscher-Banse AS (2015) Modulation of intestinal calcium and phosphate transport in young goats fed a nitrogen- and/or calcium-reduced diet. Br J Nutr 114:1949–1964. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451500375X
Eriksson L, Valtonen M (1982) Renal urea handling in goats fed high and low protein diets. J Dairy Sci 65:385–389. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(82)82202-9
Fickel J, Goritz F, Joest BA, Hildebrandt T, Hofmann RR, Breves G (1998) Analysis of parotid and mixed saliva in roe deer (Capreolus capreolus L.). J Comp Physiol B 168:257–264
Firmenich CS, Elfers K, Wilkens MR, Breves G, Muscher-Banse AS (2018) Modulation of renal Ca and Pi transporting proteins by dietary nitrogen and/or calcium in young goats. J Anim Sci. https://doi.org/10.1093/jas/sky185
Fleet IR, Peaker M (1978) Mammary function and its control at the cessation of lactation in the goat. J Physiol 279:491–507
Foote AP, Lambert BD, Brady JA, Muir JP (2011) Phosphate transporter expression in Holstein cows. J Dairy Sci 94:1913–1916. https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2010-3691
Fox J, Care AD, Blahos J (1978) Effects of low calcium and low phosphorus diets on the duodenal absorption of calcium in betamethasone-treated chicks. J Endocrinol 78:255–260
Grace ND, Ulyatt MJ, Macrae JC (1974) Quantitative digestion of fresh herbage by sheep .3. Movement of Mg, Ca, P, K and Na in digestive-tract. J Agric Sci 82:321–330
Hilfiker H, Hattenhauer O, Traebert M, Forster I, Murer H, Biber J (1998) Characterization of a murine type II sodium-phosphate cotransporter expressed in mammalian small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:14564–14569
Hoffmann N, Thees M, Kinne R (1976) Phosphate transport by isolated renal brush border vesicles. Pflugers Arch 362:147–156
Hoppe A, Lin JT, Onsgard M, Knox FG, Dousa TP (1991) Quantitation of the Na(+)-Pi cotransporter in renal cortical brush border membranes. [14C]phosphonoformic acid as a useful probe to determine the density and its change in response to parathyroid hormone. J Biol Chem 266:11528–11536
Huber K, Walter C, Schroder B, Biber J, Murer H, Breves G (2000) Epithelial phosphate transporters in small ruminants. Ann N Y Acad Sci 915:95–97
Huber K, Walter C, Schroder B, Breves G (2002) Phosphate transport in the duodenum and jejunum of goats and its adaptation by dietary phosphate and calcium. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283:R296–R302. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00760.2001
Huber K, Roesler U, Muscher A, Hansen K, Widiyono I, Pfeffer E, Breves G (2003) Ontogenesis of epithelial phosphate transport systems in goats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 284:R413–R421
Huber K, Muscher A, Breves G (2007) Sodium-dependent phosphate transport across the apical membrane of alveolar epithelium in caprine mammary gland. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 146:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.10.024
Huber K, Roesler U, Holthausen A, Pfeffer E, Breves G (2007) Influence of dietary calcium and phosphorus supply on epithelial phosphate transport in preruminant goats. J Comp Physiol B 177:193–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-006-0121-8
Jungbluth H, Binswanger U (1989) Unidirectional duodenal and jejunal calcium and phosphorus transport in the rat: effects of dietary phosphorus depletion, ethane-1-hydroxy-1,1-diphosphonate and 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol. Res Exp Med (Berl) 189:439–449
Madjdpour C, Bacic D, Kaissling B, Murer H, Biber J (2004) Segment-specific expression of sodium-phosphate cotransporters NaPi-IIa and -IIc and interacting proteins in mouse renal proximal tubules. Pflugers Arch 448:402–410. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-004-1253-x
Maunder EM, Pillay AV, Care AD (1986) Hypophosphataemia and vitamin D metabolism in sheep. Q J Exp Physiol 71:391–399
Miyoshi K, Shillingford JM, Smith GH, Grimm SL, Wagner KU, Oka T, Rosen JM, Robinson GW, Hennighausen L (2001) Signal transducer and activator of transcription (Stat) 5 controls the proliferation and differentiation of mammary alveolar epithelium. J Cell Biol 155:531–542. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200107065
Murer H, Forster I, Hernando N, Lambert G, Traebert M, Biber J (1999) Posttranscriptional regulation of the proximal tubule NaPi-II transporter in response to PTH and dietary P(i). Am J Physiol 277:F676–F684
Murer H, Hernando N, Forster I, Biber J (2000) Proximal tubular phosphate reabsorption: molecular mechanisms. Physiol Rev 80:1373–1409. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.2000.80.4.1373
Murer H, Forster I, Biber J (2004) The sodium phosphate cotransporter family SLC34. Pflugers Arch 447:763–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1072-5
Muscher A, Huber K (2010) Effects of a reduced nitrogen diet on calcitriol levels and calcium metabolism in growing goats. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 121:304–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.03.084
Muscher A, Hattendorf J, Pfeffer E, Breves G, Huber K (2008) Hormonal regulation of phosphate homeostasis in goats during transition to rumination. J Comp Physiol B 178:585–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-007-0248-2
Muscher A, Breves G, Huber K (2009) Modulation of apical Na+/Pi cotransporter type IIb expression in epithelial cells of goat mammary glands. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 93:477–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0396.2008.00831.x
Muscher AS, Piechotta M, Breves G, Huber K (2011) Modulation of electrolyte homeostasis by dietary nitrogen intake in growing goats. Br J Nutr 105:1619–1626. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114510005350
Neville MC, Peaker M (1979) The secretion of calcium and phosphorus into milk. J Physiol 290:59–67
Peterlik M, Wasserman RH (1980) Regulation by vitamin D of intestinal phosphate absorption. Horm Metab Res 12:216–219. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-996246
Pfeffer E, Thompson A, Armstrong DG (1970) Studies on intestinal digestion in the sheep. 3. Net movement of certain inorganic elements in the digestive tract on rations containing different proportions of hay and rolled barley. Br J Nutr 24:197–204
Quamme GA (1985) Phosphate transport in intestinal brush-border membrane vesicles: effect of pH and dietary phosphate. Am J Phys 249:G168–G176. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.1985.249.2.G168
Schneider KM, Straub RW, Danisi G (1985) Phosphate-transport in the gut of the ruminant. Experientia 41:834–835
Schneider KM, Straub RW, Danisi G (1985) Sodium phosphate cotransport in ruminant intestine. Miner Electrol Metab 11:339–339
Schroder B, Breves G (1996) Mechanisms of phosphate uptake into brush-border membrane vesicles from goat jejunum. J Comp Physiol B 166:230–240
Schroder B, Breves G, Pfeffer E (1990) Binding properties of duodenal 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 receptors as affected by phosphorus depletion in lactating goats. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol 96:495–498
Schroder B, Kappner H, Failing K, Pfeffer E, Breves G (1995) Mechanisms of intestinal phosphate transport in small ruminants. Br J Nutr 74:635–648
Schroder B, Pfeffer E, Failing K, Breves G (1995) Binding properties of goat intestinal vitamin D receptors as affected by dietary calcium and/or phosphorus depletion. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A 42:411–417
Schroder B, Walter C, Breves G, Huber K (2000) Comparative studies on Na-dependent Pi transport in ovine, caprine and porcine renal cortex. J Comp Physiol 170:387–393
Shennan DB (1992) K+ and Cl- transport by mammary secretory-cell apical membrane-vesicles isolated from milk. J Dairy Res 59:339–348
Shillingford JM, Shennan DB, Beechey RB (1995) The regulation of anion transport in lactating rat mammary tissue. Biochem Soc Trans 23:26S
Shirazi-Beechey SP, Gorvel JP, Beechey RB (1988) Phosphate transport in intestinal brush-border membrane. J Bioenerg Biomembr 20:273–288
Shirazi-Beechey SP, Kemp RB, Dyer J, Beechey RB (1989) Changes in the functions of the intestinal brush border membrane during the development of the ruminant habit in lambs. Comp Biochem Physiol B 94:801–806
Shirazi-Beechey SP, Beechey RB, Penny J, Vayro S, Buchan W, Scott D (1991) Mechanisms of phosphate transport in sheep intestine and parotid gland: response to variation in dietary phosphate supply. Exp Physiol 76:231–241
Shirazi-Beechey SP, Penny JI, Dyer J, Wood IS, Tarpey PS, Scott D, Buchan W (1996) Epithelial phosphate transport in ruminants, mechanisms and regulation. Kidney Int 49:992–996
Solomon DH, Browning JA, Wilkins RJ (2007) Inorganic phosphate transport in matrix vesicles from bovine articular cartilage. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 190:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1748-1716.2007.01670.x
Solomon DH, Wilkins RJ, Meredith D, Browning JA (2007) Characterisation of inorganic phosphate transport in bovine articular chondrocytes. Cell Physiol Biochem 20:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1159/000104158
Starke S, Huber K (2014) Adaptive responses of calcium and phosphate homeostasis in goats to low nitrogen intake: renal aspects. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr 98:853–859. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpn.12144
Starke S, Cox C, Sudekum KH, Huber K (2013) Adaptation of electrolyte handling to low crude protein intake in growing goats and consequences for in vivo electrolyte excretion. Small Ruminant Res 114:90–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smallrumres.2013.06.008
Starke S, Reimers J, Muscher-Banse AS, Schroder B, Breves G, Wilkens MR (2016) Gastrointestinal transport of calcium and phosphate in lactating goats. Livest Sci 189:23–31
Valtonen MH, Uusi-Rauva A, Eriksson L (1982) The effect of protein deprivation on the validity of creatinine and urea in evaluation of renal function. An experimental study in the goat. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 42:507–512
Vayro S, Kemp R, Beechey RB, Shirazi-Beechey S (1991) Preparation and characterization of basolateral plasma-membrane vesicles from sheep parotid glands. Mechanisms of phosphate and D-glucose transport. Biochem J 279(Pt 3):843–848
Widiyono I, Huber K, Failing K, Breves G (1998) Renal phosphate excretion in goats. Zentralbl Veterinarmed A 45:145–153
Wood IS, Ford LT, Scott D, Rees WD, Shirazi-Beechey SP (1998) Sequence comparisons of ruminant renal Na+/phosphate co-transporters. Biochem Soc Trans 26:S121
Xu H, Inouye M, Missey T, Collins JF, Ghishan FK (2002) Functional characterization of the human intestinal NaPi-IIb cotransporter in hamster fibroblasts and Xenopus oocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1567:97–105
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Frances Sherwood-Brock for proofreading the manuscript.
Funding
The research was partly supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 280, Br 780/4-2, Br 780/11-1, Br 780/11-2, Mu 3585/1-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the special issue on Phosphate transport in Pflügers Archiv – European Journal of Physiology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muscher-Banse, A.S., Breves, G. Mechanisms and regulation of epithelial phosphate transport in ruminants: approaches in comparative physiology. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 471, 185–191 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-018-2181-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-018-2181-5